ACCA考试成绩过期了怎么处理呢?
发布时间:2021-03-12
ACCA考试成绩过期了怎么处理呢?
最佳答案
还是要重新考试的,ACCA成绩有效7年,“7年政策”意味着从您通过P阶段的第一门科目开始,7年内需完成P阶段所要求的所有科目,否则从第8年开始您第1年所考过的P阶段科目成绩将会被视为过期作废。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Assess the extent to which social responsibility issues could and should affect his decision to move into the
new product area. (8 marks)
(b) Recent corporate scandals have increased the critical awareness of the need for business to operate ethically and in a socially
responsible way. This is seen largely in the context of large firms and their governance but as the Concrete Solutions scenario
shows small owner-managed firms are not immune from taking difficult decisions that have differing and significant impacts
on the firm’s stakeholders and their expectations. Johnson, Scholes and Whittington see corporate social responsibility as
‘concerned with the ways in which an organisation exceeds the minimum obligation to stakeholders specified through
regulation and corporate governance’. They argue it is useful to distinguish between contractual stakeholders including
customers, suppliers and employees, who have a legal relationship with an organisation and community stakeholders – such
as local communities – who do not have the same degree of legal protection as the first group. Clyde’s local community and
its representatives will face a dilemma – jobs v pollution – not an easy choice! Clearly there will be considerable negotiation
between the key stakeholders and Clyde as the owner/manager should act ethically and with integrity in reaching a decisionhaving profound effects for all parties concerned.
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
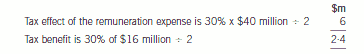
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:
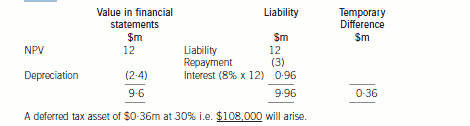
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).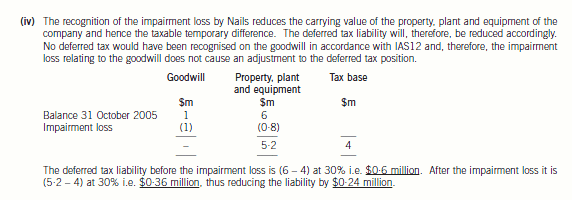
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider, and the evidence you would expect to find in respect of the
carrying value of the cost of investment of Dylan Co in the financial statements of Rosie Co; and
(7 marks)
(b) (i) Cost of investment on acquisition of Dylan Co
Matters to consider
According to the schedule provided by the client, the cost of investment comprises three elements. One matter to
consider is whether the cost of investment is complete.
It appears that no legal or professional fees have been included in the cost of investment (unless included within the
heading ‘cash consideration’). Directly attributable costs should be included per IFRS 3 Business Combinations, and
there is a risk that these costs may be expensed in error, leading to understatement of the investment.
The cash consideration of $2·5 million is the least problematical component. The only matter to consider is whether the
cash has actually been paid. Given that Dylan Co was acquired in the last month of the financial year it is possible that
the amount had not been paid before the year end, in which case the amount should be recognised as a current liability
on the statement of financial position (balance sheet). However, this seems unlikely given that normally control of an
acquired company only passes to the acquirer on cash payment.
IFRS 3 states that the cost of investment should be recognised at fair value, which means that deferred consideration
should be discounted to present value at the date of acquisition. If the consideration payable on 31 January 2009 has
not been discounted, the cost of investment, and the corresponding liability, will be overstated. It is possible that the
impact of discounting the $1·5 million payable one year after acquisition would be immaterial to the financial
statements, in which case it would be acceptable to leave the consideration at face value within the cost of investment.
Contingent consideration should be accrued if it is probable to be paid. Here the amount is payable if revenue growth
targets are achieved over the next four years. The auditor must therefore assess the probability of the targets being
achieved, using forecasts and projections of Maxwell Co’s revenue. Such information is inherently subjective, and could
have been manipulated, if prepared by the vendor of Maxwell Co, in order to secure the deal and maximise
consideration. Here it will be crucial to be sceptical when reviewing the forecasts, and the assumptions underlying the
data. The management of Rosie Co should have reached their own opinion on the probability of paying the contingent
consideration, but they may have relied heavily on information provided at the time of the acquisition.
Audit evidence
– Agreement of the monetary value and payment dates of the consideration per the client schedule to legal
documentation signed by vendor and acquirer.
– Agreement of $2·5 million paid to Rosie Co’s bank statement and cash book prior to year end. If payment occurs
after year end confirm that a current liability is recognised on the individual company and consolidated statement
of financial position (balance sheet).
– Board minutes approving the payment.
– Recomputation of discounting calculations applied to deferred and contingent consideration.
– Agreement that the discount rate used is pre-tax, and reflects current market assessment of the time value of money
(e.g. by comparison to Rosie Co’s weighted average cost of capital).
– Revenue and profit projections for the period until January 2012, checked for arithmetic accuracy.
– A review of assumptions used in the projections, and agreement that the assumptions are comparable with the
auditor’s understanding of Dylan Co’s business.
Tutorial note: As the scenario states that Chien & Co has audited Dylan Co for several years, it is reasonable to rely on
their cumulative knowledge and understanding of the business in auditing the revenue projections.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-01-16
- 2021-06-09
- 2021-05-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-05-08
- 2021-05-09
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-06-01
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-14
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-04-21
- 2021-07-14
- 2021-05-15
- 2021-01-03
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12