ACCA F1模拟练习题
发布时间:2019-01-05
1.In the context of
work planning and personal development planning,a SMART framework is often used
as a checklist of the characteristics of effective goals.
What does the';M';in
SMART stand for?
A.Measurable
B.Motivational
C.Memorable
D.Manageable
2.A manager is
assessing the performance of her team members.In accordance with the appraisal
system of the organisation,she has been given a list of characteristics and
performance elements,with notes on how to interpret and apply the
terms:';integrity';,';punctuality';and so on.She is required to comment on how
each appraisee measures up in terms of each factor.
Which appraisal
technique is this organisation using?
A.Overall assessment
B.Grading
C.Behavioural
incident
D.Guided assessment
3.Which of the
following is a disadvantage of a large panel or selection board interview
compared to individual or one-to-one interviews?
A.Specialists can
ask a questions about technical areas of the work
B.Questions tend to
be more varied and more random
C.A number of people
see the candidate at one sitting
D.There is less
opportunity for personal rapport with the candidate
4.The justification
for empowering workers,or removing levels in hierarchies that restrict
freedom,is that not only will the job be done more effectively but the people
who do the job will get more out of it in terms of
growth,challenge,responsibility and self-fulfilment';.
The thinking is in
line with which management writer?
A.Taylor
B.Herzberg
C.Fayol
D.Weber
1.Answers:A
SMART
is';Specific,Measurable,Attainable,Relevant and Time-bounded';,although
versions differ.
Manageable and
Motivational are both very plausible-and also qualities of effective goals-but
you wouldn';t want to replace';measurable';,which is essential(otherwise,how
will you know when you';ve reached your goal?).
2.Answers:D
Overall assessment
is narrative comment without the guidance on how the terms should be
applied.Grading uses rating scales(definitions of performance on each
characteristic from 1-5,say).Behavioural incident methods compare specific
behaviours against typical behaviour in each job.
3.Answers:B
This is a
disadvantage because there may not be a clear interview strategy,and candidates
may have trouble switching from one topic to another.
A number of people
see the candidate at one sitting';is an advantage,because it reduces individual
bias,and saves time in sharing assessments(eg compared to a series of
one-to-one interviews).
Specialists can ask
a questions about technical areas of the work';is an advantage,because a single
interviewer may not be able to spot candidate weaknesses in technical areas.
There is less
opportunity for personal rapport with the candidate';is an advantage,because
personal rapport may lead to favourable bias on the part of an interviewer.
4.Answers:B
Herzberg found that people';s behaviour in the workplace was affected by more than their physical and social needs;the content of the work itself had an effect on motivation and performance.
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Describe the principal matters that should be included in your firm’s submission to provide internal audit
services to RBG. (10 marks)
(b) Principal matters to be included in submission to provide internal audit services
■ Introduction/background – details about York including its organisation (of functions), offices (locations) and number of
internal auditors working within each office. The office that would be responsible for managing the contract should be
stated.
■ A description of York’s services most relevant to RBG’s needs (e.g. in the areas of risk management, IT audits, value for
money (VFM) and corporate governance).
■ Client-specific issues identified. For example, revenue audits will be required routinely for control purposes and to
substantiate the contingent rents due. Other areas of expertise that RBG may be interested in taking advantage of, for
example, special projects such as acquisitions and mergers.
■ York’s approach to assessing audit needs including the key stages and who will be involved. For example:
(1) Preliminary – review of business, industry and the entity’s operating characteristics
(2) Planning – including needs analysis and co-ordination with external audit plan
(3) Post-Audit – assurance that activities were effectively and efficiently executed
(4) Review – of services provided, reports issued and management’s responses.
■ A description of internal audit tools used and methodologies/approach to audit fieldwork including use of embedded
audit software and programs developed by York.
■ A description of York’s systems-based audit, the IT issues to be addressed and the technological support that can be
provided.
■ Any training that will be offered to RBG’s managers and staff, for example, in a risk management approach.
■ A description and quantity of resources, in particular the number of full-time staff, to be deployed in providing services
to RBG. An outline of RBG’s track record in human resource retention and development.
■ Relevant experience – e.g. in internal and external audit in the retail industry. The relative qualifications and skills of
each grade of audit staff and the contract manager in particular.
■ Insurance certifications covering, for example, public liability and professional indemnity insurance.
■ Work ethic policies relating to health and safety, equal opportunities’ and race relations.
■ How York ensures quality throughout the internal audit process including standards to be followed (e.g. Institute of
Internal Auditors’ standards).
■ Sample report templates – e.g. for reporting the results of risk analysis, audit plans and quarterly reporting of findings
to the Audit and Risk Management Committee.
■ Current clients to whom internal audit services are provided from whom RBG will be able to take up references, by
arrangement, if York is short-listed.
■ Any work currently carried out/competed for that could cause a conflict of interest (and the measures to avoid such
conflicts).
■ Fees (daily rates) for each grade of staff and travel and other expenses to be reimbursed. An indication of price increases,
if any, over the three-year contract period. Invoicing terms (e.g. on presentation of reports) and payment terms (e.g. the
end of the month following receipt of the invoice).
■ Performance targets to be met such as deadlines for completing work and submitting and issuing reports.
(iii) Calculate the cash remaining in the company as a result of the salary and dividend payments made in
(ii) above. (1 mark)
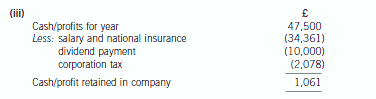
(c) Outline the problems with references. (7 marks)
(15 marks)
Part (c)
There can be significant problems with references, these include the fact that most referees are well known to the applicant and
hesitate to say anything critical. However, the more skilful reference reader learns to look for what is conspicuous by omission
although there is always the risk that the writer merely forgot.
Often there are glowing tributes designed to aid the candidate on their way and some can be too ambiguous to be useful.
It is also important to note that references are poor predictors of future performance, are time consuming for the referee and the
subsequent reader. A particular problem is that employers who want to rid themselves of unsatisfactory employees could write an
enthusiastic reference, or at best one which leaves a lot unsaid.
However, care should be taken when providing references. Potentially, there can be legal consequences if a reference is misleading
or misrepresents the person for whom the reference is provided.
In addition, problems can arise when references are sought too early in the recruitment process and therefore breach confidentiality.
(b) Explain Mintzberg’s five organisational components. (10 marks)
(b) The strategic apex is the highest level of the organisation and is therefore the highest level of management. This part ensures that the organisation’s mission is followed and manages the relationship with the environment.
The operating core is the part that represents the productive activity of the organisation, gathering inputs and, through conversion, turns them into outputs.
The middle line represents that part of the organisation where the middle managers operate. The role of this part is to turn the instructions of the strategic apex into activities for the operating core.
The technostructure includes the staff who provide a technical or supportive activity but which are not a part of the core activities. This part of the organisation includes the engineering, accounting and human resource departments.
The support staff carry out the ancillary activities that are neither part of the core nor the technostructure. Support staff have no role in the direct activities of the organisation: these activities include catering and public relations.(Students may draw the appropriate diagram)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-08-13