请知悉!2020年3月份ACCA学员免考政策
发布时间:2020-01-11
2020年3月份ACCA免考政策是什么?这是很多想要报考ACCA的考生咨询最多的问题。下面就让51题库考试学习网来为大家进行答疑解惑,一起来看看吧。
一、2020年3月份ACCA免考政策是什么
(1)教育部认可的高校毕业生


(2)教育部认可高校在校生(本科)

(3)中国注册会计师资格及美国注册管理会计师持证人员

二、免试注意事项
在校生只有顺利通过整学年的课程才能够申请免试。
针对在校生的部分课程免试政策只适用于会计学专业全日制大学本科的在读学生,而不适用于硕士学位或大专学历的在读学生。
已完成MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,还需完成论文的学员也可注册并申请免试。但须提交由学校出具的通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程的成绩单,并附注“该学员已通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,论文待完成”的说明。
政策适用于在中国教育部认可的高等院校全部完成或部分完成本科课程的学生,而不考虑目前居住地点。
欲申请牛津•布鲁克斯大学学士学位的学员需要放弃F7-F9的免试。
说明:因考试政策、内容不断变化与调整,提供的考试信息仅供参考,如有异议,请考生以权威部门公布的内容为准!
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,各位小伙伴们根据自己的实际情况自行查阅收藏,如需了解更多ACCA考试的相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
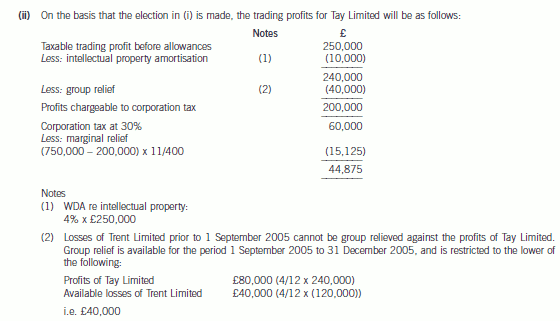
(ii) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) payable by Tay Limited for the year ended 31 March 2006, taking
advantage of all available reliefs. (3 marks)
(b) Chatam, a limited liability company, is a long-standing client. One of its subsidiaries, Ayora, has made losses
for several years. At your firm’s request, Chatam’s management has made a written representation that goodwill
arising on the acquisition of Ayora is not impaired. Your firm’s auditor’s report on the consolidated financial
statements of Chatam for the year ended 31 March 2005 is unmodified. Your firm’s auditor’s report on the
financial statements of Ayora is similarly unmodified. Chatam’s Chief Executive, Charles Barrington, is due to
retire in 2006 when his share options mature. (6 marks)
Required:
Comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of the above matters and their implications,
if any, for the continuation of each assignment.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
(b) Unmodified auditor’s reports
Ethical and professional issues
■ An unmodified opinion means, inter alia, that:
– there are no material matters giving rise to disagreement with the auditor; and
– the auditor’s report does not include an emphasis of matter paragraph (e.g. regarding going concern).
■ By implication the auditor must have obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that notwithstanding the losses:
– the going concern basis is appropriate to Ayora’s financial statements and any related matters (e.g. parental
support) are adequately disclosed therein;
– goodwill in Chatam’s consolidated financial statements is not materially impaired.
■ Management’s written representation (that the goodwill is not impaired) must have been necessary (otherwise it should
not have been asked for). This means that Bartolome does not have sufficient other audit evidence. This seems dubious
as management should have carried out an impairment test to satisfy themselves that goodwill is not impaired. This
test should similarly have satisfied Bartolome.
■ If there is evidence that goodwill is impaired management’s refusal to write it down might be considered a fraud.
■ The matter may cast doubt on the quality of audit evidence obtained in other areas. All other matters on which
management representations have been obtained should be reviewed by another audit partner/manager.
■ Charles Barrington is retiring next year and his share options would presumably be worth less if goodwill were written
down. His position in this long-standing client suggests a familiarity threat.
■ Bartolome may be threatened by self-interest to accept the representation as sufficient in order to retain the client.
■ Bartolome may be unduly influenced by a combination of factors (familiarity and previous experience) and failing to
exercise the necessary degree of professional scepticism.
Implications for continuation with assignment
There is no reason why the audit should not be continued. However, a change in senior audit staff and audit manager may
be overdue. The unmodified auditor’s reports should be subject to a cold review and any quality control issues raised with
the staff who conducted the audit.
3 (a) Financial statements often contain material balances recognised at fair value. For auditors, this leads to additional
audit risk.
Required:
Discuss this statement. (7 marks)
3 Poppy Co
(a) Balances held at fair value are frequently recognised as material items in the statement of financial position. Sometimes it is
required by the financial reporting framework that the measurement of an asset or liability is at fair value, e.g. certain
categories of financial instruments, whereas it is sometimes the entity’s choice to measure an item using a fair value model
rather than a cost model, e.g. properties. It is certainly the case that many of these balances will be material, meaning that
the auditor must obtain sufficient appropriate evidence that the fair value measurement is in accordance with the
requirements of financial reporting standards. ISA 540 (Revised and Redrafted) Auditing Accounting Estimates Including Fair
Value Accounting Estimates and Related Disclosures and ISA 545 Auditing Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures
contain guidance in this area.
As part of the understanding of the entity and its environment, the auditor should gain an insight into balances that are stated
at fair value, and then assess the impact of this on the audit strategy. This will include an evaluation of the risk associated
with the balance(s) recognised at fair value.
Audit risk comprises three elements; each is discussed below in the context of whether material balances shown at fair value
will lead to increased risk for the auditor.
Inherent risk
Many measurements based on estimates, including fair value measurements, are inherently imprecise and subjective in
nature. The fair value assessment is likely to involve significant judgments, e.g. regarding market conditions, the timing of
cash flows, or the future intentions of the entity. In addition, there may be a deliberate attempt by management to manipulate
the fair value to achieve a desired aim within the financial statements, in other words to attempt some kind of window
dressing.
Many fair value estimation models are complicated, e.g. discounted cash flow techniques, or the actuarial calculations used
to determine the value of a pension fund. Any complicated calculations are relatively high risk, as difficult valuation techniques
are simply more likely to contain errors than simple valuation techniques. However, there will be some items shown at fair
value which have a low inherent risk, because the measurement of fair value may be relatively straightforward, e.g. assets
that are regularly bought and sold on open markets that provide readily available and reliable information on the market prices
at which actual exchanges occur.
In addition to the complexities discussed above, some fair value measurement techniques will contain significant
assumptions, e.g. the most appropriate discount factor to use, or judgments over the future use of an asset. Management
may not always have sufficient experience and knowledge in making these judgments.
Thus the auditor should approach some balances recognised at fair value as having a relatively high inherent risk, as their
subjective and complex nature means that the balance is prone to contain an error. However, the auditor should not just
assume that all fair value items contain high inherent risk – each balance recognised at fair value should be assessed for its
individual level of risk.
Control risk
The risk that the entity’s internal monitoring system fails to prevent and detect valuation errors needs to be assessed as part
of overall audit risk assessment. One problem is that the fair value assessment is likely to be performed once a year, outside
the normal accounting and management systems, especially where the valuation is performed by an external specialist.
Therefore, as a non-routine event, the assessment of fair value is likely not to have the same level of monitoring or controls
as a day-to-day business transaction.
However, due to the material impact of fair values on the statement of financial position, and in some circumstances on profit,
management may have made great effort to ensure that the assessment is highly monitored and controlled. It therefore could
be the case that there is extremely low control risk associated with the recognition of fair values.
Detection risk
The auditor should minimise detection risk via thorough planning and execution of audit procedures. The audit team may
lack experience in dealing with the fair value in question, and so would be unlikely to detect errors in the valuation techniques
used. Over-reliance on an external specialist could also lead to errors not being found.
Conclusion
It is true that the increasing recognition of items measured at fair value will in many cases cause the auditor to assess the
audit risk associated with the balance as high. However, it should not be assumed that every fair value item will be likely to
contain a material misstatement. The auditor must be careful to identify and respond to the level of risk for fair value items
on an individual basis to ensure that sufficient and appropriate evidence is gathered, thus reducing the audit risk to an
acceptable level.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-05-08
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-21
- 2021-06-13
- 2020-01-11
- 2020-05-08
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-04-12