天津市对于ACCA人才的福利政策你了解吗?快来看看!
发布时间:2020-05-20
ACCA证书作为国际高端会计师资格证书,自其进入中国就一直被视为财会界的金钥匙。国内各个地区也都对ACCA人才表现出了极大诚意,纷纷出台相关政策补贴ACCA人才。天津的补贴政策有哪些呢?下面一起来看看吧!
天津市人民政府办公厅发布《关于支持金融机构和金融人才在津发展的政策措施》,明确提到,具有国际资格认证证书且在金融行业从业5年以上的人才,或者金融机构引进的当年收入超过本市职工平均工资10倍的人才都算金融高端人才。而在国际资格认证证书中,ACCA赫然在列。持有ACCA的金融人才,在天津可以获得至少“海河精英绿卡+奖励”两项福利。
除了天津,其他地区均有相关政策,来了解一下吧!
一、西安
西安高新区“五八八二”三次创业战略列为“积极吸引高端金融人才”,根据西安公布的《西安市加快金融业发展的若干扶持办法》中,明确将ACCA人才列为“具备国际资质的高端金融人才”,获得ACCA(特许公认会计师公会会员)专业资质的金融从业人员,给予每人最高50万元的工作生活补贴。
二、珠海
珠海宣布出台《关于实施“珠海英才计划”加快集聚新时代创新创业人才的若干措施》,新政提到珠海每年将为人才引进投入25亿,提供福利包括落户补贴,住房产权,医疗,子女入学等一系列优惠。
在珠海出台的人才引进政策中,ACCA人才作为获得国际权威资格认证证书的金融审计师,被列入《珠海市紧缺人才开发目录》当中,持有ACCA证书的财务人,一旦落户珠海,可以直接获得20万落户补贴。对于被评定为高端稀缺人才的,补贴额度还会更高。
三、重庆
重庆市渝北区印发了《大力实施创新驱动发展战略加快建设创新生态圈的若干政策》及相关配套文件,落实引进临空创新人才。
(1)购房补贴
ACCA被列入临空创新人才目录,最高可获200万元项目资金,60万元人才补贴,25万元一次性购房补贴。临空创新人才及其配偶、子女户口可随调随迁。
(2)人才补贴
文件中明确指出,将国际权威的职业资格认证ACCA列入临空经营管理B类及C类人才目录,分别享60万元和10万元人才补贴及其他优惠政策。
四、成都
成都天府新区成都直管区召开发布会,重磅推出成都《天府新区成都直管区“天府英才计划”实施办法》计划中指出,55周岁以下,近5年取得ACCA专业资格证书,且在直管区注册的金融机构担任高级管理职务两年以上的财会人可以直接申请成为B类高端人才。按照“天府英才计划”,高端人才B类可以获得高达80万的落户安家补贴,医疗,子女入学等优惠福利。
五、上海
已办理上海居住证的ACCA持证人,凭ACCA证书可获得落户30积分,此外,对于想去会计师事务所的ACCA持证人,可根据《上海市注册会计师协会行业人才管理培养办法》获得10,000元奖励。
六、广州
ACCA持证人可享受广州市政府提供的安家补贴,具体数额为最高不超过100万元,非广州户籍的金融人才和配偶,子女,可在购房、购车、子女入学等方面享受广州市民同等待遇,在落户上享受优先办理。
此外,深圳市罗湖区制定和实施高层次产业人才“菁英计划”对三类“菁英人才”实行不同的人才待遇标准,其中把国际职业资格——ACCA(特许公认会计师)列入B类“菁英人才”认定标准。提供住房安居、创业支持、健康管理、研修资助、联谊交流、子女入学、父母养老等服务。
七、杭州
本科学历的ACCA持证人交满连续一年社保后就可申请落户!在省内事务所工作满三年期间,未受任何处罚,考取ACCA等相关境外资格的奖励3000元。
八、北京
在京发展的16项政策中指出,加强对高端金融人才ACCA等在引进住房保障医疗健康、教育培训、子女入学等方面的服务。不仅在个人所得税方面给予优惠,还可以办理调京手续,办理本市户口,并落户积分优惠。
九、深圳
深圳是伴随改革开放而崛起的新一代一线城市。因为深交所的存在,深圳也成为金融产业聚集地,每年金融产业GDP贡献达数千亿。深圳罗湖区于2016年发布的《深圳市罗湖区“菁英人才”认定办法》中将同时满足其他附加条件的ACCA持证人认定为B类“菁英人才”。
看到这里各位小伙伴有没有心动呢?心动就赶紧行动起来吧!如果想了解更多关于ACCA的资讯可以随时到51题库考试学习网进行咨询哦!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Explain how the adoption of residual income (RI) using the annuity method of depreciation might prove to
be a superior basis for the management incentive plan operated by NCL plc.
(N.B. No illustrative calculations should be incorporated into your explanation). (4 marks)
(b) The use of residual income as a basis for the management incentive plan operated by NCL plc would have the following
advantages:
Divisional management would be more willing to accept a project with a positive residual income and this would contribute
to the improved performance of NCL plc. Also, the disincentive to accept a project with a positive residual income but a return
on investment regarded by divisional management as not being in their best interests would be removed, because divisional
management would be rewarded.
The use of annuity depreciation may improve performance appraisal by removing the effect of straight-line depreciation which
tends to distort project returns especially in the early years of a project’s life when invested capital remains relatively high due
to the constant depreciation charge. The residual income approach using annuity depreciation will only match the NPV if the
annual cashflows of a project are constant. Hence the method when applied to the North or South projects would produce
an NPV which does not exactly match that previously calculated. By way of contrast it is forecast that the East project will
have constant cashflows and in this instance the NPV and residual income based approach when discounted, will produce
the same result.
5 Crusoe has contacted you following the death of his father, Noland. Crusoe has inherited the whole of his father’s
estate and is seeking advice on his father’s capital gains tax position and the payment of inheritance tax following his
death.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Crusoe.
Noland – personal information:
– Divorcee whose only other relatives are his sister, Avril, and two grandchildren.
– Died suddenly on 1 October 2007 without having made a will.
– Under the laws of intestacy, the whole of his estate passes to Crusoe.
Noland – income tax and capital gains tax:
– Has been a basic rate taxpayer since the tax year 2000/01.
– Sales of quoted shares resulted in:
– Chargeable gains of £7,100 and allowable losses of £17,800 in the tax year 2007/08.
– Chargeable gains of approximately £14,000 each tax year from 2000/01 to 2006/07.
– None of the shares were held for long enough to qualify for taper relief.
Noland – gifts made during lifetime:
– On 1 December 1999 Noland gave his house to Crusoe.
– Crusoe has allowed Noland to continue living in the house and has charged him rent of £120 per month
since 1 December 1999. The market rent for the house would be £740 per month.
– The house was worth £240,000 at the time of the gift and £310,000 on 1 October 2007.
– On 1 November 2004 Noland transferred quoted shares worth £232,000 to a discretionary trust for the benefit
of his grandchildren.
Noland – probate values of assets held at death: £
– Portfolio of quoted shares 370,000
Shares in Kurb Ltd 38,400
Chattels and cash 22,300
Domestic liabilities including income tax payable (1,900)
– It should be assumed that these values will not change for the foreseeable future.
Kurb Ltd:
– Unquoted trading company
– Noland purchased the shares on 1 December 2005.
Crusoe:
– Long-standing personal tax client of your firm.
– Married with two young children.
– Successful investment banker with very high net worth.
– Intends to gift the portfolio of quoted shares inherited from Noland to his aunt, Avril, who has very little personal
wealth.
Required:
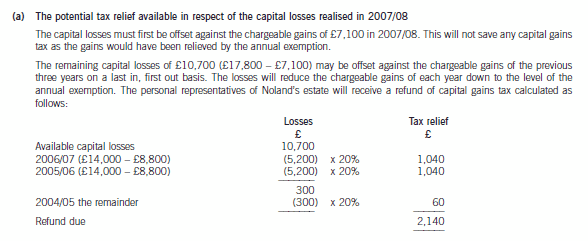
(a) Prepare explanatory notes together with relevant supporting calculations in order to quantify the tax relief
potentially available in respect of Noland’s capital losses realised in 2007/08. (4 marks)
5 A management accounting focus for performance management in an organisation may incorporate the following:
(1) the determination and quantification of objectives and strategies
(2) the measurement of the results of the strategies implemented and of the achievement of the results through a
number of determinants
(3) the application of business change techniques, in the improvement of those determinants.
Required:
(a) Discuss the meaning and inter-relationship of the terms (shown in bold type) in the above statement. Your
answer should incorporate examples that may be used to illustrate each term in BOTH profit-seeking
organisations and not-for-profit organisations in order to highlight any differences between the two types of
organisation. (14 marks)
5 (a) Objectives may be viewed as profit and market share in a profit-oriented organisation or the achievement of ‘value for money’
in a not-for-profit organisation (NFP). The overall objective of an organisation may be expressed in the wording of its mission
statement.
In order to achieve the objectives, long-term strategies will be required. In a profit-oriented organisation, this may incorporate
the evaluation of strategies that might include price reductions, product design changes, advertising campaign, product mix
change and methods changes, embracing change techniques such as BPR, JIT, TQM and ABM. In NFP situations, strategies
might address the need to achieve ‘economy’ through reduction in average cost per unit; ‘efficiency’ through maximisation of
the input:output ratio, whilst checking on ‘effectiveness’ through monitoring whether the objectives are achieved.
The annual budget will quantify the short-term results anticipated of the strategies. These results may be seen as the level of
financial performance and competitiveness achieved. This quantification may be compared with previous years and with
actual performance on an ongoing basis. Financial performance may be measured in terms of profit, liquidity, capital structure
and a range of ratios. Competitiveness may be measured by sales growth, market share and the number of new customers.
In a not-for-profit organisation, the results may be monitored by checking on the effectiveness of actions aimed at the
achievement of the objectives. For instance, the effectiveness of a University may be measured by the number of degrees
awarded and the grades achieved. The level of student ‘drop-outs’ each year may also be seen as a measure of ineffectiveness.
The determinants of results may consist of a number of measures. These may include the level of quality, customer
satisfaction, resource utilisation, innovation and flexibility that are achieved. Such determinants may focus on a range of nonfinancial
measures that may be monitored on an ongoing basis, as part of the feedback information in conjunction with
financial data.
A range of business change techniques may be used to enhance performance management.
Techniques may include:
Business process re-engineering (BPR) which involves the examination of business processes with a view to improving the
way in which each is implemented. A major focus may be on the production cycle, but it will also be applicable in areas such
as the accounting department.
Just-in-time (JIT) which requires commitment to the pursuit of ‘excellence’ in all aspects of an organisation.
Total quality management (TQM) which aims for continuous quality improvement in all aspects of the operation of an
organisation.
Activity based management systems (ABM) which focus on activities that are required in an organisation and the cost drivers
for such activities, with a view to identifying and improving activities that add value and eliminating those activities that do
not add value.
Long-term performance management is likely to embrace elements of BPR, JIT, TQM and ABM. All of these will be reflected
in the annual budget on an ongoing basis.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-03-07
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-07
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-04-01