我学的中国哲学,会计问题 ACCA F3, p...
发布时间:2021-01-02
我学的中国哲学,会计问题 ACCA F3, purchase账户是属于Income statement还是Balance sheet?
最佳答案
我也是中国哲学毕业的,看你的purchase 是 purchase 什么如果是自己的公司资产就是 属于asset 就进 balanc sheet 里面的 aseet如果purchase来 for trade 的话就是一个cost of sales 进income statement 里面的 cost of sales如果是用作operating 的话 就是一个类似general expense的 income statement 里面的 expenses但是其实这些都是有联系的
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Donald actually decided to operate as a sole trader. The first year’s results of his business were not as he had
hoped, and he made a trading loss of £8,000 in the year to 31 March 2007. However, trading is now improving,
and Donald has sufficient orders to ensure that the business will make profits of at least £30,000 in the year to
31 March 2008.
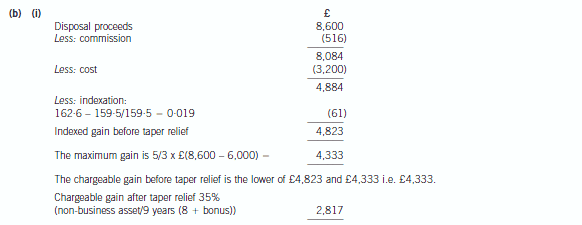
In order to raise funds to support his business over the last 15 months, Donald has sold a painting which was
given to him on the death of his grandmother in January 1998. The probate value of the painting was £3,200,
and Donald sold it for £8,084 (after deduction of 6% commission costs) in November 2006.
He also sold other assets in the year of assessment 2006/07, realising further chargeable gains of £8,775 (after
indexation of £249 and taper relief of £975).
Required:
(i) Calculate the chargeable gain on the disposal of the painting in November 2006. (4 marks)
(b) Discuss the relevance of each of the following actions as steps in trying to remedy performance measurement
problems relating to the ‘365 Sports Complex’ and suggest examples of specific problem classifications that
may be reduced or eliminated by each action:
(i) Focusing on and improving the measurement of customer satisfaction
(ii) Involving staff at all levels in the development and implementation of performance measures
(iii) Being flexible in the extent to which formal performance measures are relied on
(iv) Giving consideration to the auditing of the performance measurement system. (8 marks)
(b) Trying to focus on and improve the measurement of customer satisfaction.
This is a vital goal. Without monitoring and improvement of levels of customer satisfaction, an organisation will tend to
underachieve and is likely to have problems with its future effectiveness. Positive signals from performance measures made
earlier in the value chain are only relevant if they contribute to the ultimate requirement of customer satisfaction. Tunnel vision
and sub-optimisation are examples of measurement problems that may be reduced through recognition of the need for a
management focus on customer satisfaction. For example undue focus on the importance of maximising opening hours may
lead to lack of focus on other quality issues seen as important by customers.
Involving staff at all levels in the development and implementation of performance measures.
People are involved in the achievement of performance measures at all levels and in all aspects of an organisation. It is
important that all staff are willing to accept and work towards any performance measures that are developed to monitor their
part in the operation of the organisation and in the achievement of its objectives. This should help, for example, to reduce
gaming. At the sports complex an example of gaming might be, a deliberate attempt to understate the potential benefits of
maintaining the buildings in order to ensure that funds would be used for other purposes such as an increased advertising
budget. The directors of Astrodome Sports Ltd must recognise that leisure facilities that appear dated and in a poor state of
repair will cause customers to look for more aesthetically appealing alternatives.
Being flexible in the extent to which formal performance measures are relied on.
It is best to acknowledge that measures should not be relied on exclusively for control. A performance measure may give a
short-term signal that does not relate directly to actions that are taking place to improve the level of performance in the longer
term. To some extent, improved performance may be achieved through the informal interaction between individuals and
groups. This flexibility should help to reduce measure fixation and misrepresentation. For example the percentage increase in
the quantity of bowling equipment purchased is seen as necessarily implying increased demand for use of the bowling greens.
Giving consideration to the audit of the performance measurement system.
Actions that may be taken may include:
– Seeking expert interpretation of the performance measures in place. It is important that any audit is ‘free from bias’ and
conducted independently on an ‘arm’s length’ basis. Thus it is essential that such audits should be ‘free from the
influence’ of those personnel involved in the operation of the system.
– Maintaining a careful audit of the data used. Any assessment scheme is only as good as the data on which it is founded
and how this data is analysed and interpreted.
The above actions should help, in particular, to reduce the incidence and impact of measure fixation, misinterpretation and
gaming.
For example, an audit may show that the directors of Astrodome Sports Ltd are fixated on equipment availability and
misinterpret this as being the key to customer volume and high profitability. The audit may also provide evidence of gaming
such as a deliberate attempt to underplay the benefits of one course of action in order to release funds for use on some
alternative.
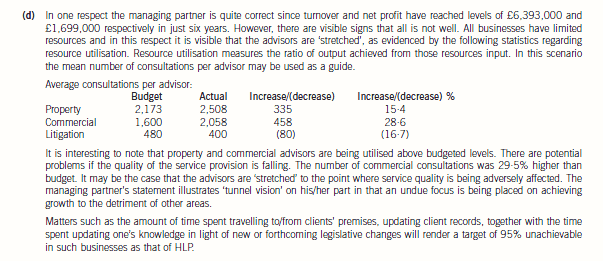
(d) The managing partner of HLP stated at a recent partners’ meeting that ‘every advisor should aim to ensure that
95% of all hours he/she works are billed to clients. This will ensure that we remain both profitable and
competitive’.
Required:
Discuss the statement of the managing partner, drawing attention to any concerns that you may have
regarding the statement. (6 marks)
(c) Critically discuss the likely effectiveness of standard questionnaires sent to other auditors as a means of
obtaining information required. (5 marks)
(c) Likely effectiveness of standard questionnaires
Most group auditors obtain information from other auditors through questionnaires in the form. of yes/no requests and/or
detailed questions.
Standard yes/no questionnaires are widely used because, for example, they:
■ can be completed more quickly by someone already familiar with their form. and content;
■ facilitate summarisation of responses from other auditors by the group auditor.
However, a standard questionnaire may be less effective than a ‘bespoke’ one in that it is likely to ask unnecessary questions.
This may result in the other auditor finding the questions to be ‘not applicable’ and regarding completion of the questionnaire
as a form-filling exercise, rather than providing the group auditor with essential information.
Nevertheless, there is a danger that questionnaires that are not based on some standard form. may overlook or otherwise omit
some significant issues and therefore fail to alert the group auditor to a potential risk area.
Thus a balance needs to be struck between requesting enough information for the group auditor to form. their own view
without requesting meaningless ‘box-ticking’ questions that do not deal with the issues. Questionnaires that get longer and
longer are likely to lose their effectiveness especially if they are to be used in different locations/jurisdictions.
Questionnaires will cover a broad range of topics such as qualifications, competence/experience, compliance with ISAs (and
ISQC 1), audit findings, subsequent events, etc. Therefore there will be a tendency to length (completeness) rather than
quality (relevance).
In conclusion, questionnaires should:
■ avoid over-use of yes/no questions which may encourage laxity;
■ not ask for information that has already been provided or which is unnecessary; and
■ be adequately tailored.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-06-06
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-06-05
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-05-06
- 2021-05-15
- 2021-06-03
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-04-01
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-13
- 2021-04-22
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-05-06
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-01-09
- 2021-04-22
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-06-05