速速查看!ACCA考试《财务会计》备考考点
发布时间:2020-08-07
ACCA考试《财务会计》备考考点,有小伙伴感兴趣吗?下面51题库考试学习网就带领大家一起来了解看看,想要了解的小伙伴赶紧来围观吧。
THE
CONTROL ENVIRONMENT OF A COMPANY (二)
1
Communication and enforcement of integrity and ethical values
Many
companies have high values and seek to promote honesty and integrity among
their employees on a day-to-day basis. Clearly, if it is evident that such
values do exist and are communicated effectively to employees and enforced,
this will have the effect of increasing confidence in the design,
administration and monitoring of controls – leading to a reduced risk of
material misstatement in a company’s financial statements. For example, where a
company adopts comprehensive anti-bribery and corruption policies and
procedures with regard to contract tendering, and has formal employee
notification and checking practices in this regard, it follows that there is
reduced risk of material misstatement due to the omission of provisions for
fines for the non-compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Alternatively,
the existence in a company of comprehensive and ethical procedures with regard
to the granting of credit facilities to customers and the pursuance of payment
of for goods and services supplied, together with regular supervisory control
in this respect, is likely to lead to increased audit confidence in the trade
receivables area. This is because the existence of a system allowing goods and
services to be a supplied on credit to customers provides the opportunity for
fraud to be perpetrated against the company by employees and customers,
particularly if controls are deficient in terms of their design or
implementation.
2
Commitment to competence
Competence
is the knowledge and skills necessary to accomplish tasks that define the
individual’s job. It is self-evident that if individual employees are tasked
with carrying out duties that are beyond their competence levels, then desired
objectives are unlikely to be met. For example, there is an increased
probability that the objective of avoiding material misstatement in a set of
complex financial statements will not be met if prepared by an inexperienced
company accountant. This is simply due to the inexperience (translating to a
lower competence level) of the accountant. From this, it follows that the
auditor will have increased confidence in internal control relevant to the
audit, where management have taken measures to ensure employees who participate
in internal control are competent to carry out relevant tasks effectively.
Measures taken by management in this regard can cover a range of activity
including for example, rigorous technical and aptitude testing at the employee
recruitment stage and in-house or external training courses and mentoring from
more senior colleagues
以上是关于ACCA考试《财务会计》备考考点的内容,小伙伴们都清楚了吗?如果大家对于ACCA考试还有其他问题,可以多多关注51题库考试学习网,我们将继续为大家答疑解惑。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Good Sports Limited is an independent sports goods retailer owned and operated by two partners, Alan and Bob. The
sports retailing business in the UK has undergone a major change over the past ten years. First of all the supply side
has been transformed by the emergence of a few global manufacturers of the core sports products, such as training
shoes and football shirts. This consolidation has made them increasingly unwilling to provide good service to the
independent sportswear retailers too small to buy in sufficiently large quantities. These independent retailers can stock
popular global brands, but have to order using the Internet and have no opportunity to meet the manufacturer’s sales
representatives. Secondly, UK’s sportswear retailing has undergone significant structural change with the rapid growth
of a small number of national retail chains with the buying power to offset the power of the global manufacturers.
These retail chains stock a limited range of high volume branded products and charge low prices the independent
retailer cannot hope to match.
Good Sports has survived by becoming a specialist niche retailer catering for less popular sports such as cricket,
hockey and rugby. They are able to offer the specialist advice and stock the goods that their customers want.
Increasingly since 2000 Good Sports has become aware of the growing impact of e-business in general and e-retailing
in particular. They employed a specialist website designer and created an online purchasing facility for their
customers. The results were less than impressive, with the Internet search engines not picking up the company
website. The seasonal nature of Good Sports’ business, together with the variations in sizes and colours needed to
meet an individual customer’s needs, meant that the sales volumes were insufficient to justify the costs of running
the site.
Bob, however, is convinced that developing an e-business strategy suited to the needs of the independent sports
retailer such as Good Sports will be key to business survival. He has been encouraged by the growing interest of
customers in other countries to the service and product range they offer. He is also aware of the need to integrate an
e-business strategy with their current marketing, which to date has been limited to the sponsorship of local sports
teams and advertisements taken in specialist sports magazines. Above all, he wants to avoid head-on competition
with the national retailers and their emphasis on popular branded sportswear sold at retail prices that are below the
cost price at which Good Sports can buy the goods.
Required:
(a) Provide the partners with a short report on the advantages and disadvantages to Good Sports of developing
an e-business strategy and the processes most likely to be affected by such a strategy. (12 marks)
(a) To: Good Sports Limited
From:
E – Business strategy
Clearly, the markets that Good Sports operates in are being affected by the development of e-business and its experiences to
date are mixed to say the least. In many ways the advantages and disadvantages of e-business are best related to the benefit
the customer gets from the activity. Firstly, through integrating and accelerating business processes e-business technologies
enable response and delivery times to be speeded up. Secondly, there are new business opportunities for information-based
products and services. Thirdly, websites can be linked with customer databases and provide much greater insights into
customer buying behaviour and needs. Fourthly, there is far greater ability for interaction with the customer, which enables
customisation and a dialogue to be developed. Finally, customers may themselves form. communities able to contact one
another.
There is considerable evidence to show how small operators like Good Sports are able to base their whole strategy on
e-business and achieve high rates of growth. The key to Good Sports survival is customer service – in strategic terms they
are very much niche marketers supplying specialist service and advice to a small section of the local market. The nature of
the business means that face-to-face contact is crucial in moving customers from awareness to action (AIDA – awareness,interest, desire and action). There are therefore limits to the ability of e-business to replace such contact.
Yours,
1 Geno Vesa Farm (GVF), a limited liability company, is a cheese manufacturer. Its principal activity is the production
of a traditional ‘Farmhouse’ cheese that is retailed around the world to exclusive shops, through mail order and web
sales. Other activities include the sale of locally produced foods through a farm shop and cheese-making
demonstrations and tours.
The farm’s herd of 700 goats is used primarily for the production of milk. Kids (i.e. goat offspring), which are a
secondary product, are selected for herd replacement or otherwise sold. Animals held for sale are not usually retained
beyond the time they reach optimal size or weight because their value usually does not increase thereafter.
There are two main variations of the traditional farmhouse cheese; ‘Rabida Red’ and ‘Bachas Blue’. The red cheese
is coloured using Innittu, which is extracted from berries found only in South American rain forests. The cost of Innittu
has risen sharply over the last year as the collection of berries by local village workers has come under the scrutiny
of an international action group. The group is lobbying the South American government to ban the export of Innittu,
claiming that the workers are being exploited and that sustaining the forest is seriously under threat.
Demand for Bachas Blue, which is made from unpasteurised milk, fell considerably in 2003 following the publication
of a research report that suggested a link between unpasteurised milk products and a skin disorder. The financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2004 recognised a material impairment loss attributable to the
equipment used exclusively for the manufacture of Bachas Blue. However, as the adverse publicity is gradually being
forgotten, sales of Bachas Blue are now showing a steady increase and are currently expected to return to their former
level by the end of September 2005.
Cheese is matured to three strengths – mild, medium and strong – depending on the period of time it is left to ripen,
which is six, 12 and 18 months respectively. When produced, the cheese is sold to a financial institution, Abingdon
Bank, at cost. Under the terms of sale, GVF has the option to buy the cheese on its maturity at cost plus 7% for
every six months which has elapsed.
All cheese is stored to maturity on wooden boards in GVF’s cool and airy sheds. However, recently enacted health
and safety legislation requires that the wooden boards be replaced with stainless steel shelves with effect from 1 July
2005. The management of GVF has petitioned the government health department that to comply with the legislation
would interfere with the maturing process and the production of medium and strong cheeses would have to cease.
In 2003, GVF applied for and received a substantial regional development grant for the promotion of tourism in the
area. GVF’s management has deferred its plan to convert a disused barn into holiday accommodation from 2004
until at least 2006.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the principal audit risks to be considered when planning the final audit of GVF for the
year ending 30 September 2005. (14 marks)
(a) Principal audit risks
Industry
‘Farming’ is an inherently risky business activity – being subject to conditions (e.g. disease, weather) outside management’s
control. In some jurisdictions, where the industry is highly regulated, compliance risk may be high.
The risks of mail order retailing ‘exclusive’ products are higher (than for ‘essential’ products, say) as demand fluctuations are
more dramatic (e.g. in times of recession). However, the Internet has provided GVF with a global customer base.
The planned audit approach should be risk-based combined with a systems approach to (say) controls in the revenue cycle.
Goat herd
The goat herd will consist of:
■ mature goats held for use in the production of milk and kids which are held for replacement purposes (i.e. of the nature
of non-current tangible assets); and
■ kids which are to be sold (i.e. of the nature of inventory).
Tutorial note: IAS 41 is not an examinable document at 2.5 and candidates are not expected to be familiar with its
requirements. However, those candidates showing an awareness that biological assets are excluded from the scope of
IAS 16 because they are covered by IAS 41 and answered accordingly were not penalised but awarded equivalent marks.
Therefore, the number of animals in each category must be accurately ascertained to determine:
■ the balance sheet carrying amounts analysed between current and non-current assets; and
■ the charge to the income statement (e.g. for depreciation (IAS 16) and fair value adjustments (IAS 41)).
There is a risk that the carrying amount of the production animals will be misstated if, for example:
■ useful lives/depreciation rates are unreasonable;
■ estimates of residual values are not kept under review;
■ they are impaired.
Tutorial note: Under IAS 41 animals raised during the year should be recognised initially and at each balance sheet date
at fair value less estimated point-of-sale costs. There is therefore a risk of misstatement if fair value cannot be measured
reliabiy (e.g. if market-determined prices are not available). However, this seems unlikely.
Kids will be understated in the balance sheet if they are not recorded on birth (i.e. their existence needs to be recorded in
order that a value be assigned to them).
The net realisable value of animals held for sale may fall below cost if they are not sold soon after reaching optimal size and
weight.
The cost of goats is likely to be subjective. For example, the cost of producing a mature goat from a kid might include direct
costs (e.g. vetinary bills and cost of feed) and attributable overheads (e.g. sheltering). Care must be taken not to carry the
goat herd at more than the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell (IAS 36 Revised).
Unrecorded revenue
Raised (bred) animals are not purchased and, in the absence of documentation supporting their origination, could be sold for
cash (and the revenue unrecorded).
Although the controls over retailing around the world are likely to be strong, there are other sources of income – the shop and
other activities at the farm. Although revenue from these sundry sources may not be material, there is a risk that it could go
unrecorded due to lack of effective controls.
‘Rabida Red’
The cost of an ingredient which is essential to the manufacturing process has increased significantly. If the cost is passed on
to the customers, demand may fall (increasing going concern risk).
Supplies of the ingredient, Innittu, may be restricted – further increasing going concern risk.
Any disclosure of GVF’s socio-environmental policies (e.g. in other information presented with the audited financial
statements), if any, should be scrutinised to ensure that it does not mislead the reader and/or undermine the credibility of the
financial statements.
‘Bachas Blue’
If ‘Bachas Blue’ has been specifically cited as a cause of a skin disorder then GVF could face contingent liabilities for pending
litigation. However, it is more likely that the fall in demand has threatened GVF’s going concern. As the fall in demand has
not been permanent, this threat has been removed for the time being.
The impairment loss previously recognised in respect of the equipment used exclusively in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
should be reversed if there has been a change in the estimates used to determine their recoverable amount (IAS 36
‘Impairment of Assets’).
The recoverable amount would have been based on value in use (since net selling price would not have been applicable).
GVF’s management will have to provide evidence to support their best estimates of future cash flows for the recalculation of
value in use at 30 September 2005.
Maturing cheese
The substance of the sale and repurchase of cheese is that of a loan secured on the inventory. Therefore revenue should not
be recognised on ‘sale’ to Abingdon Bank. The principal terms of the secured borrowings should be disclosed, including the
carrying amount of the inventory to which it applies.
Borrowing costs should all be recognised as an expense in the period unless it is GVF’s policy to capitalise them (the allowed
alternative treatment under IAS 23 ‘Borrowing Costs’). Since the cost of inventories should include all costs incurred in
bringing them to their present location and condition (of maturity), the cost of maturing cheese should include interest at 7%
per six months (as clearly the borrowings are specific). There is a risk that, if the age of maturing cheeses is not accurately
determined, the cost of cheese will be misstated.
Health and safety legislation
At 30 September 2005 the legislation will have been in effect for three months. If GVF’s management has not replaced the
shelves, a provision should be made for the penalties/fines accruing from non-compliance.
If the legislation is complied with:
■ plant and equipment may be overstated e.g:
– if the replaced shelves are not written off;
– if the value of equipment, etc is impaired because the maturing cheese business is to be downsized;
■ inventory may be overstated (e.g. if insufficient allowance is made for the deterioration in maturing cheese resulting from
handling it to replace the shelves);
■ GVF may no longer be a going concern if it does not have the produce to sell to its exclusive customers.
Grant
There is a risk that the grant received has become repayable. For example, if the terms of the grant specified a timeframe. for
the development which is now to be exceeded. In this case the grant should be presented as a payable in the balance sheet.
If the reason for deferring the implementation is related to cash flow problems, this could have implications for the going
concern of GVF.
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
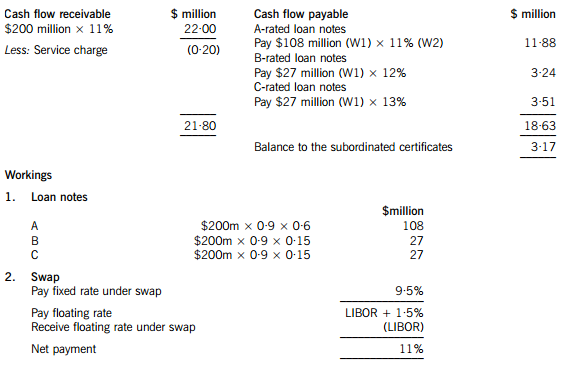
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-07-19
- 2021-05-12
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-05-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-13
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-07-19
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-08-05
- 2020-02-23
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-04-19
- 2021-05-14
- 2020-03-01