快看!要想成为一名注册会计师必须具备哪些条件?
发布时间:2020-05-11
根据国家实行注册会计师全国统一考试制度。注册会计师全国统一考试办法,由国务院财政部门制定,由中国注册会计师协会组织实施。
要想成为一名注册会计师必须具备的条件:
《中国注册会计师胜任能力指南》对注册会计师胜任能力提出了系统的要求,描述了注册会计师应该具备的素质。归纳起来有两个方面:
一个是专业素质,一个是实务能力、专业素质。专业素质包括专业知识、职业技能和职业道德三个方面。
现在大学本科的课程已基本达到行业需要的专业知识。从每年注册会计师考试的结果看,大学教育还要在基本原理、基本概念上下更多的功夫。如果对会计、审计的基本原理有较好的把握,解决具体的专业技术问题就容易得多。
注册会计师人才的成长,起点在大学。专业品质、专业能力的训练,很大程度上需要从大学阶段起步。今天到青年政治学院来,跟各位同学见面,想把我对会计行业特别是注册会计师职业的理解,跟大家作一个交流,希望对大家学习专业知识、发展职业生涯提供参考。我的基本认识是,注册会计师是一个大有前途的职业,值得在座的同学们作为人生职业的选择。
一、注册会计师是什么?
关于注册会计师,至少可以从以下四个维度来认识。
1.注册会计师是一所学校。
2.注册会计师是一个需要终生学习的职业。学习型组织、学习型社会等概念,要求人人接受继续教育,养成终生学习的习惯,这已成为世界潮流。对于注册会计师职业来说,参加资格教育和继续教育更是由职业本身所决定的,因为注册会计师是专业人士,需要以专业知识、职业道德立足于社会,可以说是一种职业要求。
3.注册会计师是一个品牌。在市场上,同样的东西,不同的品牌就有不同的价格,这就是品牌的差异。注册会计师就是人才的品牌,它区别于一般的会计师。财政部和中注协在招聘人才时,应聘者如果有注册会计师背景,往往被高看一眼。
4.注册会计师是一个承诺。注册会计师是一个承诺,因为要保持这个资格,这份信任,就需要不断的进取,保持知识的更新,按照职业道德的要求履行其职能,在遇到利益冲突的时候,要以公众利益为底线。当报名参加注册会计师考试的时候,加入注册会计师协会的时候,就必须意识到这是一个承诺。我国建立了注册会计师宣誓制度,通过这种方式将一种内涵的品质外化为庄严的宣誓。今天虽然是注册会计师,如果不履行这个承诺,也会被这个职业和社会所排斥。
好了,以上就是本次51题库考试学习网为大家分享的整体内容,如果还想了解更多关于这方面的信息,也可关注51题库考试学习网解决心中的疑惑,祝大家考出满意的成绩吧。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Compute the annual income tax saving from your recommendation in (i) above as compared with the
situation where Cindy retains both the property and the shares. Identify any other tax implications
arising from your recommendation. Your answer should consider all relevant taxes. (3 marks)

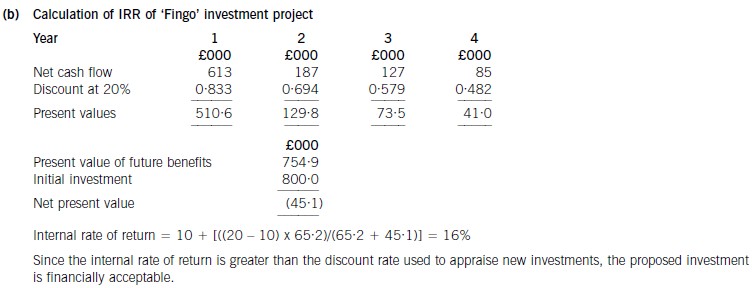
(b) Calculate the internal rate of return of the proposed investment and comment on your findings. (5 marks)
(b) Using the information provided in the case scenario, strategically evaluate the performance of the company
up to 2004, indicating any areas of particular concern. (20 marks)
(b) Essentially, Universal is a one product or service company selling its services into two main customer segments in the housing
market. From the performance information provided in Table 1, the company has achieved impressive rates of growth over
the 2001–4 period and this growth has come almost exclusively from private house owners. Universal is in the replacement
market. Its customers are looking to replace existing roofing systems with low maintenance/high attractiveness Universal
systems. To date growth has been exclusively within one region and been achieved by growing the area served through
investment in showrooms and depots.
Universal has chosen to grow its business through a differentiation focus strategy. It has identified a niche not served by the
major PVC doors and windows installers and poorly served by small independent installers. The value chain analysis
discussed above has shown the ways in which Universal has successfully distinguished itself from its competitors. Growth
has been through increasing its market penetration of one particular region. Such is the size of the private house owner market
and the lack of effective competition that the company has achieved a significant share of the market in its particular region.
However, in national terms, with 1% of the available market, Universal is a small operator. What is clear from the sales figures
is that as the firm grows bigger the relative rate of growth inevitably slows down, so that by 2004 it has an annual growth of
27% – still impressive by most companies standards. The move into supplying the commercial housing market has been
successful, but the share of total sales seems to have stabilised at around 5%. Universal clearly is finding it difficult to commit
sufficient new resources to this sector while coping with the growth from the domestic housing sector. Direct labour and other
direct costs seem to be a reasonable proportion of sales and predictably grow with the number of installation teams. Overall,
the gross margin, which sustains sales, marketing and overhead expenses, is moving in the right direction with a gross margin
of 52·6% achieved in 2004.
Labour, not surprisingly in a service business, consumes a considerable amount of costs. If one combines the direct labour
with the commission costs of sales canvassers and representatives together with salaries to staff in head office, one is in a
business where well over 50% of costs are attributable to people. Equally important is the fact that over 80% of the staff
employed by Universal is paid by results. This has significant consequences for the structure of reward systems and the
training and development of staff looking to maximise their incomes through either their individual or team performance.
Clearly, Universal sees no incompatibility between a reward system dominated by payments by results and the delivery of a
quality service differentiating it from its competitors.
Marketing has grown considerably over the period and reflects the recruitment of Mick Hendry as Sales and Marketing Director
in 2002. The marketing and sales model is very much one influenced by the one used by large PVC installers of doors and
windows. Here there is a heavy emphasis on direct selling techniques supported by increasing levels of advertising. Universal
sells to its customers directly and therefore avoids the costs and channel complications of using third parties to provide its
services. In many ways the direct selling techniques used are a very well established way of reaching the customer. Elements
of the marketing mix may be influenced by changes in communication technology, but the nature of the service requires
effective face-to-face contact with the customer. Sales to private house owners using credit generates significant finance
commission and is an important source of extra margin to Universal. Often in businesses depending on significant amounts
of credit sales the sales representative receives significant reward for selling a finance arrangement to the customer.
In terms of net profit achieved, 2001 and 2002 represents a significant change and, as argued in the scenario, this reflects
the recruitment of the Sales and Marketing Director. The achievement of this ‘step change’ in sales required commensurate
increases in most costs, but it is the significant increase in sales costs that explains the losses experienced in 2002. Sales
costs as a proportion of total sales rose from 14% in 2001 to almost 34% in 2002.
Particularly significant is the increase in sales commissions paid. The detailed changes in the way commission is paid is not
given in the case scenario, but it seems likely to reflect the previous experience of the Sales and Marketing Director in a closely
related industry. Similar levels of sales costs are incurred in 2003 and 2004 but the increase in sales, improvement in gross
margin and slower rate of growth in commissions paid explain the improved return on sales from –6·7% in 2002 to 4·2%
in 2003 and 5·8% in 2004.
Equally significant is the growth in showrooms and depots to support the growth in sales. Each additional facility costs in the
order of £30K with significant additions to costs in terms of staff and stock. Overall the performance of Universal over the
2001–2004 period is of a company achieving high rates of growth, incurring significant costs in so doing and moving into
modest levels of profit over the period. Its cost structure reflects the service it provides and the staff and reward systemsenabling the service to be provided.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-07-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-05-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-03-29
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-07-31
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-19