新疆考生想知道ACCA的科目F3怎么备考?
发布时间:2020-01-10
步入2020年,离ACCA考试越来越近了,虽然在ACCA考试中F1科目是难度比较低的一个考试科目了,但还是很多ACCAer们不知道如何备考考试科目F1。不用担心,小伙伴们所遇到的问题51题库考试学习网都一一帮助大家找寻到了答案,现在就来告诉你:
F3科目介绍
F3财务会计师ACCA很重要的一个系列,主要包括财务会计的基本框架,如何运用复式记账法对企业发生的各项交易进行记录,对于考生的计算能力是一个十分巨大的挑战。试算平衡表的编制,合并报表的基本内容(该知识点在后续的F7、P2课程会有深入的学习),如何对财务报表进行分析,进一步探索报表数字背后的故事。作为财务会计基础类的一门课,要求学生夯实基础,为阶段学习打下坚实的基础。
备考心得
听网课与做题同步
报网课其实是最简单的,帮助最大的方法,听网课可以不用听直播课,但听课一定要和做题同步。
F3我就换了一种学习方式:听了一章的课程,就去做题,这样既巩固了这章课程的内容,又可以及时补漏了这章没学懂的。我觉得这种方式特别适合我这种记性不太好的人。
重难点要死磕到底
我的网课大概刷了20多天,后面报表的部分花的时间比较多,也是F3最难但又是最重要的部分。第一遍课听过去一脸懵,不知道讲了些什么,有点晕,自己又重新把讲义看了一遍,貌似悟到了一些
我是那种一个点没搞懂绝对不会放弃的人,于是又把没看懂的地方再看了一遍,然后在笔记本看自己总结的一些套路和需要注意的点,再去做BPP上的题。说实话有几个还是挺难的,它没有按套路出题,题目有些难懂,但是多读几遍,一句一句去分析还是能搞懂的。
做报表题我的思路是首先把套路写在草稿纸上然后再去一个点一个点去对应,这样子就不容易遗漏。因为我提前一个月就报名考试了,所以课上完了就没有任何可以停留的时间,就紧接着复习
讲义和刷题,孰轻孰重?
我的复习思路可能和大多数人不太一样,大部分人都把时间花在刷题上,而我是用周末整天的时间先把讲义看了一遍,边看边总结重点,每一次看讲义我都会有不同的收获,有些点之前不怎么明白的,也会在重复看讲义的时候豁然开朗,这时候也是最开心的。
考前查漏补缺不可少
第二遍BPP我只是把错题做了一遍,把一些概念性的题目总结在笔记本上。最后,考试的前一周,我就是听冲刺班的课和习题课,去查漏补缺,我个人认为这个课很重要,因为老师带着我把整本书的思路都串了一遍,这让我的整个知识框架更加得完整。
原地徘徊一千步,抵不上向前迈出第一步;心中想过无数次,不如挽起袖子大干一次。加油各位ACCAer们~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider to determine whether capitalised development costs are
appropriately recognised; and (5 marks)
(b) (i) Materiality
The net book value of capitalised development costs represent 7% of total assets in 2007 (2006 – 7·7%), and is
therefore material. The net book value has increased by 13%, a significant trend.
The costs capitalised during the year amount to $750,000. If it was found that the development cost had been
inappropriately capitalised, the cost should instead have been expensed. This would reduce profit before tax by
$750,000, representing 42% of the year’s profit. This is highly material. It is therefore essential to gather sufficient
evidence to support the assertion that development costs should be recognised as an asset.
In 2007, $750,000 capitalised development costs have been incurred, when added to $160,000 research costs
expensed, total research and development costs are $910,000 which represents 20·2% of total revenue, again
indicating a high level of materiality for this class of transaction.
Relevant accounting standard
Development costs should only be capitalised as an intangible asset if the recognition criteria of IAS 38 Intangible Assets
have been demonstrated in full:
– Intention to complete the intangible asset and use or sell it
– Technical feasibility and ability to use or sell
– Ability to generate future economic benefit
– Availability of technical, financial and other resources to complete
– Ability to measure the expenditure attributable to the intangible asset.
Research costs must be expensed, as should development costs which do not comply with the above criteria. The
auditors must consider how Sci-Tech Co differentiates between research and development costs.
There is risk that not all of the criteria have been demonstrated, especially due to the subjective nature of the
development itself:
– Pharmaceutical development is highly regulated. If the government does not license the product then the product
cannot be sold, and economic benefits will therefore not be received.
– Market research should justify the commercial viability of the product. The launch of a rival product to Flortex
means that market share is likely to be much lower than anticipated, and the ability to sell Flortex is reduced. This
could mean that Flortex will not generate an overall economic benefit if future sales will not recover the research
and development costs already suffered, and yet to be suffered, prior to launch. The existence of the rival product
could indicate that Flortex is no longer commercially viable, in which case the capitalised development costs
relating to Flortex should be immediately expensed.
– The funding on which development is dependent may be withdrawn, indicating that there are not adequate
resources to complete the development of the products. Sci-Tech has failed to meet one of its required key
performance indicators (KPI) in the year ended 30 November 2007, as products valued at 0·8% revenue have
been donated to charity, whereas the required KPI is 1% revenue.
Given that there is currently a breach of the target KPIs, this is likely to result in funding equivalent to 25% of
research and development expenditure being withdrawn. If Sci-Tech Co is unable to source alternative means of
finance, then it would seem that adequate resources may not be available to complete the development of new
products.
(b) Donald actually decided to operate as a sole trader. The first year’s results of his business were not as he had
hoped, and he made a trading loss of £8,000 in the year to 31 March 2007. However, trading is now improving,
and Donald has sufficient orders to ensure that the business will make profits of at least £30,000 in the year to
31 March 2008.
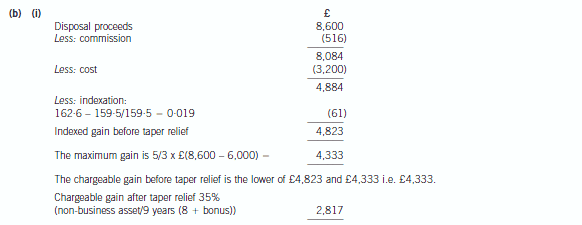
In order to raise funds to support his business over the last 15 months, Donald has sold a painting which was
given to him on the death of his grandmother in January 1998. The probate value of the painting was £3,200,
and Donald sold it for £8,084 (after deduction of 6% commission costs) in November 2006.
He also sold other assets in the year of assessment 2006/07, realising further chargeable gains of £8,775 (after
indexation of £249 and taper relief of £975).
Required:
(i) Calculate the chargeable gain on the disposal of the painting in November 2006. (4 marks)
(b) As a newly-qualified Chartered Certified Accountant in Boleyn & Co, you have been assigned to assist the ethics
partner in developing ethical guidance for the firm. In particular, you have been asked to draft guidance on the
following frequently asked questions (‘FAQs’) that will be circulated to all staff through Boleyn & Co’s intranet:
(i) What Information Technology services can we offer to audit clients? (5 marks)
Required:
For EACH of the three FAQs, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that should
be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions.
(b) FAQs
(i) Information Technology (IT) services
The greatest threats to independence arise from the provision of any service which involves auditors in:
■ auditing their own work;
■ the decision-making process;
■ undertaking management functions of the client.
IT services potentially pose all these threats:
■ self-interest threat – on-going services that provide a large proportion of Boleyn’s annual fees will contribute to a
threat to objectivity;
■ self-review threat – e.g. when IT services provided involve (i) the supervision of the audit client’s employees in the
performance of their normal duties; or (ii) the origination of electronic data evidencing the occurrence of
transactions;
■ management threat – e.g. when the IT services involve making judgments and taking decisions that are properly
the responsibility of management.
Thus, services that involve the design and implementation of financial IT systems that are used to generate information
forming a significant part of a client’s accounting system or financial statements is likely to create significant ethical
threats.
Possible safeguards include:
■ disclosing and discussing fees with the client’s audit committees (or others charged with corporate governance);
■ the audit client providing a written acknowledgment (e.g. in an engagement letter) of its responsibility for:
– establishing and monitoring a system of internal controls;
– the operation of the system (hardware or software); and
– the data used or generated by the system;
■ the designation by the audit client of a competent employee (preferably within senior management) with
responsibility to make all management decisions regarding the design and implementation of the hardware or
software system;
■ evaluation of the adequacy and results of the design and implementation of the system by the audit client;
■ suitable allocation of work within the firm (i.e. staff providing the IT services not being involved in the audit
engagement and having different reporting lines); and
■ review of the audit opinion by an audit partner who is not involved in the audit engagement.
Services in connection with the assessment, design and implementation of internal accounting controls and risk
management controls are not considered to create a threat to independence provided that the firm’s personnel do not
perform. management functions.
It would be acceptable to provide IT services to an audit client where the systems are not important to any significant
part of the accounting system or the production of financial statements and do not have significant reliance placed on
them by the auditors, provided that:
■ a member of the client’s management has been designated to receive and take responsibility for the results of the
IT work undertaken; and
■ appropriate safeguards are put in place (e.g. using separate partners and staff for each role and review by a partner
not involved in the audit engagement).
It would also generally be acceptable to provide and install off-the-shelf accounting packages to an audit client.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-05-08
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-04-30
- 2021-01-06
- 2021-06-25
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10