河北省考生:ACCA考试成绩有效期是多久?
发布时间:2020-01-10
当人生面对许多选择的时候,我们需要谨慎;当我们没有选择的时候,就把压力当挑战,给自己一个信心,近日,参加ACCA考试的小伙伴来咨询我一些关于ACCA考试成绩有效期的问题,接下来51题库考试学习网将一一为其解答,建议大家收藏起来哟~
ACCA F阶段(AB-FM)课程考试已正式取消考试期限,换句话说,已经考完的各F阶段科目的考试成绩永久有效,不必重新考试。
不过,对于ACCA核心课程(P阶段)的考试成绩还是设置了7年的有效期。每位学员必须在通过第一科战略课程之日起,7年内完成所有的P阶段科目考试。(超出规定年限就只能重新考试)
ACCA考完一般都需要多久?
ACCA每年有4次考季,每次最多可以报考4门,每年最多报考8门,而ACCA考试全科共需要通过13门考试,所以,全部都能一次通过考试的情况下,考完ACCA最快也要近两年的时间。
ACCA一般都能考多久呢?
以ACCA近年的考试通过率来看,在无免考的情况下,从F1-P阶段完成考试的时间大致是2年-3年的时间。当然,如果你有相应的免考机会,比如拥有CPA、MPAcc等证书的话则可以免除部分科目的考试。如此一来,就能大大缩短你通过考试的时间了。
ACCA免考政策如下:
教育部认可高校毕业生
1)会计学专业 - 获得学士或硕士学位(金融/财务管理/审计专业也享受等同会计学专业的免试政策,下同) 免试5门课程;(即是本科或者研究生毕业)
2)会计学 - 辅修专业 免试3门课程;(双学位的,且第二专业是会计的)
3)法律专业 免试1门课程;
4)商务及管理专业 免试1门课程;
5)MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成) 免试5门课程*;
6)MBA - 获得MBA学位 免试3门课程;
7)非相关专业 无免试课程。
*注:部分院校的MPAcc专业已专门申请ACCA总部的免试审核,因此有多于5门的免试,具体请查询 ACCA总部官网。
教育部认可高校在校生(本科)
1)会计学专业 - 完成第一学年课程 可以注册为ACCA正式学员 无免试;
2)会计学专业 - 完成第二学年课程 免试3门课程;
3)其他专业 - 在校生 ACCA全球网站查询。
中国注册会计师资格
1)CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度前获得全科合格证或者会员资格证 免试5门课程;
2)CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度后获得全科合格证或者会员资格证 免试9门课程;
3)FIA(Foundation in
Accountancy) 通过FIA(Foundation in Accountancy)所有考试并取得相关工作经验 免试4门课程。
关于ACCA有效期的介绍
ACCA考试期限跟CPA一样实行轮废制,即需要在一定的时间里面考完规定的科目,否则成绩将会无效。那么这个时间怎么算的呢?
根据以前的规则,学员必须在首次报名注册后10年内通过所有考试,否则将注销其学员资格。后特许公认会计师公会ACCA对学员通过ACCA资格认证所有考试的时限做出了重要调整。F段成绩永久有效,P段要在7年内考完。根据新规则,专业阶段考试的时限将为7年。因此,国际财会基础资格(Foundations in Accountancy,简称FIA)的考试以及ACCA资格考试的基础阶段F1-F9考试将不再有通过时限。
“7年政策”意味着从你通过P阶段的第一门科目开始,7年内需完成P阶段所要求的所有ACCA考试科目。否则,从第8年开始,你第1年所考过的P阶段科目成绩将会被视为过期作废,须重新考试。
以上就是关于ACCA考试的相关信息,51题库考试学习网想告诉大家的是,其实一个证书好不好考并不是绝对的,这取决于你自己的努力程度。俗话说,有志者事竟成,相信只要通过自己的不懈努力,通过看似很困难的ACCA考试也不是太大的问题。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Explain the advantages and the disadvantages of:
(i) the face to face interview between two people; (6 marks)
(b) (i) The face to face interview is the most common form. of interview. In this situation the candidate is interviewed by a single representative of the employing organisation.
The advantages of such interviews are that they establish an understanding between the participants, are cost effective for the organisation (only one member of the organisation’s staff is involved) and, because of the more personal nature, ensure that candidates feel comfortable.
The disadvantages are that the selection interview relies on the views and impression of a single interviewer that can be both subjective and biased. In addition, the interviewer may be selective in questioning and it is easier for the candidate to hide weaknesses or lack of ability.
(ii) If a partner, who is an actuary, provides valuation services to an audit client, can we continue with the audit?
(3 marks)
Required:
For each of the three questions, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that
should be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions above.
(ii) Actuarial services to an audit client
IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ does not deal specifically with actuarial valuation services but with
valuation services in general.
A valuation comprises:
■ making assumptions about the future;
■ applying certain methodologies and techniques;
■ computing a value (or range of values) for an asset, a liability or for a business as a whole.
A self-review threat may be created when a firm or network firm2 performs a valuation for a financial statement audit
client that is to be incorporated into the client’s financial statements.
As an actuarial valuation service is likely to involve the valuation of matters material to the financial statements (e.g. the
present value of obligations) and the valuation involves a significant degree of subjectivity (e.g. length of service), the
self-review threat created cannot be reduced to an acceptable level of the application of any safeguard. Accordingly:
■ such valuation services should not be provided; or
■ the firm should withdraw from the financial statement audit engagement.
If the net liability was not material to the financial statements the self-review threat may be reduced to an acceptable
level by the application of safeguards such as:
■ involving an additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team to review the work done
by the actuary;
■ confirming with the audit client their understanding of the underlying assumptions of the valuation and the
methodology to be used and obtaining approval for their use;
■ obtaining the audit client‘s acknowledgement of responsibility for the results of the work performed by the firm; and
■ making arrangements so that the partner providing the actuarial services does not participate in the audit
engagement.
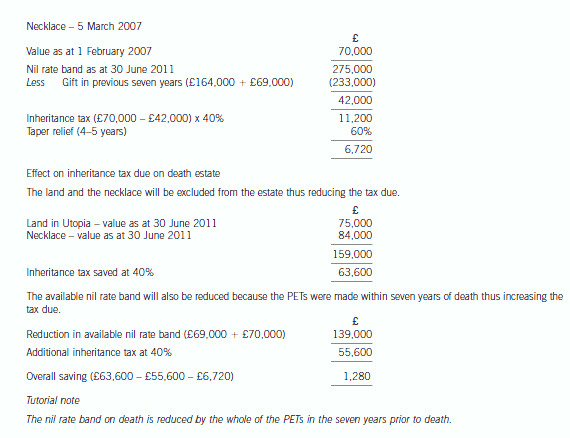
(b) Mabel has two objectives when making the gifts to Bruce and Padma:
(1) To pay no tax on any gift in her lifetime; and
(2) To reduce the eventual liability to inheritance tax on her death.
Advise Mabel which item to gift to Bruce and to Padma in order to satisfy her objectives. Give reasons for
your advice.
Your advice should include a computation of the inheritance tax saved as a result of the two gifts, on the
assumption that Mabel dies on 30 June 2011. (10 marks)

(c) Assess Mr Hogg’s belief that employing child labour is ‘always ethically wrong’ from deontological and
teleological (consequentialist) ethical perspectives. (9 marks)
(c) Mr Hogg’s belief that employing child labour is ‘always ethically wrong’
Deontological perspective:
In the case scenario, Mr Hogg is demonstrating a deontological position on child labour by saying that it is ‘always’ wrong.
He is adopting an absolutist rather than a relativist or situational stance in arguing that there are no situations in which child
labour might be ethically acceptable. The deontological view is that an act is right or wrong in itself and does not depend
upon any other considerations (such as economic necessity or the extent of the child’s willingness to work). If child labour is
wrong in one situation, it follows that it is wrong in all situations because of the Kantian principle of generalisability (in the
categorical imperative). Because child labour is wrong and potentially exploitative in some situations, the deontological
position says that it must be assumed to be wrong in all situations. The fact that it may cause favourable outcomes in some
situations does not make it ethically right, because the deontological position is not situational and the quality of the outcome
is not taken into account.
Teleological perspective:
According to the teleological perspective, an act is right or wrong depending on the favourableness of the outcome. It is
sometimes called the consequentialist perspective because the consequences of the action are considered more important
than the act itself.
In the teleological perspective, ethics is situational and not absolute. Therefore child labour is morally justified if the outcome
is favourable. The economic support of a child’s family by provision of wages for family support might be considered to be a
favourable outcome that justifies child labour. There is an ethical trade-off between the importance of the family income from
child labour and the need to avoid exploitation and interfere with the child’s education. Education is clearly important but
family financial support might be a more favourable outcome, at least in the short term, and if so, this would justify the child
working rather than being in school. For HPC, child labour is likely to be cheaper than adult labour but will alienate European
buyers and be in breach of its code of ethics. Child labour may be ethically acceptable if the negative consequences can be
addressed and overcome.
[Tutorial note: other, equally relevant points made in evaluating Mr Hogg’s opinion will be valid. The texts discuss teleology
in terms of utilitarianism and egoism. Although this distinction is not relevant to the question, candidates should not be
penalised for introducing the distinction if the other points raised are relevant]
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-06
- 2019-03-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-05-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-09-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-01
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-15