ACCA考试F4每日一练(2019-03-10)
发布时间:2019-03-10
Question:
In relation to the TORT OF NEGLIGENCE, explain:
(a)the standard of care owed by one person to another;
(b)remoteness of damage.
Answer:
(a)The law does not require unreasonable steps to be taken to avoid breaching a duty of care. In legal terms, a breach of duty of care occurs if the defendant fails:
'…… to do something which a reasonable man, guided upon those considerations which ordinarily regulate the conduct of human affairs, would do; or doing something which a prudent and reasonable man would not do.' (Blyth v BirminghamWaterworks Co (1856))
Thus the fact that the defendant has acted less skilfully than the reasonable person would expect will usually result in a breach being established. This is the case even where the defendant is inexperienced in their particular trade or activity. For example, a learner driver must drive in the manner of a driver of skill, experience and care (Nettleship v Weston (1971)). However, the standard of care expected from a child may be lower than that of an adult (Mullin v Richards (1998)).
Clearly the degree, or standard, of care to be exercised by such a reasonable person will vary depending on circumstances, but the following factors will be taken into consideration in determining the issue:
(i)The seriousness of the risk
The degree of care must be balanced against the degree of risk involved if the defendant fails in their duty. It follows, therefore, that the greater the risk of injury or the more likely it is to occur, the more the defendant will have to do to fulfil their duty. The degree of care to be exercised by the defendant may be increased if the claimant is very young, old or less able bodied in some way. The rule is that 'you must take your victim as you find him' (this is known as the egg-shell skull rule).
In Haley v London Electricity Board (1965) the defendants, in order to carry out repairs, had made a hole in the pavement. The precautions taken by the Electricity Board were sufficient to safeguard a sighted person, but Haley, who was blind, fell into the hole, striking his head on the pavement, and became deaf as a consequence. It was held that the Electricity Board was in breach of its duty of care to pedestrians. It had failed to ensure that the excavation was safe for all pedestrians, not just sighted persons. It was clearly not reasonably safe for blind persons, yet it was foreseeable that they might use the pavement.
The degree of risk has to be balanced against the social utility and importance of the defendant's activity. For example, in Watt v Hertfordshire CC (1954), the injury sustained by the plaintiff, a fireman, whilst getting to an emergency situation, was not accepted as being the result of a breach of duty of care as, in the circumstances, time was not available to take the measures which would have removed the risk.
(ii)Cost and practicability
Any foreseeable risk has to be balanced against the measures necessary to eliminate it. If the cost of these measures far outweighs the risk, the defendant will probably not be in breach of duty for failing to carry out those measures (Latimer v AEC Ltd (1952)).
(iii)Skilled persons
Individuals who hold themselves out as having particular skills are not judged against the standard of the reasonable person, but the reasonable person possessing the same professional skill as they purport to have (Roe v Minister of Health (1954)).
(b)The position in negligence is that the person ultimately liable in damages is only responsible to the extent that the loss sustained was considered not to be too remote. The test for remoteness was established in The Wagon Mound(No 1) (1961).
The defendants negligently allowed furnace oil to spill from a ship into Sydney harbour, which subsequently caused a fire, which spread to, and damaged, the plaintiff's wharf. Although the defendants were held to be in breach of their duty of care, they were only liable for the damage caused to the wharf and slipway through the fouling of the oil. They were not liable for the damage caused by fire because damage by fire was at that time unforeseeable (the oil had a high ignition point and it could not be foreseen that it would ignite on water).
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the form
to be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that the
previous auditors did not use a liability disclaimer in their audit report, and would like more information about the use
of liability disclaimer paragraphs.
Required:
(b) Discuss the ethical issues raised by the request for your firm to type the financial statements of Blod Co.
(3 marks)
(b) It is not uncommon for audit firms to word process and typeset the financial statements of their clients, especially where the
client is a relatively small entity, which may lack the resources and skills to perform. this task. It is not prohibited by ethical
standards.
However, there could be a perceived threat to independence, with risk magnified in the case of Blod Co, which is a listed
company. The auditors could be perceived to be involved with the preparation of the financial statements of a listed client
company, which is prohibited by ethical standards. IFAC’s Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants states that for a listed
client, the audit firm should not be involved with the preparation of financial statements, which would create a self-review
threat so severe that safeguards could not reduce the threat to an acceptable level. Although the typing of financial statements
itself is not prohibited by ethical guidance, the risk is that providing such a service could be perceived to be an element of
the preparation of the financial statements.
It is possible that during the process of typing the financial statements, decisions and judgments would be made. This could
be perceived as making management decisions in relation to the financial statements, a clear breach of independence.
Therefore to eliminate any risk exposure, the prudent decision would be not to type the financial statements, ensuring that
Blod Co appreciates the ethical problems that this would cause.
Tutorial note: This is an area not specifically covered by ethical guides, where different audit firms may have different views
on whether it is acceptable to provide a typing service for the financial statements of their clients. Credit will be awarded for
sensible discussion of the issues raised bearing in mind other options for the audit firm, for example, it could be argued that
it is acceptable to offer the typing service provided that it is performed by people independent of the audit team, and that
the matter has been discussed with the audit committee/those charged with governance
3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
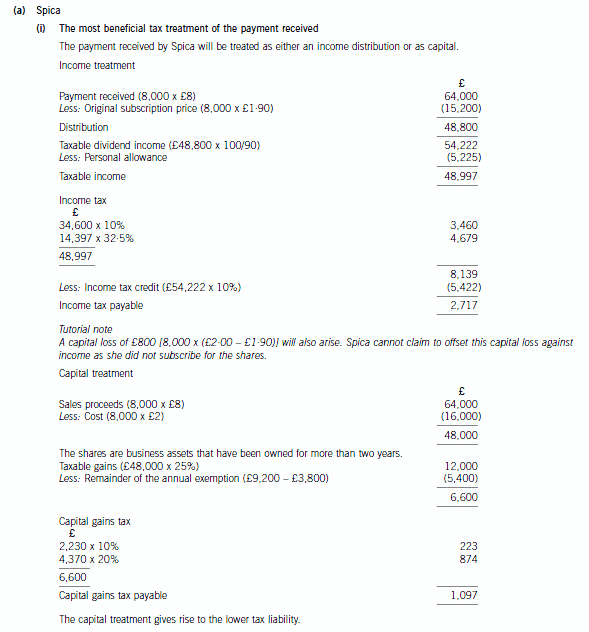
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
15 Which of the following statements about intangible assets are correct?
1 If certain criteria are met, research expenditure must be recognised as an intangible asset.
2 Goodwill may not be revalued upwards.
3 Internally generated goodwill should not be capitalised.
A 2 and 3 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 and 2 only
D All three statements are correct
6 Alasdair, aged 42, is single. He is considering investing in property, as he has heard that this represents a good
investment. In order to raise the funds to buy the property, he wants to extract cash from his personal company, Beezer
Limited, whose year end is 31 December.
Beezer Limited was formed on 1 May 1998 with £1,000 of capital issued as 1,000 £1 ordinary shares, and traded
until 1 January 2005 when Alasdair sold the trade and related assets. The company’s only asset is cash of
£120,000. Alasdair wants to extract this cash from the company with the minimum amount of tax payable. He is
considering either, paying himself a dividend of £120,000, on 31 March 2006, after which the company would have
no assets and be wound up or, leaving the cash in the company and then liquidating the company. Costs of liquidation
of £5,000 would then be incurred.
Since Beezer Limited ceased trading, Alasdair has been taken on as a partner at a marketing firm, Gallus & Co. He
estimates his profit share for the year of assessment 2005/06 will be £30,000. He has not made any capital disposals
in the current tax year.
Alasdair wishes to reinvest the cash extracted from Beezer Limited in property but is not sure whether he should invest
directly in residential or commercial property, or do so via some form. of collective investment. He is aware that Gallus
& Co are looking to rent a new warehouse which could be bought for £200,000. Alasdair thinks that he may be able
to buy the warehouse himself and lease it to his firm, but only if he can borrow the additional money to buy the
property.
Alasdair has a 25% shareholding in another company, Glaikit Limited, whose year end is 31 March. The remaining
shares in this company are held by his friend, Gill. Alasdair is considering borrowing £15,000 from Glaikit Limited
on 1 January 2006. He does not intend to pay any interest on the loan, which is likely to be written off some time
in 2007. Alasdair does not have any connection with Glaikit Limited other than his shareholding.
Required:
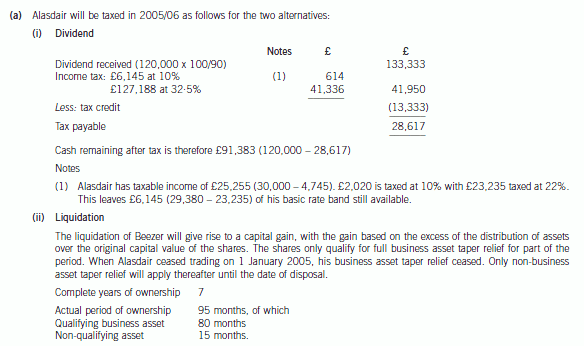
(a) Advise Alasdair whether or not a dividend payment will result in a higher after-tax cash sum than the
liquidation of Beezer Limited. Assume that either the dividend would be paid on 31 March 2006 or the
liquidation would take place on 31 March 2006. (9 marks)
Assume that Beezer Limited has always paid corporation tax at or above the small companies rate of 19%
and that the tax rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part.

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-03-14
- 2019-03-10
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-03-10
- 2019-03-14
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-03-14
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-01-04
- 2019-03-10
- 2019-01-04