听说ACCA考试挺难,是真的吗?
发布时间:2019-07-21
很多同学一听到ACCA考试科目一共有14门在加上全英文的,就觉得考试很难。那么ACCA难考吗?ACCA全球通过率高吗?通过率是多少?报名ACCA需要准备什么材料?这些问题对于一个准备报考ACCA的小伙伴来说一定是在心里徘徊已久的问题了。为此小编特地整理了如下内容。
一、ACCA考试难度
ACCA是全英文考试,教材有非常厚,有几十本,考试科目也非常多,有13门。这些因素凑在一块,无疑不在加深ACCA的难度。不过,ACCA考试的难度是以英国大学学位考试的难度为标准。具体而言,第一(f1-f3)、第二部分(f4-f9)的难度分别相当于学士学位高年级课程的考试难度,第三部分的考试相当于硕士学位最后阶段的考试。
第一部分的每门考试只是测试本门课程所包含的知识,着重于为后两个部分中实务性的课程所要运用的理论和技能打下基础。
第二部分的考试除了本门课程的内容之外,还会考到第一部分的一些知识,着重培养学员的分析能力。
第三部分的考试要求学员综合运用学到的知识、技能和决断力。不仅会考到以前的课程内容,还会考到邻近科目的内容。
二、ACCA全球单科通过率
ACCA全球单科通过率基本在30-40%左右,中国学员通过率为50-60%。
ACCA作为国际注册会计师,逐渐受到了越来越多财务人士的认可。ACCA证书的含金量比较高,但是它的报考门槛却不高,凡具有国家教育局认可的大专以上学历即可报名参加考试。
三、在线注册报名考试的时候,需要准备哪些资料呢?
1.学历/ 学位证明(高校在校生需提交学校出具的在校证明函及第一年所有课程考试合格的成绩单)的原件、复印件和译文;外地申请者不要邮寄原件,请把您的申请材料复印件加盖公司或学校公章,或邮寄公证件既可。
2.身份证的原件、复印件和译文;或提供护照,不需提交翻译件。
3.两张张两寸照片;(黑白彩色均可)
4.注册报名费(银行汇票或信用卡支付),请确认信用卡可以从国外付款,否则会影响您的注册返回时间;如果不能确定建议您用汇票交纳注册费。(信用卡支付请在英文网站上注册时直接输入信用卡详细信息,英国总部收到您的书面注册材料后才会从您的信用卡上划帐)。
综上所述就是关于ACCA问题的解答,希望对于各位小伙伴有用,小编将持续为大家更新ACCA相关内容。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(iii) State the value added tax (VAT) and stamp duty (SD) issues arising as a result of inserting Bold plc as
a holding company and identify any planning actions that can be taken to defer or minimise these tax
costs. (4 marks)
You should assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates
and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
(iii) Bold plc will be making a taxable supply of services, likely to exceed the VAT threshold. It should therefore consider
registering for VAT – either immediately on a voluntary basis, or when its cumulative taxable supplies in the previous
twelve months exceed £60,000.
As an alternative, the new group can apply for a group VAT registration. This will simplify its VAT administration as intragroup
transactions are broadly disregarded for VAT purposes, and only one VAT return is required for the group as a
whole.
Stamp duty normally applies at 0·5% on the consideration payable in respect of transactions in shares. However, an
exemption is available in the case of a takeover, reconstruction or amalgamation where there is no real change in
ownership, i.e. the new shareholdings mirror the old shareholdings, and the transaction is for commercial purposes. The
insertion of a new holding company over an existing company, as proposed here, would qualify for this exemption.
There is no VAT on transactions in shares.
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
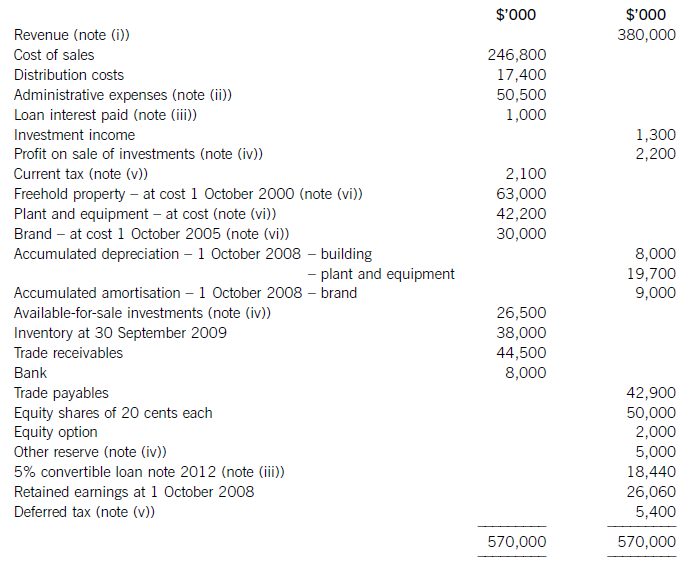
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities.
(b) On 31 May 2007, Leigh purchased property, plant and equipment for $4 million. The supplier has agreed to
accept payment for the property, plant and equipment either in cash or in shares. The supplier can either choose
1·5 million shares of the company to be issued in six months time or to receive a cash payment in three months
time equivalent to the market value of 1·3 million shares. It is estimated that the share price will be $3·50 in
three months time and $4 in six months time.
Additionally, at 31 May 2007, one of the directors recently appointed to the board has been granted the right to
choose either 50,000 shares of Leigh or receive a cash payment equal to the current value of 40,000 shares at
the settlement date. This right has been granted because of the performance of the director during the year and
is unconditional at 31 May 2007. The settlement date is 1 July 2008 and the company estimates the fair value
of the share alternative is $2·50 per share at 31 May 2007. The share price of Leigh at 31 May 2007 is $3 per
share, and if the director chooses the share alternative, they must be kept for a period of four years. (9 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
(b) Transactions that allow choice of settlement are accounted for as cash-settled to the extent that the entity has incurred a
liability (IFRS2 para 34). The share based transaction is treated as the issuance of a compound financial instrument. IFRS2
applies similar measurement principles to determine the value of the constituent parts of a compound instrument as that
required by IAS32 ‘Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation’. The purchase of the property, plant and equipment
(PPE) and the grant to the director, both fall under this section of IFRS2 as the supplier and the director have a choice of
settlement. The fair value of the goods can be measured directly as regards the purchase of the PPE and therefore this fact
determines that the transaction is treated in a certain way. In the case of the director, the fair value of the service rendered
will be determined by the fair value of the equity instruments given and IFRS2 says that this type of share based transaction
should be dealt with in a certain way. Under IFRS2, if the fair value of the goods or services received can be measured directly
and easily then the equity element is determined by taking the fair value of the goods or services less the fair value of the
debt element of this instrument. The debt element is essentially the cash payment that will occur. If the fair value of the goods
or services is measured by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments given then the whole of the compound
instrument should be fair valued. The equity element becomes the difference between the fair value of the equity instruments
granted less the fair value of the debt component. It should take into account the fact that the counterparty must forfeit its
right to receive cash in order to receive the equity instrument.
When Leigh received the property, plant and equipment it should have recorded a liability of $4 million and an increase in
equity of $0·55 million being the difference between the value of the property, plant and equipment and the fair value of theliability. The fair value of the liability is the cash payment of $3·50 x 1·3 million shares, i.e. $4·55 million.
The accounting entry would be:

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-05-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-02-20
- 2019-03-17
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-04-09
- 2021-05-06
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-10-09
- 2019-12-30
- 2020-01-09