学渣、零基础不能考ACCA?不信邪的人都这样过了!
发布时间:2020-03-11
ACCA考试科目较多,并且对考生的英语水平有一定要求。因此,一些小伙伴在了解考试详情后往往会选择放弃。事实上,选择合适的学习方法,通过ACCA考试并不难。下面,51题库考试学习网为大家带来ACCA考试备考方法的相关内容,以供参考。
首先,我们要学会在学习过程中查漏补缺。所谓查漏补缺,就是在ACCA考试中找到学习上的薄弱环节,及时采取有效措施进行补充完善,让我们可以全面化、系统化、有效化的吸收知识。具体来说,就是我们在平常做完模拟试卷后,在试卷分析过程中,通过正确答案和错误答案的对比,要重点找到掌握不牢的知识点。接着,我们就应该去巩固这些知识点,不止是复习好课本和讲义上的基础知识,我们还要做好对知识的精细加工,做到举一反三。ACCA考试的各阶段科目内容存在一定联系,这样也可以让我们在学习后面的科目时更加轻松。
其次是不断对比成绩,找到自己的进步和不足。在做ACCA教材的配套练习册时,我们不但要学会有计划的去做练习,还要拿每次模考ACCA考试成绩与上次模考成绩对照,看是否比上次有进步。在对比时,考生不仅从分数上比,更要比到细处,细化到知识点。
除此外,考生也可以拿自己的成绩跟其他同学分数比。将其他学生分数作为参照,帮助自己找到相对处弱势的地方,及时补救。这样可以让知识点掌握更加牢固。
另外,考生还要学会不断反思。考试不仅仅是考查学生对知识的掌握情况,同时也是在检验学生学习方法的优劣和与应试能力的强弱。一般来说,考生在考试中往往暴露粗心、做题方法不对、不会审题、检查不细等方面的不足,及时改正这些不足之处对后面的学习至关重要。同时,考生也要端正考试的态度,不能只关注分数,重要的是找到适合自己的高效学习法,培养适合自己的思考方式,提高自己的应试能力。要把ACCA报名条件和考试当成检验自己各方面能力的一次机遇。学会在考试中不断找准适合自己的学习方法。
以上就是关于ACCA考试学习方法的相关内容。51题库考试学习网提醒:好的学习方法离不开脚踏实地的实践,想要顺利通过ACCA考试,还是要小伙伴们坚持学习哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
6 An important part of managing people in a professional organisation is to be able to distinguish between aggressiveness and assertiveness in an employee.
Required:
(a) Explain and give examples of aggressive behaviour. (8 marks)
6 To get the best out of people, managers need to have effective communication skills. Professional accountants as managers need to understand the difference between aggressive and assertive behaviour. Often an exchange of communication can be interpreted as a belligerent response from an employee. However, a slight difference in approach can communicate different feelings and achieve a more positive result.
(a) Aggressive behaviour is competitive and directed at defeating someone else. It is standing up for oneself at the expense of other people. It is defending one’s rights but doing so in such a way that violates the rights of other people. Aggressive behaviour ignores or dismisses the needs, wants, opinions, feelings or beliefs of others.
Characteristics of aggressive behaviour include excessive ‘I’ statements, boastfulness, and the individual’s opinions expressed as fact, threatening questions or postures from the individual, sarcasm and other throw-away remarks and a constant blaming of others.
Aggressive behaviour can be self defeating. It may cause such antagonism in the others in the organisation that they will refuse to co-operate or work with the person showing aggressive behaviour.
(ii) Evaluate the relative advantages and disadvantages of Chen’s risk management committee being
non-executive rather than executive in nature. (7 marks)
(ii) Advantages and disadvantages of being non-executive rather than executive
The UK Combined Code, for example, allows for risk committees to be made up of either executive or non-executive
members.
Advantages of non-executive membership
Separation and detachment from the content being discussed is more likely to bring independent scrutiny.
Sensitive issues relating to one or more areas of executive oversight can be aired without vested interests being present.
Non-executive directors often bring specific expertise that will be more relevant to a risk problem than more
operationally-minded executive directors will have.
Chen’s four members, being from different backgrounds, are likely to bring a range of perspectives and suggested
strategies which may enrich the options open to the committee when considering specific risks.
Disadvantages of non-executive membership (advantages of executive membership)
Direct input and relevant information would be available from executives working directly with the products, systems
and procedures being discussed if they were on the committee. Non-executives are less likely to have specialist
knowledge of products, systems and procedures being discussed and will therefore be less likely to be able to comment
intelligently during meetings.
The membership, of four people, none of whom ‘had direct experience of Chen’s industry or products’ could produce
decisions taken without relevant information that an executive member could provide.
Non-executive directors will need to report their findings to the executive board. This reporting stage slows down the
process, thus requiring more time before actions can be implemented, and introducing the possibility of some
misunderstanding.
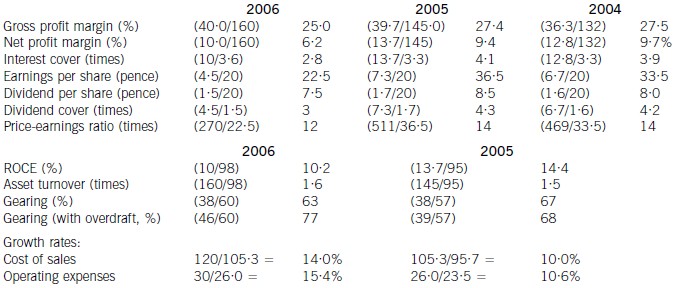
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
(ii) How existing standards could be modified to meet the needs of SMEs. (6 marks
(ii) The development of IFRSs for SMEs as a modification of existing IFRSs
Most SMEs have a narrower range of users than listed entities. The main groups of users are likely to be the owners,
suppliers and lenders. In deciding upon the modifications to make to IFRS, the needs of the users will need to be taken
into account as well as the costs and other burdens imposed upon SMEs by the IFRS. There will have to be a relaxation
of some of the measurement and recognition criteria in IFRS in order to achieve the reduction in the costs and the
burdens. Some disclosure requirements, such as segmental reports and earnings per share, are intended to meet the
needs of listed entities, or to assist users in making forecasts of the future. Users of financial statements of SMEs often
do not make such kinds of forecasts. Thus these disclosures may not be relevant to SMEs, and a review of all of the
disclosure requirements in IFRS will be required to assess their appropriateness for SMEs.
The difficulty is determining which information is relevant to SMEs without making the information disclosed
meaningless or too narrow/restricted. It may mean that measurement requirements of a complex nature may have to be
omitted.
There are, however, rational grounds for justifying different treatments because of the different nature of the entities and
the existence of established practices at the time of the issue of an IFRS.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-08-01
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-04-02
- 2021-06-25
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-04-15
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08