即将大一,选择ACCA还是CPA?
发布时间:2021-04-23
即将大一,选择ACCA还是CPA?
最佳答案
别入acca的坑,拿下cpa,acca就是一盘菜。
还有,刷爆GPA才是王道,好好学英语,这俩就够你占据绝大多数时间了,不论是保研还是出国,成绩好英语好用处远比一张纸有用的多。假期拼命实习。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner).
(b) Describe a framework to assess the risks to the progress of the Giant Dam Project. Your answer should
include a diagram to represent the framework. (6 marks)
(b) Framework for assessing risk
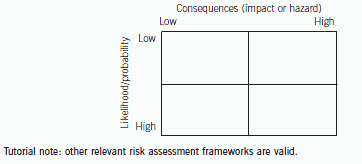
Risk is assessed by considering each identified risk in terms of two variables:
– its hazard (or consequences or impact) and,
– its probability of happening (or being realised or ‘crystallising’).
The most material risks are those identified as having high impact/hazard and the highest probability of happening. Risks
with low hazard and low probability will have low priority whilst between these two extremes are situations where judgement
is required on how to manage the risk.
In practice, it is difficult to measure both variables with any degree of certainty and so if is often sufficient to consider each
in terms of relative crude metrics such as ‘high/medium/low’ or even ‘high/low’. The framework can be represented as a ‘map’
of two intersecting continuums with each variable being plotted along a continuum.
(b) Peter, one of Linden Limited’s non-executive directors, having lived and worked in the UK for most of his adult
life, sold his home near London on 22 March 2006 and, together with his wife (a French citizen), moved to live
in a villa which she owns in the south of France. Peter is now demanding that the tax deducted from his director’s
fees, for the board meetings held on 18 April and 16 May 2006, be refunded, on the grounds that, as he is no
longer resident in the UK, he is no longer liable to UK income tax. All of the company’s board meetings are held
at its offices in Cambridge.
Despite Peter’s assurance that none of the other companies of which he is a director has disputed his change of
tax status, Damian is uncertain whether he should make the refunds requested. However, as Peter is a friend of
the company’s founder, Linden Limited’s managing director is urging him to do so, stating that if the tax does
have to be paid, then Linden Limited could always bear the cost.
Required:
Advise Damian whether Peter is correct in his assertion regarding his tax position and in the case that there
is a UK tax liability the implications of the managing director’s suggestion. You are not required to consider
national insurance (NIC) issues. (4 marks)
(b) Peter will have been resident and ordinarily resident in the UK. When such individuals leave the UK for a purpose other than
to take up full time employment abroad, they normally continue to still be so regarded unless their absence spans a complete
tax year. But, where someone intends to live permanently abroad or to do so for a period of at least three tax years, they may
be treated as non-resident and non-ordinarily resident from the day after the date of their departure, if they can provide
evidence to HMRC of that intention. Selling a residence in the UK and setting up home abroad will normally constitute such
evidence. However to retain non-resident status the intention must actually be fulfilled, and visits to the UK must not exceed
182 days in any tax year or average more than 90 days per year over a period of four tax years. Given that Peter would appear
to have several company directorships in the UK, it is possible that he might fail to satisfy the 90 day average ‘substantial
visits’ rule.
Even if Peter is classed as non-resident, any remuneration earned in the UK will still be liable to UK income tax, and subject
to PAYE, unless it is for duties incidental to an overseas employment, which is unlikely to be the case for fees paid to a nonexecutive
director for attending board meetings. Thus, income tax should still be deducted from the fees under PAYE. Where
PAYE should have been deducted from a director’s emoluments and it has not been, but the tax is nevertheless accounted
for by the company to HMRC, then to the extent that the tax is not reimbursed by the director, he will be treated as receiving
a benefit equivalent to the amount of tax.
(c) The OECD’s Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) recommends preventative measures to be
taken by independent legal professionals and accountants (including sole practitioners, partners and employed
professionals within professional firms).
Required:
Describe FOUR measures that assist in preventing professional accountants from being used for money
laundering purposes. (8 marks)
(c) Measures
The following measures are designed to assist in preventing professional accountants from being used for money laundering
purposes:
■ developing programmes against money laundering and terrorist financing;
■ compliance officer;
■ employee training programme;
■ customer due diligence (CDD);
■ establishing/enhancing record keeping systems for:
– all transactions; and
– the verification of clients’ identities;
■ reporting of suspicious transactions;
■ refusing to have relationships with ‘shell banks’.
Tutorial note: Only FOUR are required.
Developing programmes
■ Internal policies, procedures and controls should be established and recorded including:
– compliance management arrangements (including appointment of a compliance officer);
– an ongoing employee training programme;
– an audit function to test the system.
Compliance officer
■ Appointing a compliance officer having a suitable level of seniority and experience (e.g. one of the principals of an
accountancy firm).
■ Making alternative arrangements (e.g. appointing a deputy) when the compliance officer is going to be unavailable for
a period of time (as reports have to be made as soon as is reasonably practicable).
■ The compliance officer being made responsible for:
– receiving and assessing money laundering reports from colleagues;
– making reports to the FIU; and
– ensuring that individuals are adequately trained.
Employee training programme
■ Providing an employee training programme on:
– relevant legislation (e.g. the main money laundering offences);
– ethical guidance (e.g. ACCA’s ‘Guidance for Accountants’); and
– the firm’s procedures to forestall and prevent money laundering.
■ Establishing a culture of complying with money laundering requirements.
■ Documenting the provision of training (to demonstrate compliance).
■ Training methods may effectively include:
– attending conferences, seminars and training courses run by external organizations; and
– participating in computer based training courses.
Customer due diligence (CDD)
■ Firms should not keep anonymous accounts or accounts in obviously fictitious names.
■ Firms should verify the identity of their customers, when:
– establishing business relations;
– carrying out occasional transactions (e.g. above a designated threshold);
– there is a suspicion of money laundering or terrorist financing; or
– there is doubt about the reliability or adequacy of previously obtained customer identification data.
CDD measures should include:
■ Identifying the customer and verifying that customer’s identity using reliable, independent source documents, data or
information.
Tutorial note: Similarly identify and verify the beneficial owner.
■ Obtaining information on the purpose and intended nature of the business relationship.
■ Conducting ongoing due diligence on business relationships by scrutinising transactions to ensure that they are
consistent with the firm’s knowledge of:
– the customer;
– their business and risk profile;
– the source of funds.
Tutorial note: These requirements should apply to all new customers and existing customers on the basis of materiality and
risk.
Record keeping
■ Maintaining all client identification records together with a record of all transactions, in a full audit trail form.
■ Maintaining records of transactions (both domestic or international) in a readily retrievable form. for a period of at least
five years (to facilitate swift compliance with information requests from the competent authorities).
Tutorial note: Such records must be sufficient to permit reconstruction of individual transactions (including the
amounts and types of currency involved, if any) so as to provide, if necessary, evidence for prosecution of criminal
activity.
■ Retaining client verification records throughout the period of the relationship and for five years after termination of the
relationship.
■ Making available identification data and transaction records to domestic competent authorities upon appropriate
authority.
■ Applying ACCA’s Rules of Professional Conduct ‘Retention of books, files, working papers and other documents’.
■ Paying special attention to all complex, unusual large transactions, and all unusual patterns of transactions, which have
no apparent economic or visible lawful purpose (in accordance with ISA 240 ‘The Auditor’s Responsibility to Consider
Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements ’).
Client identification
■ For an individual – inspecting official documents, with a photograph, establishing the client’s full name and permanent
address, e.g:
– a driving licence or passport, supported by;
– a recent utility bill.
■ For the entity – obtaining from the Registrar of Companies:
– certificate of incorporation;
– company’s registered address; and
– a list of shareholders and directors.
■ Checking the names of new clients against lists of known terrorists and other sanctions information.
■ For trusts – ascertaining:
– the nature and purpose of the trust;
– the original source of funding; and
– the identities of the trustees/controllers, principal settlers and beneficiaries.
Suspicion reporting
■ Prompt reporting of suspicions to the (FIU) in a suspicious transaction report (STR).
■ There should be no ‘de minimis’ concessions. Reporting should be irrespective of:
– the amount involved; or
– whether tax matters are involved.
Tutorial note: Attempted transactions should also be reported.
■ Enhancing confidentiality of the source of reports by:
– disclosing the compliance officer only once; and
– not naming the personnel making reports to the compliance officer.
■ Disclosing further information only if:
– legally required to do so; or
– otherwise justified, in the public interest.
Shell banks
Tutorial note: A ‘shell bank’ is a bank incorporated in a jurisdiction in which it has no physical presence and which is
unaffiliated with a regulated financial group.
■ Firms should guard against relationships with parties that permit their accounts to be used by shell banks.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-22
- 2021-04-15
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-01-04
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-04-17
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-21
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-14
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-08
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-02-23
- 2021-05-09
- 2021-01-04
- 2021-03-29
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-03
- 2021-03-11