山西省考生想知道ACCA的科目F3怎么备考?
发布时间:2020-01-10
步入2020年,离ACCA考试越来越近了,虽然在ACCA考试中F1科目是难度比较低的一个考试科目了,但还是很多ACCAer们不知道如何备考考试科目F1。不用担心,小伙伴们所遇到的问题51题库考试学习网都一一帮助大家找寻到了答案,现在就来告诉你:
F3科目介绍
F3财务会计师ACCA很重要的一个系列,主要包括财务会计的基本框架,如何运用复式记账法对企业发生的各项交易进行记录,对于考生的计算能力是一个十分巨大的挑战。试算平衡表的编制,合并报表的基本内容(该知识点在后续的F7、P2课程会有深入的学习),如何对财务报表进行分析,进一步探索报表数字背后的故事。作为财务会计基础类的一门课,要求学生夯实基础,为阶段学习打下坚实的基础。
备考心得
听网课与做题同步
报网课其实是最简单的,帮助最大的方法,听网课可以不用听直播课,但听课一定要和做题同步。
F3我就换了一种学习方式:听了一章的课程,就去做题,这样既巩固了这章课程的内容,又可以及时补漏了这章没学懂的。我觉得这种方式特别适合我这种记性不太好的人。
重难点要死磕到底
我的网课大概刷了20多天,后面报表的部分花的时间比较多,也是F3最难但又是最重要的部分。第一遍课听过去一脸懵,不知道讲了些什么,有点晕,自己又重新把讲义看了一遍,貌似悟到了一些
我是那种一个点没搞懂绝对不会放弃的人,于是又把没看懂的地方再看了一遍,然后在笔记本看自己总结的一些套路和需要注意的点,再去做BPP上的题。说实话有几个还是挺难的,它没有按套路出题,题目有些难懂,但是多读几遍,一句一句去分析还是能搞懂的。
做报表题我的思路是首先把套路写在草稿纸上然后再去一个点一个点去对应,这样子就不容易遗漏。因为我提前一个月就报名考试了,所以课上完了就没有任何可以停留的时间,就紧接着复习
讲义和刷题,孰轻孰重?
我的复习思路可能和大多数人不太一样,大部分人都把时间花在刷题上,而我是用周末整天的时间先把讲义看了一遍,边看边总结重点,每一次看讲义我都会有不同的收获,有些点之前不怎么明白的,也会在重复看讲义的时候豁然开朗,这时候也是最开心的。
考前查漏补缺不可少
第二遍BPP我只是把错题做了一遍,把一些概念性的题目总结在笔记本上。最后,考试的前一周,我就是听冲刺班的课和习题课,去查漏补缺,我个人认为这个课很重要,因为老师带着我把整本书的思路都串了一遍,这让我的整个知识框架更加得完整。
原地徘徊一千步,抵不上向前迈出第一步;心中想过无数次,不如挽起袖子大干一次。加油各位ACCAer们~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
11 Which of the following statements are correct?
1 A company might make a rights issue if it wished to raise more equity capital.
2 A rights issue might increase the share premium account whereas a bonus issue is likely to reduce it.
3 A bonus issue will reduce the gearing (leverage) ratio of a company.
4 A rights issue will always increase the number of shareholders in a company whereas a bonus issue will not.
A 1 and 2
B 1 and 3
C 2 and 3
D 2 and 4
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
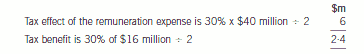
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:
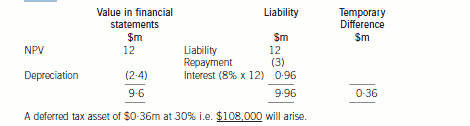
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).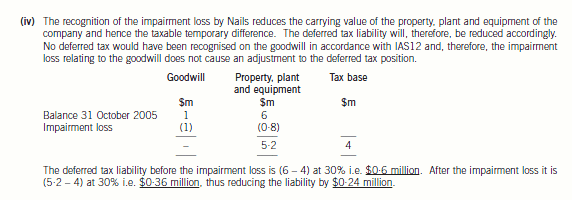
(ii) Any increase or decrease in the group’s budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June
2008 due to the restructuring on the assumption that trading losses will be used as efficiently as
possible. (8 marks)
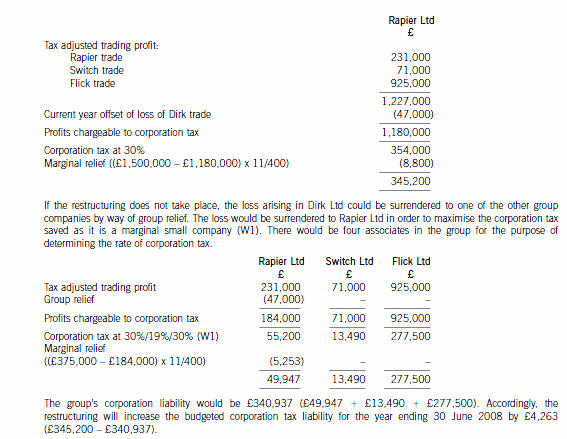
(ii) The budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June 2008
Following the proposed restructuring, Rapier Ltd will be carrying on four separate trades. The current year loss arising
in the Dirk trade can be offset against its total profits. Its three subsidiaries will be dormant and will not be associates
for the purpose of determining the rate of corporation tax.
(iii) State any disadvantages to the relief in (i) that Sharon should be aware of, and identify and describe
another relief that she might use. (4 marks)
(iii) There are several disadvantages to incorporation relief as follows:
1. The requirement to transfer all business assets to the company means that it will not be possible to leave behind
certain assets, such as the property. This might lead to a double tax charge (sale of the property, then extraction
of sale proceeds) at a future date.
2. Taper relief is lost on the transfer of the business. This means that any disposal of chargeable business assets (the
shares) within two years of the incorporation will lead to a higher chargeable gain, as the full rate of business asset
taper relief will not be available.
3. The relief does not eliminate the tax charge, it merely defers the payment of tax until some future event. The
deferred gain will become taxable when Sharon sells her shares in the company.
Gift relief could be used instead of incorporation relief. The assets would be gifted to the company for no consideration,
with the base cost of the assets to the company being reduced by the deferred gain arising. Unlike incorporation relief,
gift relief applies to individual assets used in a trade and not to an entire business. This is particularly useful if the
transferor wishes to retain some assets, such as property outside the company, as not all assets have to be transferred.
Note: If the business was non-trading, incorporation relief would still be available, but gift relief would not. However,
this restriction should not apply to Sharon and gift relief remains an option in this case.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-03-23
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-04-24
- 2019-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-14
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-02-15
- 2020-04-24
- 2020-05-18
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-03-25