ACCA考试常用公式汇总,值得湖南省考生收藏!
发布时间:2020-01-10
距离2020年3月份的ACCA考试还有两个多月左右的时间,想必备考ACCA的同学们正在如火如荼地进行着复习。那么,今天这条“公式宝典”你一定要收好,或许会帮助你成功通过ACCA考试哦!接下来,51题库考试学习网将这份“公式宝典”分享给大家:
因为ACCA考试毕竟是国际性质的考试,因此一些题的计算可能就存在不同的计算方式,计算方式的不同也会导致结果的不同。
一、境内
1、税额=销项税-进项税
2、销项税=销售额×税率
3、视销征税无销额(1)当月类平均;(2)近类货平均,(3)组税价=成本×(1+成利率)
4、征增税及消税:
组税价=成本×(1+成润率)+消税
组税价=成本×(1+成润率)/(1-消率)
5、含税额换
不含税销额=含税销额/1+率(一般)
不含税销额=含税销额/1+征率(小规模)
6、购农销农品,或向小纳人购农品:
准扣的进税=买价×扣率(13%)
7、一般纳人外购货物付的运费
准扣的进税=运费×扣除率
*随运付的装卸、保费不扣
8、小纳人纳额=销项额×征率(6%或4%)
*不扣进额
9、小纳人不含税销额=含额/(1+征率)
10、自来水公司销水(6%)
不含税销额=发票额×(1+征率)
以上是国内物品的计算方式,接下来是国外进口的相关公式
二、进口货
1、组税价=关税完价+关税+消税
2、纳额=组税价×税率
三、出口货物退(免)税
1、"免、抵、退"计算方法(指生产企自营委外贸代出口自产)
(1)纳额=内销销税-(进税-免抵退税不免、抵税)
(2)免抵退税=FOB×外汇RMB牌价×退率-免抵退税抵减额
*FOB:出口货物离岸价。
*免抵退税抵减额=免税购原料价×退税率
免税购原料=国内购免原料+进料加工免税进料
进料加工免税进口料件组税价=到岸价+关、消税
(3)应退税和免抵税
A、如期末留抵税≤免抵退税,则:
应退税=期末留抵税
免抵税=免抵退税-应退税
B、期末留抵税>免抵退税,则:
应退税=免抵退税
免抵税=0
*期末留抵税额据《增值税纳税申报表》中"期末留抵税额"定。
(4)免抵退税不得免和抵税
免抵退税不免和抵税=FOB×外汇RMB牌价×(出口征率-出口退率)-免抵退税不免抵税抵减额
免抵退税不免和抵扣税抵减额=免税进原料价×(出口征率-出口货物退率)
2、先征后退
(1)外贸及外贸制度工贸企购货出口,出口增税免;出口后按收购成本与退税率算退税还外贸,征、退税差计企业成本
应退税额=外贸购不含增税购进金额×退税率
(2)外贸企购小纳人出货口增税退税规定:
A、从小纳人购并持普通发票准退税的抽纱、工艺品等12类出口货物,销售出口货入免,退还出口货进税
退税=[发票列(含税)销额]/(1+征率)×6%或5%
B、从小纳人购代开的增税发票的出口货:
退税=增税发票金额×6%或5%
C、外企托生企加工出口货的退税规定:
原辅料退税=国内原辅料增税发票进项×原辅料退税率
以上这些就是全部ACCA考试常用公式,希望对大家有所帮助!最后51题库考试学习网想告诉大家:“放弃可以找到一万个理由,但坚持只需一个信念!致敬那些在ACCA备考路上永不放弃的人,好结果只留给有毅力的人。”
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
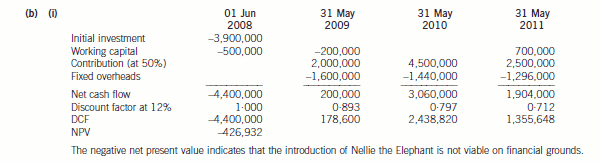
(b) The marketing director of CTC has suggested the introduction of a new toy ‘Nellie the Elephant’ for which the
following estimated information is available:
1. Sales volumes and selling prices per unit
Year ending, 31 May 2009 2010 2011
Sales units (000) 80 180 100
Selling price per unit ($) 50 50 50
2. Nellie will generate a contribution to sales ratio of 50% throughout the three year period.
3. Product specific fixed overheads during the year ending 31 May 2009 are estimated to be $1·6 million. It
is anticipated that these fixed overheads would decrease by 10% per annum during each of the years ending
31 May 2010 and 31 May 2011.
4. Capital investment amounting to $3·9 million would be required in June 2008. The investment would have
no residual value at 31 May 2011.
5. Additional working capital of $500,000 would be required in June 2008. A further $200,000 would be
required on 31 May 2009. These amounts would be recovered in full at the end of the three year period.
6. The cost of capital is expected to be 12% per annum.
Assume all cash flows (other than where stated) arise at the end of the year.
Required:
(i) Determine whether the new product is viable purely on financial grounds. (4 marks)
(b) Explain the corporation tax and value added tax (VAT) implications of the following aspects of the proposed
restructuring of the Rapier Ltd group.
(i) The immediate tax implications of the restructuring. (6 marks)
(b) The tax implications of the proposed restructuring of the Rapier Ltd group
(i) Immediate implications
Corporation tax
Rapier Ltd and its subsidiaries are in a capital gains group as Rapier Ltd owns at least 75% of the ordinary share capital
of each of the subsidiary companies. Any non-exempt items of plant and machinery owned by the subsidiaries will
therefore be transferred to Rapier Ltd at no gain, no loss.
No taxable credit or allowable debit will arise on the transfer of the subsidiaries’ goodwill to Rapier Ltd because the
companies are in a capital gains group.
The trading losses brought forward in Dirk Ltd will be transferred with the trade to Rapier Ltd as the effective ownership
of the three trades will not change (Rapier Ltd owns the subsidiaries which own the trades and, following the
restructuring, will own the three trades directly). The losses will be restricted to being offset against the future trading
profits of the Dirk trade only.
There will be no balancing adjustments in respect of the plant and machinery transferred to Rapier Ltd. Writing down
allowances will be claimed by the subsidiaries in respect of the year ending 30 June 2007 and by Rapier Ltd in respect
of future periods.
Value added tax (VAT)
No VAT should be charged on the sales of the businesses to Rapier Ltd as they are outside the scope of VAT. This is
because the trades are to be transferred as going concerns to a VAT registered person with no significant break in trading.
Switch Ltd must notify HM Revenue and Customs by 30 July 2007 that it has ceased to make taxable supplies.
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for.
(e) Job instruction. (3 marks)
(e) Job instruction is a one to one method of training through which the trainee is shown how to fulfill a task and then allowed to get on with that task. It is a systematic approach to training involving immediate supervision and by allowing the trainee to complete the task is a cost effective way of training.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-09
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-02
- 2021-08-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10