2020年ACCA考试“四选二”科目特点及报考建议
发布时间:2020-03-04
从2018年开始,ACCA考试的F阶段均实行机考。相比笔试,机考所需的物品以及考试要求都有所不同,如果不按要求答题可能会导致白丢分。因此,在新年到来之后就有小伙伴在网上询问ACCA考试的机考规则有哪些。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来ACCA考试机考要求相关信息,以供参考。
参加ACCA考试,考生需要携带准考证及带有照片的官方有效身份证件、准考证及计算器。(另外,如果考生携带有个人物品,请将其放至指定区域,考试结束后才能带走。)
具体考场规则:考生在到达考场并进行签到后,如因特殊原因需要离场,请主动联系监考人员,不得擅自离开。如果擅自离开,可能会导致失去考试资格。
另外,参加考试所需要的证件均需要在有效期内,包括护照、驾照和身份证等。
除了需要携带的物品之外,考生如果携带有电子产品,在入场前请提前将手机及其他电子产品关闭,包括闹钟及任何提示音,并放在指定区域,切勿随身携带。如考试期间发现随身携带有手机及其他智能电子产品,将被视为违规行为,将被取消考试成绩或考试资格。
除了电子产品外,食品及饮料不可带入(除去包装的透明瓶装水除外),如果考试中需要服食药物请提前告知监考,做好准备。
ACCA学员在参加考试时携带的任何书籍、笔记、或者其他与考试相关材料都需存放在指定区域,不可带入考试座位。如被发现违反上述规定,将被取消成绩。
ACCA机考可使用计算器,考生在考试中可以使用不具备编程功能、无线通讯功能和文字存储功能的科学计算器,如果是有其他额外功能的计算器,则不允许使用,监考人员有权暂时收走不符合要求的计算器。注意,计算器需要考生提前准备好,现场没有备用计算器提供,考试期间也不能互相借用。ACCA考试的各机考点都会提供草稿纸。
另外,ACCA考试在考试开始后不可以提前结束考试离场。小伙伴们要注意合理分配时间。
以上就是关于ACCA考试机考规则的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA考试需要考生自己携带圆珠笔,请各位小伙伴注意。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 Local neighbourhood shops are finding it increasingly difficult to compete with supermarkets. However, three years
ago, the Perfect Shopper franchise group was launched that allowed these neighbourhood shops to join the group
and achieve cost savings on tinned and packaged goods, particularly groceries. Perfect Shopper purchases branded
goods in bulk from established food suppliers and stores them in large purpose-built warehouses, each designed to
serve a geographical region. When Perfect Shopper was established it decided that deliveries to these warehouses
should be made by the food suppliers or by haulage contractors working on behalf of these suppliers. Perfect Shopper
places orders with these suppliers and the supplier arranges the delivery to the warehouse. These arrangements are
still in place. Perfect Shopper has no branded goods of its own.
Facilities are available in each warehouse to re-package goods into smaller units, more suitable for the requirements
of the neighbourhood shop. These smaller units, typically containing 50–100 tins or packs, are usually small trays,
sealed with strong transparent polythene. Perfect Shopper delivers these to its neighbourhood shops using specialist
haulage contractors local to the regional warehouse. Perfect Shopper has negotiated significant discounts with
suppliers, part of which it passes on to its franchisees. A recent survey in a national grocery magazine showed that
franchisees saved an average of 10% on the prices they would have paid if they had purchased the products directly
from the manufacturer or from an intermediary – such as cash and carry wholesalers.
As well as offering savings due to bulk buying, Perfect Shopper also provides, as part of its franchise:
(i) Personalised promotional material. This usually covers specific promotions and is distributed locally, either using
specialist leaflet distributors or loosely inserted into local free papers or magazines.
(ii) Specialised signage for the shops to suggest the image of a national chain. The signs include the Perfect Shopper
slogan ‘the nation’s local’.
(iii) Specialist in-store display units for certain goods, again branded with the Perfect Shopper logo.
Perfect Shopper does not provide all of the goods required by a neighbourhood shop. Consequently, it is not an
exclusive franchise. Franchisees agree to purchase specific products through Perfect Shopper, but other goods, such
as vegetables, fruit, stationery and newspapers they source from elsewhere. Deliveries are made every two weeks to
franchisees using a standing order for products agreed between the franchisee and their Perfect Shopper sales
representative at a meeting they hold every three months. Variations to this order can be made by telephone, but only
if the order is increased. Downward variations are not allowed. Franchisees cannot reduce their standing order
requirements until the next meeting with their representative.
Perfect Shopper was initially very successful, but its success has been questioned by a recent independent report that
showed increasing discontent amongst franchisees. The following issues were documented.
(i) The need to continually review prices to compete with supermarkets
(ii) Low brand recognition of Perfect Shopper
(iii) Inflexible ordering and delivery system based around forecasts and restricted ability to vary orders (see above)
As a result of this survey, Perfect Shopper has decided to review its business model. Part of this review is to reexamine
the supply chain, to see if there are opportunities for addressing some of its problems.
Required:
(a) Describe the primary activities of the value chain of Perfect Shopper. (5 marks)
(a) Inbound logistics: Handling and storing bulk orders delivered by suppliers and stored on large pallets in regional warehouses.
All inbound logistics currently undertaken by the food suppliers or by contractors appointed by these suppliers.
Operations: Splitting bulk pallets into smaller packages, packing, sealing and storing these packages.
Outbound logistics: Delivery to neighbourhood shops using locally contracted distribution companies.
Marketing & Sales: Specially commissioned signs and personalised sales literature. Promotions and special offers.
Service: Specialist in-store display units for certain goods, three monthly meeting between franchisee and representative.
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner).
1 Stuart is a self-employed business consultant aged 58. He is married to Rebecca, aged 55. They have one child,
Sam, who is aged 24 and single.
In November 2005 Stuart sold a house in Plymouth for £422,100. Stuart had inherited the house on the death of
his mother on 1 May 1994 when it had a probate value of £185,000. The subsequent pattern of occupation was as
follows:
1 May 1994 to 28 February 1995 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca as main residence
1 March 1995 to 31 December 1998 unoccupied
1 January 1999 to 31 March 2001 let out (unfurnished)
1 April 2001 to 30 November 2001 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca
1 December 2001 to 30 November 2005 used occasionally as second home
Both Stuart and Rebecca had lived in London from March 1995 onwards. On 1 March 2001 Stuart and Rebecca
bought a house in London in their joint names. On 1 January 2002 they elected for their London house to be their
principal private residence with effect from that date, up until that point the Plymouth property had been their principal
private residence.
No other capital disposals were made by Stuart in the tax year 2005/06. He has £29,500 of capital losses brought
forward from previous years.
Stuart intends to invest the gross sale proceeds from the sale of the Plymouth house, and is considering two
investment options, both of which he believes will provide equal risk and returns. These are as follows:
(1) acquiring shares in Omikron plc; or
(2) acquiring further shares in Omega plc.
Notes:
1. Omikron plc is a listed UK trading company, with 50,250,000 shares in issue. Its shares currently trade at 42p
per share.
2. Stuart and Rebecca helped start up the company, which was then Omega Ltd. The company was formed on
1 June 1990, when they each bought 24,000 shares for £1 per share. The company became listed on 1 May
1997. On this date their holding was subdivided, with each of them receiving 100 shares in Omega plc for each
share held in Omega Ltd. The issued share capital of Omega plc is currently 10,000,000 shares. The share price
is quoted at 208p – 216p with marked bargains at 207p, 211p, and 215p.
Stuart and Rebecca’s assets (following the sale of the Plymouth house but before any investment of the proceeds) are
as follows:
Assets Stuart Rebecca
£ £
Family house in London 450,000 450,000
Cash from property sale 422,100 –
Cash deposits 165,000 165,000
Portfolio of quoted investments – 250,000
Shares in Omega plc see above see above
Life insurance policy note 1 note 1
Note:
1. The life insurance policy will pay out a sum of £200,000 on the death of the first spouse to die.
Stuart has recently been diagnosed with a serious illness. He is expected to live for another two or three years only.
He is concerned about the possible inheritance tax that will arise on his death. Both he and Rebecca have wills whose
terms transfer all assets to the surviving spouse. Rebecca is in good health.
Neither Stuart nor Rebecca has made any previous chargeable lifetime transfers for the purposes of inheritance tax.
Required:
(a) Calculate the taxable capital gain on the sale of the Plymouth house in November 2005 (9 marks)
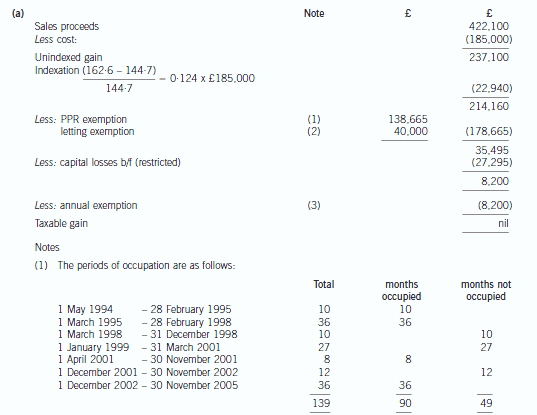
Note that the last 36 months count as deemed occupation, as the house was Stuart’s principal private residence (PPR)
at some point during his period of ownership.
The first 36 months of the period from 1 March 1995 to 31 March 2001 qualifies as a deemed occupation period as
Stuart and Rebecca returned to occupy the property on 1 April 2001. The remainder of the period will be treated as a
period of absence, although letting relief is available for part of the period (see below).
The exempt element of the gain is the proportion during which the property was occupied, real or deemed. This is
£138,665 (90/139 x £214,160).
(2) The chargeable gain is restricted for the period that the property was let out. This is restricted to the lowest of the
following:
(i) the gain attributable to the letting period (27/139 x 214,160) = £41,599
(ii) £40,000
(iii) the total exempt PPR gain = £138,665
i.e. £40,000.
(3) The taper relief is effectively wasted, having restricted losses b/f to preserve the annual exemption.
5 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Blod Co, a listed company, for the year ended 31 March 2008. Your
firm was appointed as auditors of Blod Co in September 2007. The audit work has been completed, and you are
reviewing the working papers in order to draft a report to those charged with governance. The statement of financial
position (balance sheet) shows total assets of $78 million (2007 – $66 million). The main business activity of Blod
Co is the manufacture of farm machinery.
During the audit of property, plant and equipment it was discovered that controls over capital expenditure transactions
had deteriorated during the year. Authorisation had not been gained for the purchase of office equipment with a cost
of $225,000. No material errors in the financial statements were revealed by audit procedures performed on property,
plant and equipment.
An internally generated brand name has been included in the statement of financial position (balance sheet) at a fair
value of $10 million. Audit working papers show that the matter was discussed with the financial controller, who
stated that the $10 million represents the present value of future cash flows estimated to be generated by the brand
name. The member of the audit team who completed the work programme on intangible assets has noted that this
treatment appears to be in breach of IAS 38 Intangible Assets, and that the management refuses to derecognise the
asset.
Problems were experienced in the audit of inventories. Due to an oversight by the internal auditors of Blod Co, the
external audit team did not receive a copy of inventory counting procedures prior to attending the count. This caused
a delay at the beginning of the inventory count, when the audit team had to quickly familiarise themselves with the
procedures. In addition, on the final audit, when the audit senior requested documentation to support the final
inventory valuation, it took two weeks for the information to be received because the accountant who had prepared
the schedules had mislaid them.
Required:
(a) (i) Identify the main purpose of including ‘findings from the audit’ (management letter points) in a report
to those charged with governance. (2 marks)
5 Blod Co
(a) (i) A report to those charged with governance is produced to communicate matters relating to the external audit to those
who are ultimately responsible for the financial statements. ISA 260 Communication of Audit Matters With Those
Charged With Governance requires the auditor to communicate many matters, including independence and other ethical
issues, the audit approach and scope, the details of management representations, and the findings of the audit. The
findings of the audit are commonly referred to as management letter points. By communicating these matters, the auditor
is confident that there is written documentation outlining all significant matters raised during the audit process, and that
such matters have been formally notified to the highest level of management of the client. For the management, the
report should ensure that they fully understand the scope and results of the audit service which has been provided, and
is likely to provide constructive comments to help them to fulfil their duties in relation to the financial statements and
accounting systems and controls more effectively. The report should also include, where relevant, any actions that
management has indicated they will take in relation to recommendations made by the auditors.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-18
- 2019-12-06
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14
- 2019-12-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-18
- 2019-07-21
- 2019-12-28
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-04