【总结】2020年ACCA考试难度分析报告
发布时间:2020-03-08
ACCA作为国际性会计师组织,其会员获取难度自然不低,考试科目达到了16门。如何安排这些科目的考试计划,是不少学员面对的主要难题之一。因此,一些小伙伴不免在网上询问ACCA各科目考试难度如何。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来有关2020年ACCA考试难度的相关情况,以供参考。
从整体上看,ACCA全球单科通过率基本在30-40%左右,中国学员通过率为50-60%。从数据来看,ACCA考试通过率不算低,考试难度并不算太高。从考试内容来看,ACCA考试难度很大程度上是来自于英语和坚持,学员在英语过关的情况下,一般平时认真看书,做题还是很容易通过的。当然了,如果是英语水平一般的小伙伴,则需要付出更多的努力。
ACCA考试可分为三个部分,每部分难度略有不同。我们以英国大学学位考试的难度为标准来分析ACCA考试难度,第一、第二部分的难度分别相当于学士学位高年级课程的考试难度,但是第三部分的考试相当于硕士学位最后阶段的考试。因此,ACCA考试的难点主要在最后阶段,也就是选修阶段,必修阶段的难度并不算高。
从内容上来说,第一部分的每门考试只是测试本门课程所包含的知识,主要是为了给后两个部分中实务性的课程所要运用的理论和技能打下基础。因此,第一部分考试虽然难度不高,但是非常关键,属于打基础的阶段。因此,小伙伴们在学习这部分知识时,不应该仅仅抱着应对考试的态度去学习。
而第二部分的考试除了本门课程的内容之外,还会考到第一部分的一些知识,着重培养学生的分析能力。这一部分的考生已经脱离单纯的知识学习,进入能力培养阶段,同时也是在为最后阶段做准备。这一阶段,考生最好多去做一些练习题。
最后一部分的考试要求学生综合运用学到的知识、技能和决断力。不仅会考到以前的课程内容,还会考到邻近科目的内容。这就需要考生能够灵活掌握所有课程的内容。F阶段的部分科目与最后阶段科目的内容存在一定关联,因此小伙伴们可以通过F阶段的学习情况,选择适合自己的选修科目。
以上就是关于ACCA考试难度的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA考试难度是呈阶梯式上升,并且各部分内容之间都有所关联,所以小伙伴们在备考第一、二部分时,也要踏踏实实的去学习哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Briefly discuss why the directors of HFL might choose contract D irrespective of whether or not contract D
would have been selected using expected values as per part (a). (2 marks)
(c) The directors might select Contract D under which 360,000 kilograms of organic mushrooms would be supplied to HFL for
each outlet. This is the entire capacity of HFL which would ensure that competitors would not be able to supply the same
product and hence the competitive advantage held by HFL might be preserved.
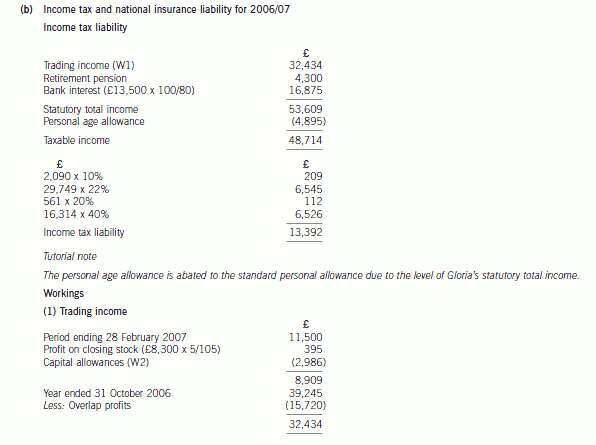
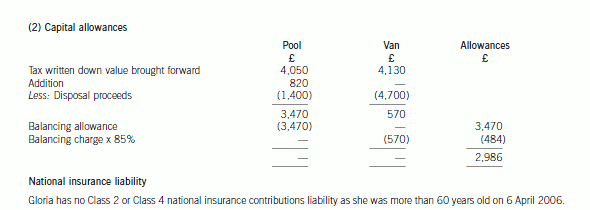
(b) Compute Gloria’s total income tax and national insurance liability for 2006/07. (7 marks)
(ii) If a partner, who is an actuary, provides valuation services to an audit client, can we continue with the audit?
(3 marks)
Required:
For each of the three questions, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that
should be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions above.
(ii) Actuarial services to an audit client
IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ does not deal specifically with actuarial valuation services but with
valuation services in general.
A valuation comprises:
■ making assumptions about the future;
■ applying certain methodologies and techniques;
■ computing a value (or range of values) for an asset, a liability or for a business as a whole.
A self-review threat may be created when a firm or network firm2 performs a valuation for a financial statement audit
client that is to be incorporated into the client’s financial statements.
As an actuarial valuation service is likely to involve the valuation of matters material to the financial statements (e.g. the
present value of obligations) and the valuation involves a significant degree of subjectivity (e.g. length of service), the
self-review threat created cannot be reduced to an acceptable level of the application of any safeguard. Accordingly:
■ such valuation services should not be provided; or
■ the firm should withdraw from the financial statement audit engagement.
If the net liability was not material to the financial statements the self-review threat may be reduced to an acceptable
level by the application of safeguards such as:
■ involving an additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team to review the work done
by the actuary;
■ confirming with the audit client their understanding of the underlying assumptions of the valuation and the
methodology to be used and obtaining approval for their use;
■ obtaining the audit client‘s acknowledgement of responsibility for the results of the work performed by the firm; and
■ making arrangements so that the partner providing the actuarial services does not participate in the audit
engagement.
4 Graham Smith is Operations Director of Catering Food Services (CFS) a £1·5 billion UK based distributor of foods to
professional catering organisations. It has 30 trading units spread across the country from which it can supply a
complete range of fresh, chilled and frozen food products. Its customers range from major fast food chains, catering
services for the armed forces down to individual restaurants and cafes. Wholesale food distribution is very much a
price driven service, in which it is very difficult to differentiate CFS’s service from its competitors.
Graham is very aware of the Government’s growing interest in promoting good corporate environmental practices and
encouraging companies to achieve the international quality standard for environmentally responsible operations. CFS
operates a fleet of 1,000 lorries and each lorry produces the equivalent of its own weight in pollutants over the course
of a year without the installation of expensive pollution control systems. Graham is also aware that his larger
customers are looking to their distributors to become more environmentally responsible and the ‘greening’ of their
supply chain is becoming a real issue. Unfortunately his concern with developing a company-wide environmental
management strategy is not shared by his fellow managers responsible for the key distribution functions including
purchasing, logistics, warehousing and transportation. They argued that time spent on corporate responsibility issues
was time wasted and simply added to costs.
Graham has decided to propose the appointment of a project manager to develop and implement a company
environmental strategy including the achievement of the international quality standard. The person appointed must
have the necessary project management skills to see the project through to successful conclusion.
You have been appointed project manager for CFS’s ‘environmentally aware’ project.
Required:
(a) What are the key project management skills that are necessary in achieving company-wide commitment in
CFS to achieve the desired environmental strategy? (15 marks)
(a) Simply defined, a project is ‘activity that has a start, a middle and an end and consumes resources’ – it is therefore a discrete
activity aimed at achieving a specific objective or range of objectives. Graham is intent on using the ‘environmentally aware’
project to achieve a specific objective – the attainment of the international environmental standard. He is, however, aware
that there are a number of internal stakeholders inside the company who question the significance of such a project.
Externally, he can point to significant stakeholders, including customers and government who are looking for CFS to become
more environmentally aware. The project is likely to have strategic and not simply operational or administrative significance
and the person appointed into the role of project manager, ideally, should have both the traditional skills associated with
project management plus those of strategic management. Grundy and Brown list the traditional project management
techniques as:

Clearly, the project manager must have the technical project management skills, being able to manage the project through its
life cycle, which involves defining the project in terms of project objectives and scope as defined by time, cost and quality.
Planning the project in terms of breaking the overall project down into separate activities, estimating the resources required
and linking activities to resources in terms of time and priorities. Implementing the plan, including reviewing the progress in
meeting time and cost objectives and taking corrective action where and when necessary. Finally, reviewing the outcomes of
the project in terms of what was delivered to the customer and the extent to which client expectations were met.
The strategic nature of the project means that the project manager must have significant leadership skills, not only of the
project team, who are likely to come from different functions and parts of the company, but also influential stakeholders inside
and outside the company. This implies they should have good ‘political’ and communication skills as the project is of strategic
significance to the company. The ability to show how this particular project fits with the overall strategy of the firm is
important. The project is an important part in the achievement of the company strategy and in CFS’s case may help it
differentiate itself from its competitors. However, the project manager must recognise that there will be resistance from existing
managers reluctant to see resources committed to projects outside of the traditional value chain of the company. Certainly,
the project manager for the ‘environmentally aware’ project will themselves need to be aware of the external environmental
pressures prompting the firm to set itself specific environmental objectives and be able to link into supportive networks and
alliances. Finally, Grundy and Brown argue that the project manager will be the key to reviewing and learning from the project,
assessing whether defined objectives were achieved, the effectiveness or otherwise of the implementation process and how
key stakeholders were managed. The danger is that projects are seen as ‘one-off’ rather than contributing to the knowledge
and learning of the organisation. There may be a significant ‘learning curve’ that the firm has to go down and look tocontinuously improve its project management process.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-02-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-02-26
- 2020-02-28
- 2021-06-19
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-05-19
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-13