ACCA考试到底是属于审计还是属于会计呢?
发布时间:2021-03-12
ACCA考试到底是属于审计还是属于会计呢?
最佳答案
属于会计的,acca的课程设置有会计也有审计。作为英国本土来讲,它相当于中国的cpa在本国有作为注册会计师的执业资格,但放在中国,它只是一个证书,没有在审计报告上的签字权。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
6 Proposed ISA 600 (Revised and Redrafted) The Audit of Group Financial Statements is likely to substantially increase
the formal requirements in the area of group audits.
Required:
(a) Outline the significant issues that are being addressed in the IAASB’s project on group audits. (5 marks)
6 REQUIREMENTS IN GROUP AUDITS
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will be
given suitable credit.
(a) Significant issues
Tutorial note: The objective of the IAASB’s project on the audit of group financial statements (‘group audits’) was to deal
with special considerations in group audits and, in particular, the involvement of other auditors. The re-exposure of ISA 600
(Revised and Redrafted) in March 2006 (following initial publication of a proposed revised ISA in December 2003 and an
exposure draft in March 2005) reflects the significance of the issues that the IAASB has sought to address.
Sole vs divided responsibility
The IAASB has concluded that the group auditor has sole responsibility for the group audit opinion. Thus the exposure drafts
eliminate the distinction between sole and divided responsibility. Therefore no reference to another auditor (e.g. of significant
components) should be made in the group auditor’s report. The practice of referring to another auditor may, arguably, be more
transparent to users of group financial statements. However, it may also mislead users to believe that the group auditor does
not have sole responsibility.
Definition of group auditor
The group auditor is the auditor who signs the auditor’s report on the group financial statements. The project has sought to
clarify whether, for example, an auditor from another office of the group engagement partner’s firm is a member of the group
engagement team or an ‘other auditor’.
‘Related’ vs ‘unrelated’ auditors
IAASB recognises that the nature, timing and extent of procedures performed by the group auditor, including the review of
the other auditor’s audit documentation, are affected by the group auditor’s relationship with the other audit. (For example,
if the other auditor operates under the quality control policies and procedures of the group auditor.) However, IAASB
acknowledges that a consistent distinction between ‘related’ and ‘unrelated’ auditors cannot be made due to the varying
structures of audit firms and their networks. Consequently, the only distinction that is made is between the ‘group’ and ‘other’
auditors.
Acceptance/continuance as group auditor
A group auditor should only accept or continue an engagement if sufficient appropriate evidence is expected to be obtained
on which to base the group audit opinion. Acceptance and continuance as group auditors therefore requires an assessment
of the risk of misstatement in components. IAASB has therefore proposed guidance on the benchmarks that might be used
in identifying significant components.
Access to information
IAASB has concluded that a group audit engagement should be refused (or resigned from) if the group engagement partner
concludes that it will not be possible to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence, the result of which would be a disclaimer.
However, if the group engagement partner is prohibited from refusing or resigning an engagement, the group audit opinion
must be disclaimed.
Aggregation of components
Sufficient appropriate audit evidence must be obtained in respect of components that are not individually significant (but
significant in aggregate). This requires that components be selected for audit procedures (e.g. on specified account balances).
Analytical procedures are required to be performed on components that are not selected. IAASB has therefore identified factors
to be considered in selecting components that are not individually significant.
Responsibilities of other auditors
Historically, other auditors, knowing the context in which their work will be used by the group auditor, have been required to
cooperate with the group auditor. However, the project did not address guidance for other auditors. Therefore, in providing
guidance on the group audit, the IAASB requires the group auditor to obtain an understanding of the requirements for other
auditors to cooperate with the group auditor and provide access to relevant documentation.
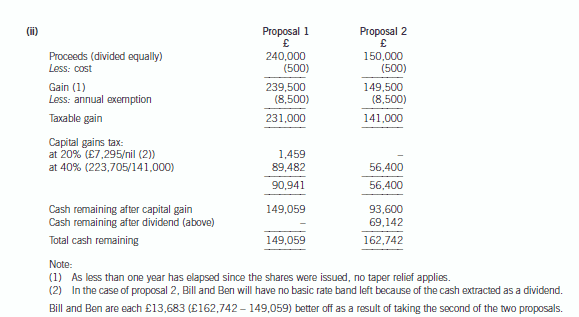
(ii) Following on from your answer to (i), evaluate the two purchase proposals, and advise Bill and Ben
which course of action will result in the highest amount of after tax cash being received by the
shareholders if the disposal takes place on 31 March 2006. (4 marks)
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider, and the evidence you would expect to find in respect of the
carrying value of the cost of investment of Dylan Co in the financial statements of Rosie Co; and
(7 marks)
(b) (i) Cost of investment on acquisition of Dylan Co
Matters to consider
According to the schedule provided by the client, the cost of investment comprises three elements. One matter to
consider is whether the cost of investment is complete.
It appears that no legal or professional fees have been included in the cost of investment (unless included within the
heading ‘cash consideration’). Directly attributable costs should be included per IFRS 3 Business Combinations, and
there is a risk that these costs may be expensed in error, leading to understatement of the investment.
The cash consideration of $2·5 million is the least problematical component. The only matter to consider is whether the
cash has actually been paid. Given that Dylan Co was acquired in the last month of the financial year it is possible that
the amount had not been paid before the year end, in which case the amount should be recognised as a current liability
on the statement of financial position (balance sheet). However, this seems unlikely given that normally control of an
acquired company only passes to the acquirer on cash payment.
IFRS 3 states that the cost of investment should be recognised at fair value, which means that deferred consideration
should be discounted to present value at the date of acquisition. If the consideration payable on 31 January 2009 has
not been discounted, the cost of investment, and the corresponding liability, will be overstated. It is possible that the
impact of discounting the $1·5 million payable one year after acquisition would be immaterial to the financial
statements, in which case it would be acceptable to leave the consideration at face value within the cost of investment.
Contingent consideration should be accrued if it is probable to be paid. Here the amount is payable if revenue growth
targets are achieved over the next four years. The auditor must therefore assess the probability of the targets being
achieved, using forecasts and projections of Maxwell Co’s revenue. Such information is inherently subjective, and could
have been manipulated, if prepared by the vendor of Maxwell Co, in order to secure the deal and maximise
consideration. Here it will be crucial to be sceptical when reviewing the forecasts, and the assumptions underlying the
data. The management of Rosie Co should have reached their own opinion on the probability of paying the contingent
consideration, but they may have relied heavily on information provided at the time of the acquisition.
Audit evidence
– Agreement of the monetary value and payment dates of the consideration per the client schedule to legal
documentation signed by vendor and acquirer.
– Agreement of $2·5 million paid to Rosie Co’s bank statement and cash book prior to year end. If payment occurs
after year end confirm that a current liability is recognised on the individual company and consolidated statement
of financial position (balance sheet).
– Board minutes approving the payment.
– Recomputation of discounting calculations applied to deferred and contingent consideration.
– Agreement that the discount rate used is pre-tax, and reflects current market assessment of the time value of money
(e.g. by comparison to Rosie Co’s weighted average cost of capital).
– Revenue and profit projections for the period until January 2012, checked for arithmetic accuracy.
– A review of assumptions used in the projections, and agreement that the assumptions are comparable with the
auditor’s understanding of Dylan Co’s business.
Tutorial note: As the scenario states that Chien & Co has audited Dylan Co for several years, it is reasonable to rely on
their cumulative knowledge and understanding of the business in auditing the revenue projections.
(ii) Briefly discuss TWO factors which could reduce the rate of return earned by the investment as per the
results in part (a). (4 marks)
(ii) Two factors which might reduce the return earned by the investment are as follows:
(i) Poor product quality
The very nature of the product requires that it is of the highest quality i.e. the cakes are made for human
consumption. Bad publicity via a ‘product recall’ could potentially have a catastrophic effect on the total sales to
Superstores plc over the eighteen month period.
(ii) The popularity of the Mighty Ben character
There is always the risk that the popularity of the character upon which the product is based will diminish with a
resultant impact on sales volumes achieved. In this regard it would be advisable to attempt to negotiate with
Superstores plc in order to minimise potential future losses.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-06-10
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-01-23
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-05-29
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-15
- 2021-01-02
- 2021-05-08
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-05-09
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-20
- 2021-06-08
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-02-11
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-05-11