提问:ACCA是什么?考ACCA有用吗?
发布时间:2020-02-20
ACCA是什么?考ACCA有用吗?为使广大考生及时了解ACCA的相关信息,现将有关事项分享如下,一起来看看吧。
ACCA在国内称为"国际注册会计师",实际上是特许公认会计师公会(The Association Of Chartered Certified Accountants)的缩写,它是英国具有特许头衔的4家注册会计师协会之一,也是当今最知名的国际性会计师组织之一。ACCA资格被认为是"国际财会界的通行证",许多国家立法许可ACCA会员从事审计、投资顾问和破产执行工作。ACCA在欧洲会计专家协会(FEE)、亚太会计师联合会(CAPA)和加勒比特许会计师协会(ICAC)等会计组织中起着非常重要的作用。
ACCA考试是按现代企业财务人员需要具备的技能和技术的要求而设计的,共有13门课程,两门选修课,课程分为3个部分:第一部分涉及基本会计原理;第二部分涵盖专业财会人员应具备的核心专业技能;第三部分培养学员以专业知识对信息进行评估,并提出合理的经营建议和忠告。
ACCA证书在求职、升职和跳槽时均能发挥不同的价值:
1、求职
ACCA证书在HR眼里是一个黄金标签,ACCA证书是求职者对财务知识掌握的证明,也是求职者学习能力和时间管理能力的证明,这些都是工作中最重要的能力,自然也是最吸引HR的东西。
2、升职
ACCA作为一张稀有且高含金量的财会类高端证书,一直以来,都被视为财务管理层岗位招聘条件之一。特别是在外企或是涉及跨国业务的本土企业,ACCA会员掌握的国际会计准则一直是企业财务报告的刚需。在四大中,毕马威的咨询板块一直将ACCA视为升经理的qualification之一,ACCA的重要性毋庸置疑。
3、跳槽
ACCA证书是资深财务人最好的证明,一大原因在于,在拿下ACCA证书多年后可以直接变为FCCA,即资深ACCA会员。别人简历上写“5年财务管理经验”,而你,写的则是“8年ACCA会员”,一下就从众多求职者中脱颖而出了。
据统计,ACCA会员大都能够任职于企业、政府部门的高层职位,担任权威会计师事务所的合伙人,所以他们比普通财务人更具有升值和跳槽的机会。过硬的专业知识,也让那些尚未获得工作经验的ACCA准会员们,也能够凭借它获得良好的发展机会,让他们边实践边成长。
说明:因考试政策、内容不断变化与调整,提供的考试信息仅供参考,如有异议,请考生以权威部门公布的内容为准!
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,考生根据自己的情况自行收藏查阅,如需了解更多ACCA考试的相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Identify and explain the financial statement risks to be taken into account in planning the final audit.
(12 marks)
(b) Financial statement risks
Tutorial note: Note the timeframe. Financial statements for the year to 30 June 2006 are draft. Certain misstatements
may therefore exist due to year-end procedures not yet having taken place.
Revenue/(Receivables)
■ Revenue has increased by 11·8% ((161·5 – 144·4)/144·4 × 100). Overstatement could arise if rebates due to customers
have not yet been accounted for in full (as they are calculated in arrears). If rebates have still to be accounted for trade
receivables will be similarly overstated.
Materials expense
■ Materials expense has increased by 17·8% ((88.0 – 74·7)/74·7 × 100). This is more than the increase in revenue. This
could be legitimate (e.g. if fuel costs have increased significantly). However, the increase could indicate misclassification
of:
– revenue expenditure (see fall in other expenses below);
– capital expenditure (e.g. on overhauls or major refurbishment) as revenue;
– finance lease payments as operating lease.
Depreciation/amortisation
■ This has fallen by 10·5% ((8·5 – 9·5)/9·5 × 100). This could be valid (e.g. if Yates has significant assets already fully
depreciated or the asset base is lower since last year’s restructuring). However, there is a risk of understatement if, for
example:
– not all assets have been depreciated (or depreciated at the wrong rates, or only for 11 months of the year);
– cost of non-current assets is understated (e.g. due to failure to recognise capital expenditure)1;
– impairment losses have not been recognised (as compared with the prior year).
Tutorial note: Depreciation on vehicles and transport equipment represents only 7% of cost. If all items were being
depreciated on a straight-line basis over eight years this should be 12·5%. The depreciation on other equipment looks more
reasonable as it amounts to 14% which would be consistent with an average age of vehicles of seven years (i.e. in the middle
of the range 3 – 13 years).
Other expenses
■ These have fallen by 15·5% ((19·6 – 23·2)/23·2 × 100). They may have fallen (e.g. following the restructuring) or may be
understated due to:
– expenses being misclassified as materials expense;
– underestimation of accrued expenses (especially as the financial reporting period has not yet expired).
Intangibles
■ Intangible assets have increased by $1m (16% on the prior year). Although this may only just be material to the
financial statements as a whole (see (a)) this is the net movement, therefore additions could be material.
■ Internally-generated intangibles will be overstated if:
– any of the IAS 38 recognition criteria cannot be demonstrated;
– any impairment in the year has not yet been written off in accordance with IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’.
Tangible assets
■ The net book value of property (at cost) has fallen by 5%, vehicles are virtually unchanged (increased by just 2·5%)
and other equipment (though the least material category) has fallen by 20·4%.
■ Vehicles and equipment may be overstated if:
– disposals have not been recorded;
– depreciation has been undercharged (e.g. not for a whole year);
– impairments have not yet been accounted for.
■ Understatement will arise if finance leases are treated as operating leases.
Receivables
■ Trade receivables have increased by just 2·2% (although sales increased by 11·8%) and may be understated due to a
cutoff error resulting in overstatement of cash receipts.
■ There is a risk of overstatement if sufficient allowances have not been made for the impairment of individually significant
balances and for the remainder assessed on a portfolio or group basis.
Restructuring provision
■ The restructuring provision that was made last year has fallen/been utilised by 10·2%. There is a risk of overstatement
if the provision is underutilised/not needed for the purpose for which it was established.
Finance lease liabilities
■ Although finance lease liabilities have increased (by $1m) there is a greater risk of understatement than overstatement
if leased assets are not recognised on the balance sheet (i.e. capitalised).
■ Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 17 ‘Leases’ (e.g. in respect of minimum lease payments) are not met.
Trade payables
■ These have increased by only 5·3% compared with the 17·8% increase in materials expense. There is a risk of
understatement as notifications (e.g. suppliers’ invoices) of liabilities outstanding at 30 June 2006 may have still to be
received (the month of June being an unexpired period).
Other (employee) liabilities
■ These may be understated as they have increased by only 7·5% although staff costs have increased by 14%. For
example, balances owing in respect of outstanding holiday entitlements at the year end may not yet be accurately
estimated.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given to other financial statements risks specific to the scenario. For example, ‘time-sensitive
delivery schedules’ might give rise to penalties or claims, that could result in understated provisions or undisclosed
contingent liabilities. Also, given that this is a new audit and the result has changed significantly (from loss to profit) might
suggest a risk of misstatement in the opening balances (and hence comparative information).
1 Tutorial note: This may be unlikely as other expenses have fallen also.
(b) One of the hotels owned by Norman is a hotel complex which includes a theme park, a casino and a golf course,
as well as a hotel. The theme park, casino, and hotel were sold in the year ended 31 May 2008 to Conquest, a
public limited company, for $200 million but the sale agreement stated that Norman would continue to operate
and manage the three businesses for their remaining useful life of 15 years. The residual interest in the business
reverts back to Norman after the 15 year period. Norman would receive 75% of the net profit of the businesses
as operator fees and Conquest would receive the remaining 25%. Norman has guaranteed to Conquest that the
net minimum profit paid to Conquest would not be less than $15 million. (4 marks)
Norman has recently started issuing vouchers to customers when they stay in its hotels. The vouchers entitle the
customers to a $30 discount on a subsequent room booking within three months of their stay. Historical
experience has shown that only one in five vouchers are redeemed by the customer. At the company’s year end
of 31 May 2008, it is estimated that there are vouchers worth $20 million which are eligible for discount. The
income from room sales for the year is $300 million and Norman is unsure how to report the income from room
sales in the financial statements. (4 marks)
Norman has obtained a significant amount of grant income for the development of hotels in Europe. The grants
have been received from government bodies and relate to the size of the hotel which has been built by the grant
assistance. The intention of the grant income was to create jobs in areas where there was significant
unemployment. The grants received of $70 million will have to be repaid if the cost of building the hotels is less
than $500 million. (4 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above income would be treated in the financial statements of Norman for the year ended
31 May 2008.
(b) Property is sometimes sold with a degree of continuing involvement by the seller so that the risks and rewards of ownership
have not been transferred. The nature and extent of the buyer’s involvement will determine how the transaction is accounted
for. The substance of the transaction is determined by looking at the transaction as a whole and IAS18 ‘Revenue’ requires
this by stating that where two or more transactions are linked, they should be treated as a single transaction in order to
understand the commercial effect (IAS18 paragraph 13). In the case of the sale of the hotel, theme park and casino, Norman
should not recognise a sale as the company continues to enjoy substantially all of the risks and rewards of the businesses,
and still operates and manages them. Additionally the residual interest in the business reverts back to Norman. Also Norman
has guaranteed the income level for the purchaser as the minimum payment to Conquest will be $15 million a year. The
transaction is in substance a financing arrangement and the proceeds should be treated as a loan and the payment of profits
as interest.
The principles of IAS18 and IFRIC13 ‘Customer Loyalty Programmes’ require that revenue in respect of each separate
component of a transaction is measured at its fair value. Where vouchers are issued as part of a sales transaction and are
redeemable against future purchases, revenue should be reported at the amount of the consideration received/receivable less
the voucher’s fair value. In substance, the customer is purchasing both goods or services and a voucher. The fair value of the
voucher is determined by reference to the value to the holder and not the cost to the issuer. Factors to be taken into account
when estimating the fair value, would be the discount the customer obtains, the percentage of vouchers that would be
redeemed, and the time value of money. As only one in five vouchers are redeemed, then effectively the hotel has sold goods
worth ($300 + $4) million, i.e. $304 million for a consideration of $300 million. Thus allocating the discount between the
two elements would mean that (300 ÷ 304 x $300m) i.e. $296·1 million will be allocated to the room sales and the balance
of $3·9 million to the vouchers. The deferred portion of the proceeds is only recognised when the obligations are fulfilled.
The recognition of government grants is covered by IAS20 ‘Accounting for government grants and disclosure of government
assistance’. The accruals concept is used by the standard to match the grant received with the related costs. The relationship
between the grant and the related expenditure is the key to establishing the accounting treatment. Grants should not be
recognised until there is reasonable assurance that the company can comply with the conditions relating to their receipt and
the grant will be received. Provision should be made if it appears that the grant may have to be repaid.
There may be difficulties of matching costs and revenues when the terms of the grant do not specify precisely the expense
towards which the grant contributes. In this case the grant appears to relate to both the building of hotels and the creation of
employment. However, if the grant was related to revenue expenditure, then the terms would have been related to payroll or
a fixed amount per job created. Hence it would appear that the grant is capital based and should be matched against the
depreciation of the hotels by using a deferred income approach or deducting the grant from the carrying value of the asset
(IAS20). Additionally the grant is only to be repaid if the cost of the hotel is less than $500 million which itself would seem
to indicate that the grant is capital based. If the company feels that the cost will not reach $500 million, a provision should
be made for the estimated liability if the grant has been recognised.
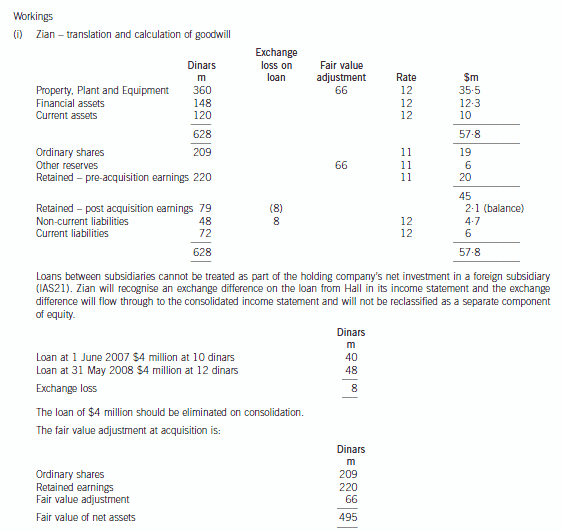
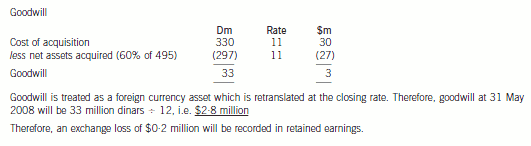
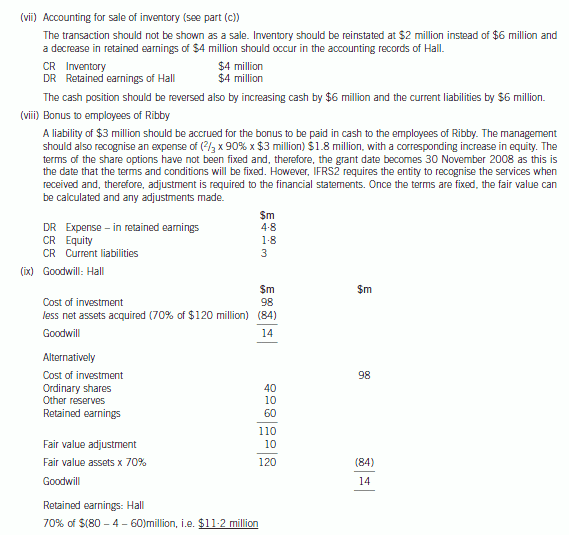
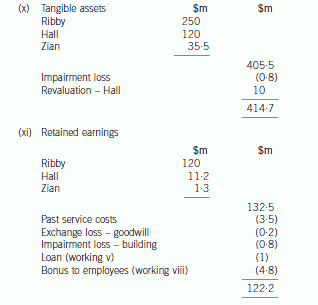
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)




声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-04-19
- 2021-06-18
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-05-08