海南省考生注意:2020年ACCA考试,科目要这么选!
发布时间:2020-01-10
ACCA考试一共有13门考试科目,这对于一个刚学习ACCA的考生来说,多少有点难以下手的感觉。按照以往考霸学习经验,ACCA考试13门科目如何搭配比较合理呢?今天51题库考试学习网就给大家介绍一下吧!当然,51题库考试学习网推荐大家的报名顺序不一定是适用于每一个人的,仅供大家参考哟~大家一定要根据自己的学习能力和进度来调整报考顺序,毕竟适合自己的才是最好的。
ACCA考试科目共13科,分为四个大模块:知识模块(ACCA考试科目AB-FA)、技能模块(ACCA考试科目LW-FM)、核心模块(ACCA考试科目SBL&SBR)、选修模块(ACCA考试科目AFM-AAA)。学员只需要通过11门必修科目及2门选修科目共13门课程即可通过考试。
不过,总体来说,ACCA考试科目有两个部分:基础阶段和专业阶段。他们各自有哪些特点呢?
第一部分为基础阶段,主要分为知识课程和技能课程两个部分。知识课程主要涉及财务会计和管理会计方面的核心知识,也为接下去进行技能阶段的详细学习搭建了一个平台。技能课程共有六门课程,广泛的涵盖了一名会计师所涉及的知识领域及必须掌握的技能。
第二部分为专业阶段,主要分为核心课程和选修(四选二)课程。该阶段的课程相当于硕士阶段的课程难度,是对第一部分课程的引申和发展。该阶段课程引入了作为未来的高级会计师所必须的更高级的职业技能和知识技能。选修课程为从事高级管理咨询或顾问职业的学员,设计了解决更高级和更复杂的问题的技能。
对于ACCA考生来说,这必考的13门科目必须按模块顺序来报考,即知识模块-技能模块-核心模块-选修模块。必须按照这个顺序来报考,但是各个模块内部的科目是可以打乱顺序考的。例如:F1-F3,可以先考F3,再考F2,再考F1,后面的依此类推。
当然,ACCA每一次考试最多可以报满4科,那么可以把前面模块的都报上,报完以后还有剩余科目可以给后面模块的再报上后面模块的科目。
例如,可以一次把F1、F2、F3、F4都报上,考试结束后,F4、F3、F2都通过了,F1没通过,那么下次报F678等科目时,必须先把F1报上,如果考完了F4-F9的科目,F1还是没通过,报P阶段时,F1也必须先报上。就是说前一个模块没有考完的科目,必须在下一次报考下一个模块考试时都带上继续报考,直到通过。后面的依此类推。
F阶段的考试相对比较简单,P阶段考试科目是专业的阶段课程,相对于前面二部分是有难度的,对综合应用英语的能力和专业知识部分提出了新的挑战。ACCA考试科目P2、P4、P5偏向于计算,ACCA考试科目P1和P3的计算量较少。所以想一次性报考的话,ACCA考试科目P2、P4、P5偏向于计算,ACCA考试科目P1和P3的计算量较少,建议交叉考试分配,在告诉大家分配考试顺序之前,温馨提示一下大家:这里的可以随机顺序报考,指的是阶段内部的报考,譬如F阶段里面F1-F9你可以任意顺序报考,而硬性规定的一点就是F阶段的全部通过之后,才可以报考P阶段的考试。
这里给出的组合建议是:
1.毅力有精力有可以F6+F7+F9,然后F8+P1+P2,若是求稳,应该选择F6+F9,然后F7+F8
2.学习 F9 P2
3.学习 P1 P3
4.学习 P4 P5
为梦想孤注一掷,让努力苦尽甘来。以上信息希望可以帮助到你,最后51题库考试学习网祝你考试成功
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
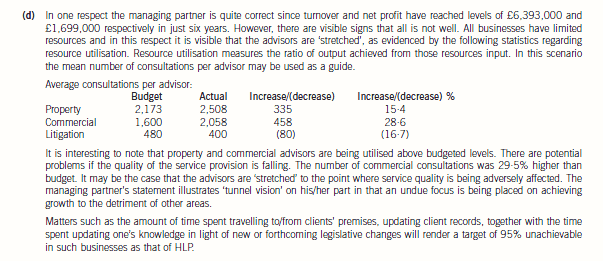
(d) The managing partner of HLP stated at a recent partners’ meeting that ‘every advisor should aim to ensure that
95% of all hours he/she works are billed to clients. This will ensure that we remain both profitable and
competitive’.
Required:
Discuss the statement of the managing partner, drawing attention to any concerns that you may have
regarding the statement. (6 marks)
Glove Co makes high quality, hand-made gloves which it sells for an average of $180 per pair. The standard cost of labour for each pair is $42 and the standard labour time for each pair is three hours. In the last quarter, Glove Co had budgeted production of 12,000 pairs, although actual production was 12,600 pairs in order to meet demand.
37,000 hours were used to complete the work and there was no idle time. The total labour cost for the quarter was $531,930.
At the beginning of the last quarter, the design of the gloves was changed slightly. The new design required workers to sew the company’s logo on to the back of every glove made and the estimated time to do this was 15 minutes for each pair. However, no-one told the accountant responsible for updating standard costs that the standard time per pair of gloves needed to be changed. Similarly, although all workers were given a 2% pay rise at the beginning of the last quarter, the accountant was not told about this either. Consequently, the standard was not updated to reflect these changes.
When overtime is required, workers are paid 25% more than their usual hourly rate.
Required:
(a) Calculate the total labour rate and total labour efficiency variances for the last quarter. (2 marks)
(b) Analyse the above total variances into component parts for planning and operational variances in as much detail as the information allows. (6 marks)
(c) Assess the performance of the production manager for the last quarter. (7 marks)
(a)BasicvariancesLabourratevarianceStandardcostoflabourperhour=$42/3=$14perhour.Labourratevariance=(actualhourspaidxactualrate)–(actualhourspaidxstdrate)Actualhourspaidxactualrate=$531,930.Actualhourspaidxstdrate=37,000x$14=$518,000.Thereforeratevariance=$531,930–$518,000=$13,930ALabourefficiencyvarianceLabourefficiencyvariance=(actualproductioninstdhours–actualhoursworked)xstdrate[(12,600x3)–37,000]x$14=$11,200F(b)PlanningandoperationalvariancesLabourrateplanningvariance(Revisedrate–stdrate)xactualhourspaid=[$14·00–($14·00x1·02)]x37,000=$10,360A.LabourrateoperationalvarianceRevisedratexactualhourspaid=$14·28x37,000=$528,360.Actualcost=$531,930.Variance=$3,570A.Labourefficiencyplanningvariance(Standardhoursforactualproduction–revisedhoursforactualproduction)xstdrateRevisedhoursforeachpairofgloves=3·25hours.[37,800–(12,600x3·25)]x$14=$44,100A.Labourefficiencyoperationalvariance(Revisedhoursforactualproduction–actualhoursforactualproduction)xstdrate(40,950–37,000)x$14=$55,300F.(c)AnalysisofperformanceAtafirstglance,performancelooksmixedbecausethetotallabourratevarianceisadverseandthetotallabourefficiencyvarianceisfavourable.However,theoperationalandplanningvariancesprovidealotmoredetailonhowthesevarianceshaveoccurred.Theproductionmanagershouldonlybeheldaccountableforvarianceswhichhecancontrol.Thismeansthatheshouldonlybeheldaccountablefortheoperationalvariances.Whentheseoperationalvariancesarelookedatitcanbeseenthatthelabourrateoperationalvarianceis$3,570A.Thismeansthattheproductionmanagerdidhavetopayforsomeovertimeinordertomeetdemandbutthemajorityofthetotallabourratevarianceisdrivenbythefailuretoupdatethestandardforthepayrisethatwasappliedatthestartofthelastquarter.Theovertimeratewouldalsohavebeenimpactedbythatpayincrease.Then,whenthelabourefficiencyoperationalvarianceislookedat,itisactually$55,300F.Thisshowsthattheproductionmanagerhasmanagedhisdepartmentwellwithworkerscompletingproductionmorequicklythanwouldhavebeenexpectedwhenthenewdesignchangeistakenintoaccount.Thetotaloperatingvariancesaretherefore$51,730Fandsooverallperformanceisgood.Theadverseplanningvariancesof$10,360and$44,100donotreflectontheperformanceoftheproductionmanagerandcanthereforebeignoredhere.
6 Sergio and Gerard each inherited a half interest in a property, ‘Hilltop’, in October 2005. ‘Hilltop’ had a probate value
of £124,000, but in November 2005 it was badly damaged by fire. In January 2006 the insurance company made
a payment of £81,700 each to Sergio and Gerard. In February 2006 Sergio and Gerard each spent £55,500 of the
insurance proceeds on restoring the property. ‘Hilltop’ was worth £269,000 following the restoration work. In July
2006, Sergio and Gerard sold ‘Hilltop’ for £310,000.
Sergio is 69 years old and a widower with three adult children and seven grandchildren. His annual income consists
of a pension of £9,900 and interest of £300 on savings of £7,600 in a bank deposit account. Sergio owns his home
but no other significant assets. He plans to buy a domestic rental property with the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’,
such that on his death he will have a significant asset which can be sold and divided between the members of his
family.
Gerard is 34 years old. He is employed by Fizz plc on a salary of £66,500 per year together with a performance
related bonus. Gerard estimates that he will receive a bonus in December 2007 of £4,500, in line with previous
years, and that his taxable benefits in the tax year 2007/08 will amount to £7,140. He also expects to receive
dividends from UK companies of £1,935 and bank interest of £648 in the tax year 2007/08. Gerard intends to set
up a personal pension plan in August 2007. He has not made any pension contributions in the past and proposes to
use part of the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’ to make the maximum possible tax allowable contribution.
Fizz plc has announced that it intends to replace the performance related bonus scheme with a share incentive plan,
also linked to performance, with effect from 6 April 2008. Gerard estimates that Fizz plc will award him free shares
worth £2,100 each year. He will also purchase partnership shares worth £700 each year and, as a result, will be
awarded matching shares (further free shares) worth £1,400.
Required:
(a) Calculate the chargeable gains arising on the receipt of the insurance proceeds in January 2006 and the sale
of ‘Hilltop’ in July 2006. You should assume that any elections necessary to minimise the gain on the receipt
of the insurance proceeds have been submitted. (4 marks)
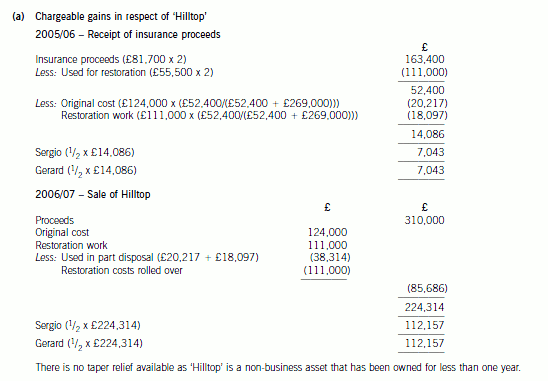
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-05-01
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-21
- 2021-05-12
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-07-15
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-08-16
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08