2020年ACCA考试报名时间,考生须知!
发布时间:2020-03-27
51题库考试学习网今天想和小伙伴们分享2020年ACCA考试报名时间,想要了解的小伙伴快跟随51题库考试学习网的脚步一起来看看吧!
ACCA采用了全球统考的考试形式。ACCA考试总共含有15门考试科目。其中必须考过13门才可以申请成为ACCA持证会员,是财会资格考试中科目比较多的资格考试。
虽然ACCA的考试科目较多,但ACCA报考时间较为灵活,因为ACCA考试实施了一年四考的考试时间政策,意思是一年之中有四个考试季,分别为3、6、9、12月的第一个周一至周五的时间进行机考考试。
ACCA考试注册报名时间:
注册报名随时都可以进行,但注册时间的早晚,决定了第一次参加考试的时间。注册完成后必须在官方考试报名截止前获得审核,才可以参加考试报名。
ACCA的注册费、年费、考试费用可以使用双币信用卡及银联及支付宝付款。
51题库考试学习网还给大家带来了ACCA免考政策:
部分财务相关专业大学在校或毕业学生,参加ACCA考试注册时,将获得一定科目的免试权。ACCA对于参加专业会计师考试(ACCA)的中国学员的免试政策详情为:
1、教育部认可高校毕业生(金融、财务管理、审计专业也享受等同于会计学专业的免试政策):
会计学专业-获得学士学位或硕士学位:免试5门课程(AB-PM)。
会计学–辅修专业:免试3门课程(AB-FA)。
法律专业:免试1门课程 (LW)。
商务及管理专业:免试1门课程(AB)。
MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成):免试5门课程(AB-PM)。注:部分院校的MPAcc专业已专门申请ACCA总部的免试审核,因此有多于5门的免试。
MBA学位–获得MBA学位:免试3门课程(AB-FA)。
2、教育部认可高校在校生(本科):
会计学专业-完成第一学年课程:可以注册为ACCA正式学员,无免试。
会计学专业-完成第二学年课程:免试3门课程(AB-FA)。
其他专业 - 在校生:登录ACCA全球网站(www.accaglobal.com)查询。
3、中国注册会计师资格:
CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度前获得全科合格证或者会员资格证:免试5门课程(AB-LW和TX)。
CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度后获得全科合格证或者会员资格证:免试9门课程(AB-FM)。
以上专业所对应的免试门数仅供参考,最终免试结果由ACCA英国总部审核确认。
以上就是51题库考试学习网带来的ACCA考试的全部内容,最后,51题库考试学习网祝愿大家早日成功上岸!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
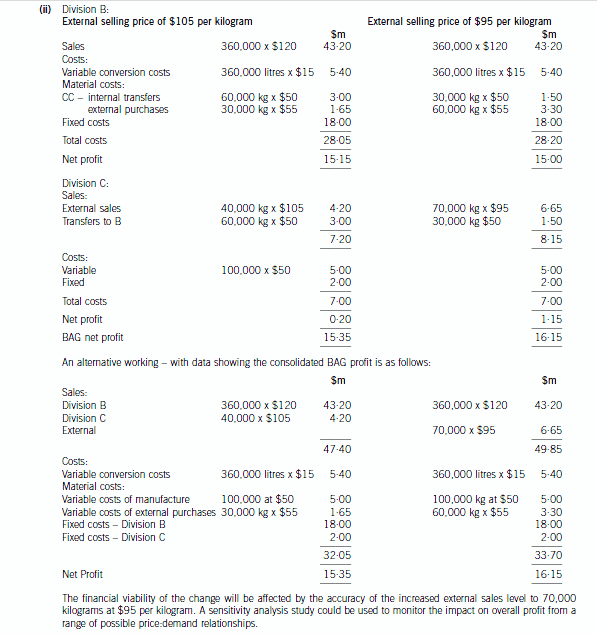
(ii) Division C is considering a decision to lower its selling price to customers external to the group to $95
per kilogram. If implemented, this decision is expected to increase sales to external customers to
70,000 kilograms.
Required:
For BOTH the current selling price of CC of $105 per kilogram and the proposed selling price of $95
per kilogram, prepare a detailed analysis of revenue, costs and net profits of BAG.
Note: in addition, comment on other considerations that should be taken into account before this selling
price change is implemented. (6 marks)
3 (a) Discuss why the identification of related parties, and material related party transactions, can be difficult for
auditors. (5 marks)
3 Pulp Co
(a) Identification of related parties
Related parties and associated transactions are often difficult to identify, as it can be hard to establish exactly who, or what,
are the related parties of an entity. IAS 24 Related Party Disclosures contains definitions which in theory serve to provide a
framework for identifying related parties, but deciding whether a definition is met can be complex and subjective. For example,
related party status can be obtained via significant interest, but in reality it can be difficult to establish the extent of influence
that potential related parties can actually exert over a company.
The directors may be reluctant to disclose to the auditors the existence of related parties or transactions. This is an area of
the financial statements where knowledge is largely confined to management, and the auditors often have little choice but to
rely on full disclosure by management in order to identify related parties. This is especially the case for a close family member
of those in control or having influence over the entity, whose identity can only be revealed by management.
Identification of material related party transactions
Related party transactions may not be easy to identify from the accounting systems. Where accounting systems are not
capable of separately identifying related party transactions, management need to carry out additional analysis, which if not
done makes the transactions extremely difficult for auditors to find. For example sales made to a related party will not
necessarily be differentiated from ‘normal’ sales in the accounting systems.
Related party transactions may be concealed in whole, or in part, from auditors for fraudulent purposes. A transaction may
not be motivated by normal business considerations, for example, a transaction may be recognised in order to improve the
appearance of the financial statements by ‘window dressing’. Clearly if the management is deliberately concealing the true
nature of these items it will be extremely difficult for the auditor to discover the rationale behind the transaction and to consider
the impact on the financial statements.
Finally, materiality is a difficult concept to apply to related party transactions. Once a transaction has been identified, the
auditor must consider whether it is material. However, materiality has a particular application in this situation. ISA 550
Related Parties states that the auditor should consider the effect of a related party transaction on the financial statements.
The problem is that a transaction could occur at an abnormally small, even nil, value. Determining materiality based on
monetary value is therefore irrelevant, and the auditor should instead be alert to the unusual nature of the transaction making
it material.
(iii) assesses TSC in terms of financial performance, competitiveness, service quality, resource utilisation,
flexibility and innovation and discusses the interrelationships between these terms, incorporating
examples from within TSC; and (10 marks)
(iii) The terms listed may be seen as representative of the dimensions of performance. The dimensions may be analysed into
results and determinants.
The results may be measured by focusing on financial performance and competitiveness. Financial performance may
be measured in terms of revenue and profit as shown in the data in the appendix of the question in respect of TSC. The
points system in part (a) of the answer shows which depots have achieved or exceeded the target set. In addition,
liquidity is another aspect of the measurement of financial performance. The points total in part (a) showed that
Leonardotown and Michaelangelotown depots appear to have the best current record in aspects of credit control.
15
Competitiveness may be measured in terms of sales growth but also in terms of market share, number of new
customers, etc. In the TSC statistics available in (a) we only have data for the current quarter. This shows that three of
the four depots listed have achieved increased revenue compared to target.
The determinants are the factors which may be seen to contribute to the achievement of the results. Quality, resource
utilisation, flexibility and innovation are cited by Fitzgerald and Moon as examples of factors that should contribute to
the achievement of the results in terms of financial performance and competitiveness. In TSC a main quality issue
appears to be customer care and service delivery. The statistics in the points table in part (a) of the answer show that
the Raphaeltown depot appears to have a major problem in this area. It has only achieved one point out of the six
available in this particular segment of the statistics.
Resource utilisation for TSC may be measured by the level of effective use of drivers and vehicles. To some extent, this
is highlighted by the statistics relating to customer care and service delivery. For example, late collection of consignments
from customers may be caused by a shortage of vehicles and/or drivers. Such shortages could be due to staff turnover,
sickness, etc or problems with vehicle maintenance.
Flexibility may be an issue. There may, for example, be a problem with vehicle availability. Possibly an increased focus
on sources for short-term sub-contracting of vehicles/collections/deliveries might help overcome delay problems.
The ‘target v actual points system’ may be seen as an example of innovation by the company. This gives a detailed set
of measures that should provide an incentive for improvement at all depots. The points system may illustrate the extent
of achievement/non-achievement of company strategies for success. For example TSC may have a customer care
commitment policy which identifies factors that should be achieved on a continuing basis. For example, timely collection
of consignments, misdirected consignments re-delivered at no extra charge, prompt responses to customer claims and
compensation for customers.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-04-24
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-28
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-15
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-04-17