近期有关ACCA和CPA哪个含金量高的内容新鲜出炉啦!
发布时间:2020-04-23
ACCA和CPA作为财会行业两大证书,时常有人会把二者拿出来进行比较,ACCA证书和CPA证书哪个含金量比较高,二者如何选择?但其实从不同的角度看这两个证书,其含金量是不同的。接下来就跟随51题库考试学习网一起来看看具体内容吧。
知识体系设置不同
CPA考试专业六门,再加一门综合,分别是会计、审计、财务管理、税法、经济法、战略,这六门科目基本呈并列关系,难度相差不大,钻研得也很深。CPA太精,所以从业范围限于会计和审计几个领域。
ACCA包括财务呈报、审计、财务管理、法律和税收在内的十三门课程,这些课程分布在三个阶段,层层递进、逐渐深入,涵盖了本科财务教学的所有科目和硕士研究生教学的部分科目,能让你拥有一个很扎实的且具有国际性的财务知识框架。
基础要求不同
学习CPA必须要有一定会计专业基础,其内容是建立在会计专业基础知识之上的。而且本科在读阶段没办法参加考试,需要大学毕业证才可以。
知识体系呈阶梯状,难度层层递进,ACCA课程设置上已经考虑到了零基础学员的存在,因此零基础和基础较差的学员也能学好ACCA。
培养人才不同
中国注册会计师,顾名思义只在中国适用,培养的是专业执业的注册会计师,属于会计和审计的专业技术人才,一般做的是专业会计的工作。ACCA培养的是复合型的高级财务管理人才,而非专注于某一领域的执业者。不管你去国企、外企、内资企业、私营企业,事务所、或机关单位都是可以的,而且是国际适用。
考试角度不同
CPA侧重于会计和审计,最终服务于审计,因此一般只考虑财务因素,考的更多的是计算,要求精准、快速,考试的题型一般是主客观题各占一半,大部分都不需要论述,具有标准的答案。
ACCA以实际案例为背景,强调的是分析与解决问题的能力,需要综合考虑财务因素和非财务因素,题型除第一阶段的客观题外,之后阶段全部为主观题,且没有绝对的标准答案,考官喜欢看到独到的见解,出其不意却言之有理的逻辑分析,以及恰当地联系实际生活中的案例。
考试语言不同
CPA是国内注会考试,自然用的是中文考试。而ACCA是国际注册会计师,由于它是英国的财会证书,因此在全球施行统一标准,全部使用英文教学和答题。因此,这对参加ACCA考试的人来说,英语能力也有一定的要求,而最终完成ACCA考试的人毫无疑问是精通英语的国际复合型财务人才。
愉快的时光总是很短暂,以上就是今天51题库考试学习网为大家分享的全部内容,大家是否清楚了呢?如有其他疑问请继续关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
On 1 April 2009 Pandar purchased 80% of the equity shares in Salva. The acquisition was through a share exchange of three shares in Pandar for every five shares in Salva. The market prices of Pandar’s and Salva’s shares at 1 April
2009 were $6 per share and $3.20 respectively.
On the same date Pandar acquired 40% of the equity shares in Ambra paying $2 per share.
The summarised income statements for the three companies for the year ended 30 September 2009 are:
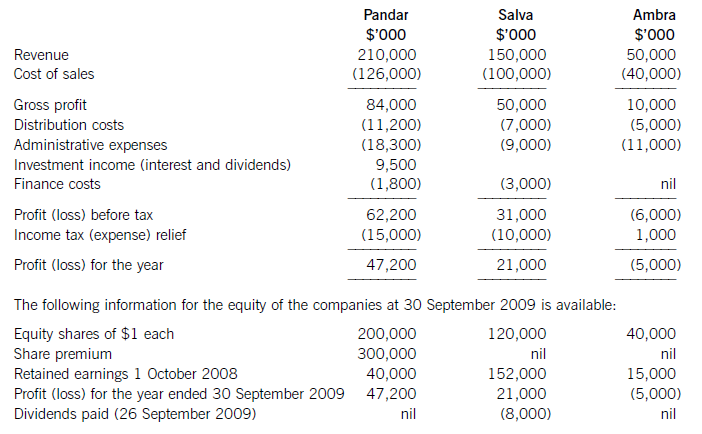
The following information is relevant:
(i) The fair values of the net assets of Salva at the date of acquisition were equal to their carrying amounts with the exception of an item of plant which had a carrying amount of $12 million and a fair value of $17 million. This plant had a remaining life of five years (straight-line depreciation) at the date of acquisition of Salva. All depreciation is charged to cost of sales.
In addition Salva owns the registration of a popular internet domain name. The registration, which had a
negligible cost, has a five year remaining life (at the date of acquisition); however, it is renewable indefinitely at a nominal cost. At the date of acquisition the domain name was valued by a specialist company at $20 million.
The fair values of the plant and the domain name have not been reflected in Salva’s financial statements.
No fair value adjustments were required on the acquisition of the investment in Ambra.
(ii) Immediately after its acquisition of Salva, Pandar invested $50 million in an 8% loan note from Salva. All interest accruing to 30 September 2009 had been accounted for by both companies. Salva also has other loans in issue at 30 September 2009.
(iii) Pandar has credited the whole of the dividend it received from Salva to investment income.
(iv) After the acquisition, Pandar sold goods to Salva for $15 million on which Pandar made a gross profit of 20%. Salva had one third of these goods still in its inventory at 30 September 2009. There are no intra-group current account balances at 30 September 2009.
(v) The non-controlling interest in Salva is to be valued at its (full) fair value at the date of acquisition. For this
purpose Salva’s share price at that date can be taken to be indicative of the fair value of the shareholding of the non-controlling interest.
(vi) The goodwill of Salva has not suffered any impairment; however, due to its losses, the value of Pandar’s
investment in Ambra has been impaired by $3 million at 30 September 2009.
(vii) All items in the above income statements are deemed to accrue evenly over the year unless otherwise indicated.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Salva at 1 April 2009; (6 marks)
(ii) Calculate the carrying amount of the investment in Ambra to be included within the consolidated
statement of financial position as at 30 September 2009. (3 marks)
(b) Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pandar Group for the year ended 30 September 2009.(16 marks)
2 Chen Products produces four manufactured products: Products 1, 2, 3 and 4. The company’s risk committee recently
met to discuss how the company might respond to a number of problems that have arisen with Product 2. After a
number of incidents in which Product 2 had failed whilst being used by customers, Chen Products had been presented
with compensation claims from customers injured and inconvenienced by the product failure. It was decided that the
risk committee should meet to discuss the options.
When the discussion of Product 2 began, committee chairman Anne Ricardo reminded her colleagues that, apart from
the compensation claims, Product 2 was a highly profitable product.
Chen’s risk management committee comprised four non-executive directors who each had different backgrounds and
areas of expertise. None of them had direct experience of Chen’s industry or products. It was noted that it was
common for them to disagree among themselves as to how risks should be managed and that in some situations,
each member proposed a quite different strategy to manage a given risk. This was the case when they discussed
which risk management strategy to adopt with regard to Product 2.
Required:
(a) Describe the typical roles of a risk management committee. (6 marks)
(a) Typical roles of a risk management committee
The typical roles of a risk management committee are as follows:
To agree and approve the risk management strategy and policies. The design of risk policy will take into account the
environment, the strategic posture towards risk, the product type and a range of other relevant factors.
Receiving and reviewing risk reports from affected departments. Some departments will file regular reports on key risks (such
as liquidity assessments from the accounting department, legal risks from the company secretariat or product risks from the
sales manager).
Monitoring overall exposure and specific risks. If the risk policy places limits on the total risk exposure for a given risk then
this role ensures that limits are adhered to. In the case of certain strategic risks, monitoring could occur on a very frequent
basis whereas for more operational risks, monitoring will more typically occur to coincide with risk management committee
meetings.
Assessing the effectiveness of risk management systems. This involves getting feedback from departments and the internal
audit function on the workings of current management and risk mitigation systems.
Providing general and explicit guidance to the main board on emerging risks and to report on existing risks. This will involve
preparing reports on apparent risks and assessing their probability of being realised and their potential impact if they do.
To work with the audit committee on designing and monitoring internal controls for the management and mitigation of risks.
If the risk committee is part of the executive structure, it will likely have an advisory role in respect of its input into the audit
committee. If it is non-executive, its input may be more directly influential.
[Tutorial note: other roles may be suggested that, if relevant, will be rewarded]
(b) Historically, all owned premises have been measured at cost depreciated over 10 to 50 years. The management
board has decided to revalue these premises for the year ended 30 September 2005. At the balance sheet date
two properties had been revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another 15 properties have since been revalued by
$5·4 million and there remain a further three properties which are expected to be revalued during 2006. A
revaluation surplus of $7·1 million has been credited to equity. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
(b) Revaluation of owned premises
(i) Matters
■ The revaluations are clearly material as $1·7 million, $5·4 million and $7·1 million represent 5·5% , 17·6% and
23·1% of total assets, respectively.
■ The change in accounting policy, from a cost model to a revaluation model, should be accounted for in accordance
with IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’ does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
■ The basis on which the valuations have been carried out, for example, market-based fair value (IAS 16).
■ Independence, qualifications and expertise of valuer(s).
■ IAS 16 does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class of premises should have been
revalued.
■ The valuations of properties after the year end are adjusting events (i.e. providing additional evidence of conditions
existing at the year end) per IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be
expected to reflect year-end values.
■ If $5·4 million is a net amount of surpluses and deficits it should be grossed up so that the credit to equity reflects
the sum of the surpluses with any deficits being expensed through profit and loss (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ The revaluation exercise is incomplete. If the revaluations on the remaining three properties are expected to be
material and cannot be reasonably estimated for inclusion in the financial statements for the year ended
30 September 2005 perhaps the change in policy should be deferred for a year.
■ Depreciation for the year should have been calculated on cost as usual to establish carrying amount before
revaluation.
■ Any premises held under finance leases should be similarly revalued.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of owned premises extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Calculation of difference between valuation and depreciated cost by property. Separate summation of surpluses
and deficits.
■ Copy of valuation certificate for each property.
■ Physical inspection of properties with largest surpluses (including the two valued before the year end) to confirm
condition.
■ Extracts from local property guides/magazines indicating a range of values of similarly styled/sized properties.
■ Separate presentation of the revaluation surpluses (gross) in:
– the statement of changes in equity; and
– reconciliation of carrying amount at the beginning and end of the period.
■ IAS 16 disclosures in the notes to the financial statements including:
– the effective date of revaluation;
– whether an independent valuer was involved;
– the methods and significant assumptions applied in estimating fair values; and
– the carrying amount that would have been recognised under the cost model.
(ii) the strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies. (3 marks)
(Marks will be awarded in part (b) for the identification and discussion of relevant points and for the style. of the
report.)
(ii) Strategy of the business regarding its treasury policies
Treasury policies are reviewed regularly by the Board. It is group policy to account for all financial instruments as cash
flow hedges. As a result, changes in the fair values of financial instruments are deferred in reserves to the extent the
hedge is effective and released to profit or loss in the time periods in which the hedged item impacts profit or loss.
The Group contracts fixed rate currency swaps and issues floating to fixed rate interest rate swaps to meet the objective
of protecting borrowing costs. The cash flow effects of the interest rate swaps match the cash flows on the underlying
instruments so that there is no net cash flow effect from movements in market interest rates. If the interest rate swaps
had not been transacted there could have been an increase in the annual net interest payable to the Group. The strategy
of the group is to minimise the exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-15