2020年ACCA考试会计师与企业财经词汇汇编(19)
发布时间:2020-10-21
今日51题库考试学习网为大家分享2020年ACCA考试会计师与企业财经词汇汇编(19),供大家参考,希望对大家有所帮助,查看更多备考内容请关注51题库考试学习网ACCA考试频道。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Long Bond
【English Terms】
Long Bond
【中文翻译】
长期债券
【详情解释/例子】
年期 10 年以上的债券,经常指 30 年美国国库券。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Long Term
Assets
【English Terms】
Long Term Assets
【中文翻译】
长期资产
【详情解释/例子】
1.资产负债表上项目,指公司物业、设备及其他资本资产的价值减折旧。
2.计划长期在投资组合中持有的股票、债券或其他资产。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Life
Insurance
【English Terms】
Life Insurance
【中文翻译】
人寿保险
【详情解释/例子】
对受保人士过世造成收入损失的保障。指定受益人可获得赔偿,以舒缓受保人死亡造成的财务影响。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Lock-up
Agreement
【English Terms】
Lock-up Agreement
【中文翻译】
锁定协议
【详情解释/例子】
承销商与公司的内部人士之间具有法律约束力的合约,规定在特定时期内,这些人士不可出售任何该公司的股票。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Loan
Sharking
【English Terms】
Loan Sharking
【中文翻译】
高利贷
【详情解释/例子】
借方支付的利息高于法定利率。贷方一般不能收取高于每年60%的利息,但实际规定视乎国家而定。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Loan
Syndication
【English Terms】
Loan Syndication
【中文翻译】
贷款银团
【详情解释/例子】
多个贷方共同出资的贷款,各贷方的出资比例可能不同。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Loan to
Value Ratio
【English Terms】
Loan to Value Ratio
【中文翻译】
贷款与价值比率
【详情解释/例子】
放贷风险比率,计算方法为抵押或贷款总额除以物业的估值。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Loan Loss
Provision
【English Terms】
Loan Loss Provision
【中文翻译】
贷款损失准备金
【详情解释/例子】
预留应付坏账的款项(客户违约、需要重新磋商贷款条款等)。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Liability
【English Terms】
Liability
【中文翻译】
负债
【详情解释/例子】
负债指通过权责发生会计制度估计的合法债务或负债责任,是资产负债表的一个项目,在一年内偿还的属于流动负债,而距离到期日还有一年以上的属于长期负债。
以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的全部内容,预祝大家在12月份ACCA考试中取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Analyse THREE potential problems, based solely on the information provided above, that TMC might
encounter in the acquisition of CBC. (5 marks)
(b) Three potential problems that TMC might encounter in the proposed acquisition of CBC are as follows:
(i) TMC is forecast to have a 22% share of the market for disposable nappies at the end of 2008. If TMC was to acquire
CBC at that time it would then have a market share of ($681m + $155m)/$3,095m = 27%. Much will depend on
prevailing legislation. For example, in the UK it might be the case that the Director General of Fair Trading may ask the
Competition Commission (CC) to investigate if any organisation controls 25% or more of the market. The Secretary of
State may do likewise in circumstances where the proposed takeover would lead to the creation of a firm that would
control 25% or more of the market. (Similar examples from other countries would be equally acceptable.)
(ii) The directors of TMC need to be aware of the precise nature of the cultural problems that CBC has experienced during
recent years as this could be very damaging to its business if the acquisition of CBC goes ahead. In an extreme case
the organisational cultures of TMC and CBC might be incompatible. The directors of TMC need to make a very careful
assessment as to whether it would be possible to transform. a negative culture into a positive one. If they consider that
this would prove to be very difficult then they might be best advised not to proceed with the acquisition.
(iii) The directors of TMC have no experience of managing such acquisitions and this might mean that the integration of CBC
into TMC would prove problematic. It is probable that the systems are different as well as the management styles,
employee skills and business infrastructure.
(Alternative relevant discussion would be acceptable)
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
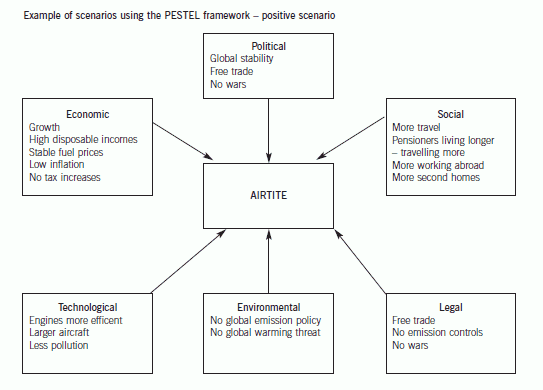
(b) Explain how the process of developing scenarios might help John better understand the macro-environmental
factors influencing Airtite’s future strategy. (8 marks)
(b) Carrying out a systematic PESTEL analysis is a key step in developing alternative scenarios about the future. Johnson and
Scholes define scenarios as ‘detailed and plausible views of how the business environment of an organisation might develop
in the future based on groupings of key environmental influences and drivers of change about which there is a high level of
uncertainty’. In developing scenarios it is necessary to isolate the key drivers of change, which have the potential to have a
significant impact on the company and are associated with high levels of uncertainty. Development of scenarios enables
managers to share assumptions about the future and the key variables shaping that future. This provides an opportunity for
real organisational learning. They are then in a position to monitor these key variables and amend strategies accordingly. It
is important to note that different stakeholder groups will have different expectations about the future and each may provide
a key input to the process of developing scenarios. By their very nature scenarios should not attempt to allocate probabilities
to the key factors and in so doing creating ‘spurious accuracy’ about those factors. A positive scenario is shown below and
should provide a shared insight into the external factors most likely to have a significant impact on Airtite‘s future strategy.
For most companies operating in global environments the ability to respond flexibly and quickly to macro-environmental
change would seem to be a key capability.
The scenario as illustrated below, clearly could have a major impact on the success or otherwise of Airtite’s strategy for the
future. The key drivers for change would seem to be the link between technology and global emissions, fuel prices and the
stability of the global political environment. Through creating a process which considers the drivers which will have most
impact on Airtite and which are subject to the greatest uncertainty, Airtite will have a greater chance of its strategy adaptingto changing circumstances.
21 Which of the following items must be disclosed in a company’s published financial statements?
1 Authorised share capital
2 Movements in reserves
3 Finance costs
4 Movements in non-current assets
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2, 3 and 4 only
D All four items
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-10-10
- 2021-05-29
- 2020-08-14
- 2021-02-13
- 2021-02-13
- 2020-10-21
- 2019-06-22
- 2021-03-05
- 2020-10-10
- 2021-05-29
- 2021-05-29
- 2021-05-29
- 2020-10-18
- 2021-02-13
- 2021-02-13
- 2020-10-10
- 2021-02-21
- 2020-10-21
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-09-04
- 2021-02-13
- 2020-09-04
- 2021-05-30
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-09-05
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-10
- 2021-05-29
- 2019-03-29