考ACCA可以获得什么证书?了解一下!
发布时间:2020-04-22
你知道考ACCA可以获得什么证书?很多小伙伴都还不是很了解,今天51题库考试学习网就带大家一起来看看吧!
其实在报考ACCA的过程中,ACCA官方协会都会颁发相应的证书鼓励ACCA考试小伙伴继续考下去,同时这些证书都可以帮助你找工作、申请国外留学等等。
那总共可以获得哪些证书呢?51题库考试学习网今天就给各位分享一下!
1. 商业会计证书 当学员完成前三门考试,并且通过基础阶段道德测试,即可获得商业会计证书。如已免试,无法获得此证书。
2. 高级商业会计证书 当学员完成前九门考试,并且完成道德测试模块,即可获得高级商业会计证书。如全部免试将无法获得此证书。
3. 牛津布鲁克斯大学学士学位 考完ACCA前9门可申请英国牛津布鲁克斯大学应用会计学学士学位,想要申请学位需要提前提交英语成绩证明,并且写一篇英文论文,通过后即可获得此学位。
4. 牛津布鲁克斯大学硕士学位 13门全部通过以后将有机会申请牛津布鲁克斯大学MBA硕士学位,需要去英国学习答辩,论文答辩通过即可获得硕士学位。
5. ACCA会员证书 通过13门考试,即可获得ACCA准会员证书。累计三年工作经验,即可申请转为正式ACCA member。
ACCA在国内称为"国际注册会计师",实际上是英国的注册会计师协会之一(,但它是英国具有特许头衔的4家注册会计师协会之一,也是当今知名的国际性会计师组织之一。
ACCA是国际会计准则委员会(IASC)的创始成员,也是国际会计师联合会(IFAC)的主要成员。ACCA在欧洲会计专家协会(FEE)、亚太会计师联合会(CAPA)和加勒比特许会计师协会(ICAC)等会计组织中起着非常重要的作用。
以上就是51题库考试学习网带来的全部内容了,如果想要了解更多关于考试的信息,大家可以关注51题库考试学习网哦!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Calculate the probability of the net profit being less than £75 million. (2 marks)
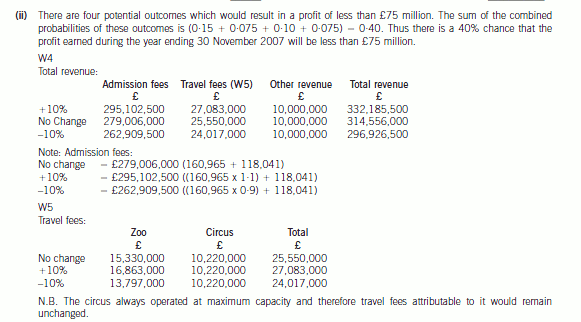
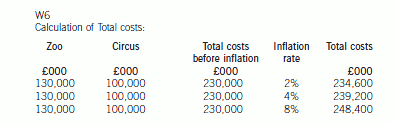
2 Marrgrett, a public limited company, is currently planning to acquire and sell interests in other entities and has asked
for advice on the impact of IFRS3 (Revised) ‘Business Combinations’ and IAS27 (Revised) ‘Consolidated and Separate
Financial Statements’. The company is particularly concerned about the impact on earnings, net assets and goodwill
at the acquisition date and any ongoing earnings impact that the new standards may have.
The company is considering purchasing additional shares in an associate, Josey, a public limited company. The
holding will increase from 30% stake to 70% stake by offering the shareholders of Josey, cash and shares in
Marrgrett. Marrgrett anticipates that it will pay $5 million in transaction costs to lawyers and bankers. Josey had
previously been the subject of a management buyout. In order that the current management shareholders may remain
in the business, Marrgrett is going to offer them share options in Josey subject to them remaining in employment for
two years after the acquisition. Additionally, Marrgrett will offer the same shareholders, shares in the holding company
which are contingent upon a certain level of profitability being achieved by Josey. Each shareholder will receive shares
of the holding company up to a value of $50,000, if Josey achieves a pre-determined rate of return on capital
employed for the next two years.
Josey has several marketing-related intangible assets that are used primarily in marketing or promotion of its products.
These include trade names, internet domain names and non-competition agreements. These are not currently
recognised in Josey’s financial statements.
Marrgrett does not wish to measure the non-controlling interest in subsidiaries on the basis of the proportionate
interest in the identifiable net assets, but wishes to use the ‘full goodwill’ method on the transaction. Marrgrett is
unsure as to whether this method is mandatory, or what the effects are of recognising ‘full goodwill’. Additionally the
company is unsure as to whether the nature of the consideration would affect the calculation of goodwill.
To finance the acquisition of Josey, Marrgrett intends to dispose of a partial interest in two subsidiaries. Marrgrett will
retain control of the first subsidiary but will sell the controlling interest in the second subsidiary which will become
an associate. Because of its plans to change the overall structure of the business, Marrgrett wishes to recognise a
re-organisation provision at the date of the business combination.
Required:
Discuss the principles and the nature of the accounting treatment of the above plans under International Financial
Reporting Standards setting out any impact that IFRS3 (Revised) ‘Business Combinations’ and IAS27 (Revised)
‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’ might have on the earnings and net assets of the group.
Note: this requirement includes 2 professional marks for the quality of the discussion.
(25 marks)
2 IFRS3 (Revised) is a further development of the acquisition model and represents a significant change in accounting for business
combinations. The consideration is the amount paid for the business acquired and is measured at fair value. Consideration will
include cash, assets, contingent consideration, equity instruments, options and warrants. It also includes the fair value of all equity
interests that the acquirer may have held previously in the acquired business. The principles to be applied are that:
(a) a business combination occurs only in respect of the transaction that gives one entity control of another
(b) the identifiable net assets of the acquiree are re-measured to their fair value on the date of the acquisition
(c) NCI are measured on the date of acquisition under one of the two options permitted by IFRS3 (Revised).
An equity interest previously held in the acquiree which qualified as an associate under IAS28 is similarly treated as if it were
disposed of and reacquired at fair value on the acquisition date. Accordingly, it is re-measured to its acquisition date fair value, and
any resulting gain or loss compared to its carrying amount under IAS28 is recognised in profit or loss. Thus the 30% holding in
the associate which was previously held will be included in the consideration. If the carrying amount of the interest in the associate
is not held at fair value at the acquisition date, the interest should be measured to fair value and the resulting gain or loss should
be recognised in profit or loss. The business combination has effectively been achieved in stages.
The fees payable in transaction costs are not deemed to be part of the consideration paid to the seller of the shares. They are not
assets of the purchased business that are recognised on acquisition. Therefore, they should be expensed as incurred and the
services received. Transaction costs relating to the issue of debt or equity, if they are directly attributable, will not be expensed but
deducted from debt or equity on initial recognition.
It is common for part of the consideration to be contingent upon future events. Marrgrett wishes some of the existing
shareholders/employees to remain in the business and has, therefore, offered share options as an incentive to these persons. The
issue is whether these options form. part of the purchase consideration or are compensation for post-acquisition services. The
conditions attached to the award will determine the accounting treatment. In this case there are employment conditions and,
therefore, the options should be treated as compensation and valued under IFRS2 ‘Share based payment’. Thus a charge will
appear in post-acquisition earnings for employee services as the options were awarded to reward future services of employees
rather than to acquire the business.
The additional shares to a fixed value of $50,000 are contingent upon the future returns on capital employed. Marrgrett only wants
to make additional payments if the business is successful. All consideration should be fair valued at the date of acquisition,
including the above contingent consideration. The contingent consideration payable in shares where the number of shares varies
to give the recipient a fixed value ($50,000) meets the definition of a financial liability under IAS32 ‘Financial Instruments:
Presentation’. As a result the liability will have to be fair valued and any subsequent remeasurement will be recognised in the
income statement. There is no requirement under IFRS3 (Revised) for the payments to be probable.
Intangible assets should be recognised on acquisition under IFRS3 (Revised). These include trade names, domain names, and
non-competition agreements. Thus these assets will be recognised and goodwill effectively reduced. The additional clarity in
IFRS3 (Revised) could mean that more intangible assets will be recognised on acquisition. As a result of this, the post-combination
income statement may have more charges for amortisation of the intangibles than was previously the case.
The revised standard gives entities the option, on a transaction by transaction basis, to measure non-controlling interests (NCI) at
the fair value of the proportion of identifiable net assets or at full fair value. The first option results in measurement of goodwill on
consolidation which would normally be little different from the previous standard. The second approach records goodwill on the
NCI as well as on the acquired controlling interest. Goodwill is the residual but may differ from that under the previous standard
because of the nature of the valuation of the consideration as previously held interests are fair valued and also because goodwill
can be measured in the above two ways (full goodwill and partial goodwill). The standard gives entities a choice for each separate
business combination of recognising full or partial goodwill. Recognising full goodwill will increase reported net assets and may
result in any future impairment of goodwill being of greater value. Measuring NCI at fair value may have some difficulties but
goodwill impairment testing may be easier under full goodwill as there is no need to gross-up goodwill for partly-owned
subsidiaries. The type of consideration does not affect goodwill regardless of how the payment is structured. Consideration is
recognised in total at its fair value at the date of acquisition. The form. of the consideration will not affect goodwill but the structure
of the payments can affect post-acquisition profits. Contingent payments which are deemed to be debt instruments will be
remeasured at each reporting date with the change going to the income statement.
Marrgrett has a maximum period of 12 months to finalise the acquisition accounting but will not be able to recognise the
re-organisation provision at the date of the business combination. The ability of the acquirer to recognise a liability for reducing or
changing the activities of the acquiree is restricted. A restructuring provision can only be recognised in a business combination
when the acquiree has at the acquisition date, an existing liability which complies with IAS37 ‘Provisions, contingent liabilities and
contingent assets’. These conditions are unlikely to exist at the acquisition date. A restructuring plan that is conditional on the
completion of a business combination is not recognised in accounting for the acquisition but the expense will be met against
post-acquisition earnings.
IAS27 (Revised) uses the economic entity model whereas previous practice used the parent company approach. The economic
entity model treats all providers of equity capital as shareholders of the entity even where they are not shareholders in the parent.
A partial disposal of an interest in a subsidiary in which control is still retained is seen as a treasury transaction and accounted for
in equity. It does not result in a gain or loss but an increase or decrease in equity. However, where a partial disposal in a subsidiary
results in a loss of control but the retention of an interest in the form. of an associate, then a gain or loss is recognised in the whole
interest. A gain or loss is recognised on the portion that has been sold, and a holding gain or loss is recognised on the interest
retained being the difference between the book value and fair value of the interest. Both gains/losses are recognised in the income
statement.
(c) Discuss the quality control issues raised by the audit senior’s comments. (3 marks)
(c) Quality control issues raised from the senior’s comments
There are several issues raised, all of which indicate that quality control procedures have not functioned adequately. The
planned audit procedures appear to be inadequate, further tests should have been performed to confirm the completeness,
existence and valuation of the balance.
In last year’s audit, the management representation was accepted as sufficient evidence in relation to the receivable. Possibly
the item was not identified as a related party transaction, or it was not considered to be material enough to warrant further
investigation.
At the planning stage, it is standard procedure to identify key related parties of an entity, and to plan procedures specific to
them. Inadequate planning may lead to a lack of prioritisation of this as an area of relatively high audit risk.
Work on receivables is often carried out by a relatively inexperienced member of the audit team. Audit juniors may not
appreciate the potential breach of IAS 24, or the complexities regarding materiality assessment for this type of transaction.
Insufficient review by the audit manager has been performed on completed working papers, which then failed to spot the
weakness of the management representation as a source of evidence. This year the audit senior has highlighted the matter,
which can now be resolved through additional audit procedures.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-02-15
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-08-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-11-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10