浙江省考生:如何利用零散时间学习ACCA?
发布时间:2020-01-10
在我国职称会计师考试中,ACCA考试属于难度比较大的考试,由于严苛的报考条件,备考ACCA考试的朋友大多数都是工作比较忙碌的上班族,那么如何在繁忙的工作中合理安排备考时间对于考生来说就非常重要了。除去完整系统的备考时间外,生活中零散时间也是能够备考的,今天就来教大家如何高效利用零散时间学习ACCA考试,大家可以作为参考。
每天至少一道题
ACCA考试的类型有很多种,主要考察应试人员分析、解决财务工作的能力,同时对计算能力和语言能力也是极大的挑战。所以在平时的备考中是一定缺少不了习题的辅助的。建议大家每天至少要做一套ACCA真题训练,每道小问控制在8分钟左右,这就足够大家利用空闲时间进行做题。
生活空档看考点
在上班路上看新闻时间,午休后的看剧时间在备考期间大家都可以转换成“高会学习时间”,带上《轻松过关》辅导书,看里面的“考点精讲”,让你在短时间内了解学习内容。你可以选择将学过的知识点复习一遍,或者将要学习的知识点提前预习一遍,要知道只有多一份努力才能多一份胜算。
备考笔记随身带
很多考生在备考中有记笔记或者是记错题本的好习惯,将整理的内容随身携带,空闲时间可以随时拿出来进行学习也是不错的选择。选择自己整理的笔记可以加深学习的印象,在考试的过程中也能当成考试资料带入考场,寻找知识点也会更快。
用完整时间来学习,用零散时间来备考,两者结合高效备考!
以上就是为大家准备的备考方法,希望对大家有所帮助,预祝大家都能轻松过ACCA考试~加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Assess the benefits of the separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman that Alliya Yongvanich
argued for and explain her belief that ‘accountability to shareholders’ is increased by the separation of these
roles. (12 marks)
(b) Separation of the roles of CEO and chairman
Benefits of separation of roles
The separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman was first provided for in the UK by the 1992 Cadbury provisions
although it has been included in all codes since. Most relevant to the case is the terms of the ICGN clause s.11 and OECD
VI (E) both of which provide for the separation of these roles. In the UK it is covered in the combined code section A2.
The separation of roles offers the benefit that it frees up the chief executive to fully concentrate on the management of the
organisation without the necessity to report to shareholders or otherwise become distracted from his or her executive
responsibilities. The arrangement provides a position (that of chairman) that is expected to represent shareholders’ interests
and that is the point of contact into the company for shareholders. Some codes also require the chairman to represent the
interests of other stakeholders such as employees.
Having two people rather than one at the head of a large organisation removes the risks of ‘unfettered powers’ being
concentrated in a single individual and this is an important safeguard for investors concerned with excessive secrecy or
lack of transparency and accountability. The case of Robert Maxwell is a good illustration of a single dominating
executive chairman operating unchallenged and, in so doing, acting illegally. Having the two roles separated reduces
the risk of a conflict of interest in a single person being responsible for company performance whilst also reporting on
that performance to markets. Finally, the chairman provides a conduit for the concerns of non-executive directors who,
in turn, provide an important external representation of external concerns on boards of directors.
Tutorial note: Reference to codes other than the UK is also acceptable. In all cases, detailed (clause number) knowledge
of code provisions is not required.
Accountability and separation of roles
In terms of the separation of roles assisting in the accountability to shareholders, four points can be made.
The chairman scrutinises the chief executive’s management performance on behalf of the shareholders and will be
involved in approving the design of the chief executive’s reward package. It is the responsibility of the chairman to hold
the chief executive to account on shareholders’ behalfs.
Shareholders have an identified person (chairman) to hold accountable for the performance of their investment. Whilst
day-to-day contact will normally be with the investor relations department (or its equivalent) they can ultimately hold
the chairman to account.
The presence of a separate chairman ensures that a system is in place to ensure NEDs have a person to report to outside the
executive structure. This encourages the freedom of expression of NEDs to the chairman and this, in turn, enables issues to
be raised and acted upon when necessary.
The chairman is legally accountable and, in most cases, an experienced person. He/she can be independent and more
dispassionate because he or she is not intimately involved with day-to-day management issues.
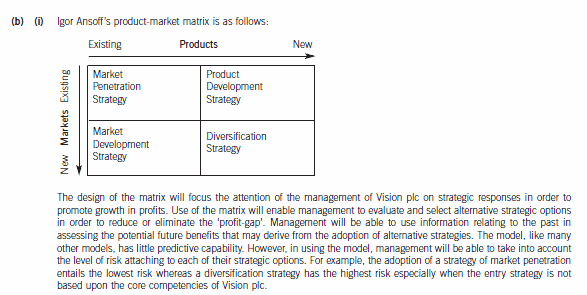
(b) (i) Explain how the use of Ansoff’s product-market matrix might assist the management of Vision plc to
reduce the profit-gap that is forecast to exist at 30 November 2009. (3 marks)
(c) Discuss the ethical and social responsibilities of the Beth Group and whether a change in the ethical and
social attitudes of the management could improve business performance. (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks for development of the discussion of the ethical and social
responsibilities of the Beth Group.
(c) Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is concerned with business ethics and the company’s accountability to its stakeholders,
and about the way it meets its wider obligations. CSR emphasises the need for companies to adopt a coherent approach to
a range of stakeholders including investors, employees, suppliers, and customers. Beth has paid little regard to the promotion
of socially and ethically responsible policies. For example, the decision to not pay the SME creditors on the grounds that they
could not afford to sue the company is ethically unacceptable. Additionally, Beth pays little regard to local customs and
cultures in its business dealings.
The stagnation being suffered by Beth could perhaps be reversed if it adopted more environmentally friendly policies. The
corporate image is suffering because of its attitude to the environment. Environmentally friendly policies could be cost effective
if they help to increase market share and reduce the amount of litigation costs it has to suffer. The communication of these
policies would be through the environmental report, and it is critical that stakeholders feel that the company is being
transparent in its disclosures.
Evidence of corporate misbehaviour (Enron, World.com) has stimulated interest in the behaviour of companies. There has
been pressure for companies to show more awareness and concern, not only for the environment but for the rights and
interests of the people they do business with. Governments have made it clear that directors must consider the short-term
and long-term consequences of their actions, and take into account their relationships with employees and the impact of the
business on the community and the environment. The behaviour of Beth will have had an adverse effect on their corporate
image.
CSR requires the directors to address strategic issues about the aims, purposes, and operational methods of the organisation,
and some redefinition of the business model that assumes that profit motive and shareholder interests define the core purpose
of the company. The profits of Beth will suffer if employees are not valued and there is poor customer support.
Arrangements should be put in place to ensure that the business is conducted in a responsible manner. The board should
look at broad social and environmental issues affecting the company and set policy and targets, monitoring performance and
improvements.
6 Discuss how developments in each of the following areas has affected the scope of the audit and the audit work
undertaken:
(a) fair value accounting; (6 marks)
6 DEVELOPMENTS
General comments
Tutorial note: The following comments, that could be made in respect of any of the three areas of development, will be given
credit only once.
■ Audit scope – the scope of a statutory audit should be as necessary to form. an audit opinion (i.e. unlimited).
■ Audit work undertaken – the nature, timing and extent of audit procedures should be as necessary to implement the overall
audit plan.
(a) Fair value accounting
■ Different definitions of fair value exist (among financial reporting frameworks or for different assets and liabilities within
a particular framework). For example, under IFRS it is ‘the amount for which an asset could be exchanged (or a liability
settled) between knowledgeable, willing parties in an arm’s length transaction’.
■ The term ‘fair value accounting’ is used to describe the measurement and disclosure of assets and/or liabilities at fair
value and the charging to profit and loss (or directly to equity) of any changes in fair value measurements.
■ Fair value accounting concerns measurements and disclosures but not initial recognition of assets and liabilities in
financial statements. It does not then, for example, affect the nature, timing and extent of audit procedures to confirm
the existence and completeness of rights and obligations.
■ Fair value may be determined with varying degrees of subjectivity. For example, there will be little (if any) subjectivity
for assets bought and sold in active and open markets that readily provide reliable information on the prices at which
exchange transactions occur. However, the valuation of assets with unique characteristics (or entity-specific assets) often
requires the projection and discounting of future cash flows.
■ The audit of estimates of fair values based on valuation models/techniques can be approached like other accounting
estimates (in accordance with ISA 540 ‘Audit of Accounting Estimates’). However, although the auditor should be able
to review and test the process used by management to develop the estimate, there may be:
? a much greater need for an independent estimate (and hence greater reliance on the work of experts in accordance
with ISA 620);
? no suitable subsequent events to confirm the estimate made (e.g. for assets that are held for use and not for
trading).
Tutorial note: Consider, for example, how the audit of ‘in-process research and development’ might compare with that
for an allowance for slow-moving inventory.
■ Different financial reporting frameworks require or permit a variety of fair value measures and disclosures in financial
statements. They also vary in the level of guidance provided (to preparers of the financial statements – and hence their
auditors). Under IFRS, certain fair values are based on management intent and ‘reasonable supportable assumptions’.
■ The audit of management intent potentially increases the auditor’s reliance on management representations. The auditor
must obtain such representations from the highest level of management and exercise an appropriate degree of
professional scepticism, being particularly alert to the implications of any conflicting evidence.
■ A significant development in international financial reporting is that it is no longer sufficient to report transactions and
past and future events that may only be possible. IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ (Revised) requires that
key assumptions (and other key sources of estimation uncertainty) be disclosed. This requirement gives rise to yet
another area on which auditors may qualify their audit opinion, on grounds of disagreement, where such disclosure is
incorrect or inadequate.
■ Perhaps one of the most significant impacts of fair value accounting on audit work is that it necessarily increases it.
Consider for example, that even where the fair value of an asset is as easily vouched as original cost, fair value is
determined at least annually whereas historic cost is unchanged (and not re-vouched to original purchase
documentation).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-04-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-04-15