ACCA报考流程谁知道呢?
发布时间:2021-03-12
ACCA报考流程谁知道呢?
最佳答案
ACCA报考流程如下:
一、填写注册表
1.请登陆ACCA官方网站填写英文注册信息,进行网上注册。
2.获得英文注册编号后,登录ACCA官方中文网站请用中文填写中文学员登记表。
二、提供注册所需资料
①学历/学位证明(高校在校生需提交学校出具的在校证明函及第一年所有课程考试合格的成绩单)的原件、复印件和译文;外地申请者不要邮寄原件,请把您的申请材料复印件加盖公司或学校公章,或邮寄公证件既可。②身份证的原件、复印件和译文;或提供护照,不需提交翻译件。
③一张两寸照片;(黑白彩色均可)
④注册报名费(银行汇票或信用卡支付),请确认信用卡可以从国外付款,否则会影响您的注册返回时间;如果不能确定建议您用汇票交纳注册费。(信用卡支付请在英文网站上注册时直接输入信用卡详细信息,英国总部收到您的书面注册材料后才会从您的信用卡上划账)。
三、交纳报名注册费
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Identify and discuss the implications for the audit report if:
(i) the directors refuse to disclose the note; (4 marks)
(c) (i) Audit report implications
Audit procedures have shown that there is a significant level of doubt over Dexter Co’s going concern status. IAS 1
requires that disclosure is made in the financial statements regarding material uncertainties which may cast significant
doubt on the ability of the entity to continue as a going concern. If the directors refuse to disclose the note to the financial
statements, there is a clear breach of financial reporting standards.
In this case the significant uncertainty is caused by not knowing the extent of the future availability of finance needed
to fund operating activities. If the note describing this uncertainty is not provided, the financial statements are not fairly
presented.
The audit report should contain a qualified or an adverse opinion due to the disagreement. The auditors need to make
a decision as to the significance of the non-disclosure. If it is decided that without the note the financial statements are
not fairly presented, and could be considered misleading, an adverse opinion should be expressed. Alternatively, it could
be decided that the lack of the note is material, but not pervasive to the financial statements; then a qualified ‘except
for’ opinion should be expressed.
ISA 570 Going Concern and ISA 701 Modifications to the Independent Auditor’s Report provide guidance on the
presentation of the audit report in the case of a modification. The audit report should include a paragraph which contains
specific reference to the fact that there is a material uncertainty that may cast significant doubt about the entity’s ability
to continue as a going concern. The paragraph should include a clear description of the uncertainties and would
normally be presented immediately before the opinion paragraph.
5 The directors of Blaina Packaging Co (BPC), a well-established manufacturer of cardboard boxes, are currently
considering whether to enter the cardboard tube market. Cardboard tubes are purchased by customers whose
products are wound around tubes of various sizes ranging from large tubes on which carpets are wound, to small
tubes around which films and paper products are wound. The cardboard tubes are usually purchased in very large
quantities by customers. On average, the cardboard tubes comprise between 1% and 2% of the total cost of the
customers’ finished product.
The directors have gathered the following information:
(1) The cardboard tubes are manufactured on machines which vary in size and speed. The lowest cost machine is
priced at $30,000 and requires only one operative for its operation. A one-day training course is required in order
that an unskilled person can then operate such a machine in an efficient and effective manner.
(2) The cardboard tubes are made from specially formulated paper which, at times during recent years, has been in
short supply.
(3) At present, four major manufacturers of cardboard tubes have an aggregate market share of 80%. The current
market leader has a 26% market share. The market shares of the other three major manufacturers, one of which
is JOL Co, are equal in size. The product ranges offered by the four major manufacturers are similar in terms of
size and quality. The market has grown by 2% per annum during recent years.
(4) A recent report on the activities of a foreign-based multinational company revealed that consideration was being
given to expanding operations in their packaging division overseas. The division possesses large-scale automated
machinery for the manufacture of cardboard tubes of any size.
(5) Another company, Plastic Tubes Co (PTC) produces a narrow, but increasing, range of plastic tubes which are
capable of housing small products such as film and paper-based products. At present, these tubes are on average
30% more expensive than the equivalent sized cardboard tubes sold in the marketplace.
Required:
(a) Using Porter’s five forces model, assess the attractiveness of the option to enter the market for cardboard
tubes as a performance improvement strategy for BPC. (10 marks)
(a) In order to assess the attractiveness of the option to enter the market for spirally-wound paper tubes, the directors of BPC
could make use of Michael Porter’s ‘five forces model’.
In applying this model to the given scenario one might conclude that the relatively low cost of the machine together with the
fact that an unskilled person would only require one day’s training in order to be able to operate a machine, constitute
relatively low costs of entry to the market. Therefore one might reasonably conclude that the threat of new entrants might be
high. This is especially the case where the market is highly fragmented.
The fact that products are usually purchased in very large quantities by customers together with the fact that there is little real
difference between the products of alternative suppliers suggests that customer (buyer) power might well be very high. The
fact that the paper tubes on average only comprise between 1% and 2% of the total cost of the purchaser’s finished product
also suggests that buyer power may well be very high.
The threat from suppliers could be high due to the fact that the specially formulated paper from which the tubes are made is
sometimes in short supply. Hence suppliers might increase their prices with consequential diminution in gross margin of the
firms in the marketplace.
The threat from competitive rivals will be strong as the four major players in the market are of similar size and that the market
is a slow growing market. The market leader currently has 26% of the market and the three nearest competitors hold
approximately 18% of the market.
The fact that Plastic Tubes Co (PTC) produces a narrow range of plastic tubes constitutes a threat from a substitute product.
This threat will increase if the product range of PTC is extended and the price of plastic tubes is reduced.
The fact that a foreign-based multinational company is considering entering this market represents a significant threat from a
potential new entrant as it would appear that the multinational company might well be able to derive economies of scale from
large scale automated machinery and has manufacturing flexibility.
Low capital barriers to entry might appeal to BPC but they would also appeal to other potential entrants. The low growth
market, the ease of entry, the existence of established competitors, a credible threat of backward vertical integration by
suppliers, the imminent entry by a multi-national, a struggling established competitor and the difficulty of differentiating an
industrial commodity should call into question the potential of BPC to achieve any sort of competitive advantage. If BPC can
achieve the position of lowest cost producer within the industry then entry into the market might be a good move. In order
to assess whether this is possible BPC must consider any potential synergies that would exist between its cardboard business
and that of the tubes operation.
From the information available, the option to enter the market for cardboard tubes appears to be unattractive. The directors
of BPC should seek alternative performance improvement strategies.
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
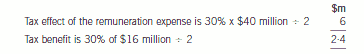
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:
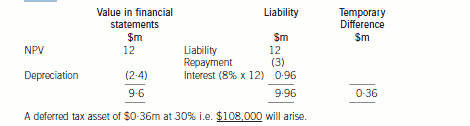
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).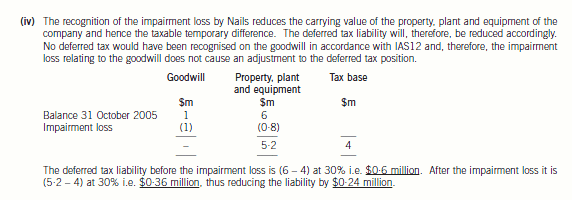
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-02-23
- 2021-05-08
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-06-12
- 2021-05-15
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-11-30
- 2021-06-01
- 2021-04-21
- 2021-04-20
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-07-15
- 2021-02-16
- 2021-06-01
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-07-01
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-06-01