你为什么要考ACCA证书?
发布时间:2020-03-07
近年来,ACCA学员的注册人数不断上升。在新增的学员当中,一些小伙伴是为了通过ACCA会员进入“四大”。事实上,除了四大以外,报考ACCA的原因还有其能够给我们带来很好的发展空间。下面,51题库考试学习网为大家带来有关2020年ACCA会员就业前景的相关信息,以供参考。
首先,考ACCA可以提升我们的能力。ACCA的课程就是根据现时商务社会对财会人员的实际要求进行开发、设计的,并且格外注意培养学员的分析能力和在复杂条件下的决策、判断能力。这些能力在实际工作中都是非常实用、重要的。因此,ACCA课程所带来的系统的、高质量的培训会给予学生真才实学,让学员学成后能适应各种环境,并使会员成为具有全面管理素质的高级财务管理专家。完善、科学的培训方式,是ACCA会员拥有高薪待遇的主要原因。
其次,ACCA本身就是国际上知名的会计师会组织。ACCA属于国际专业会计师组织,在国际上享有很高的声誉,与众多国际知名企业建立了密切的合作关系,比如跨国企业、各国地方企业、其他会计师组织、教育机构、以及联合国、世界银行等世界性组织。这些组织和企业都能给予学员优厚的待遇。
第三,是ACCA会员的就业方向广泛:ACCA学员毕业后的就职方向:外资银行金融投资分析师;跨国公司的财务、内审、金融、风险控制岗位;国际会计师事务所的审计师、咨询师岗位;国内境外上市公司的财务、金融分析岗位;国内审计师事务所的涉外部门主管等。这些岗位都属于涉外岗位,不但拥有良好的薪资待遇,还能带来较高的社会地位。
除此外,ACCA会员还具有以下优势:
首先,ACCA会员资格在国际上得到广泛认可,尤其得到欧盟立法以及许多国家公司法的承认。因此可以说,拥有ACCA会员资格,就拥有了在世界各地就业的“通行证”。在世界上的很多国家,ACCA会员就是许多公司青睐的人才。
其次,ACCA会员在工商企业财务部门、(四大)审计/会计师事务所、金融机构和财政、税务部门从事财务以及财务管理工作,ACCA会员中有很多在世界各地大公司担任高级职位(财务经理、财务总监CFO,甚至总裁CEO)。因此,ACCA会员的就业前景是非常好的。
此外,ACCA还受到在中国的跨国公司、大型企业和国际“五大”会计公司全面认可。总的来说,ACCA会员年薪在中国50-100万RMB。
以上就是关于ACCA就业前景的相关内容。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA会员的就业前景很好,与之对应的是其考试难度较高,尤其是多达16门的考试科目以及全英文的考试模式,小伙伴们在备考时一定要坚定信念哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Describe the audit procedures you should perform. to determine the validity of the amortisation rate of five
years being applied to development costs in relation to Plummet. (5 marks)
(c) Audit procedures to determine the validity of the amortisation rate of five years being applied to development costs in relation
to the product Plummet would include the following:
– Obtain the papers documenting market research carried out on Plummet. Review and ascertain that the market research
supports a product life span of five years.
– Review actual sales patterns since the launch of Plummet and compare to the predicted sales per the market research
document.
Tutorial note: this will help to demonstrate the accuracy of the predicted sales forecast of Plummet.
– Read the assumptions underpinning the market research sales projections, and consider whether these assumptions
agree with the auditors’ understanding of the business.
– Discuss sales trends with the sales/marketing directors and ascertain whether sales are in line with management’s
expectations.
– Read correspondence with retail outlets to ensure there is continued support for selling Plummet.
– Obtain marketing/advertising budgets and ascertain enough expenditure is continuing on Plummet to support continued
sales.
(b) Explain the major benefits of pursuing a policy of internal development. (4 marks)
(b) The major benefits of pursuing a policy of internal development that may accrue to Taliesin Ltd are as follows:
– By confining their activities to its internal environment the company avoids the need to manage the integration of
businesses which is necessitated by an acquisition. Management teams, when considering the acquisition of another
organisation, very often underestimate the costs of integration.
– There is no need for the board of directors of Taliesin Ltd to familiarise itself with different organisational and national
cultures, values etc, thereby avoiding many potential problems.
– The board of directors of Taliesin Ltd is better able to control the activities of the business and the need for more complex
supply chains and strategic alliances with foreign organisations is rendered unnecessary.
– All investments are made at market price whereas if the board of directors was to attempt to grow the business
acquisition then significant outlays would probably be made in respect of purchased goodwill.
– As the organisation develops and expands, staff are provided with development and learning activities that may
precipitate an increase in the level of their commitment to the organisation.
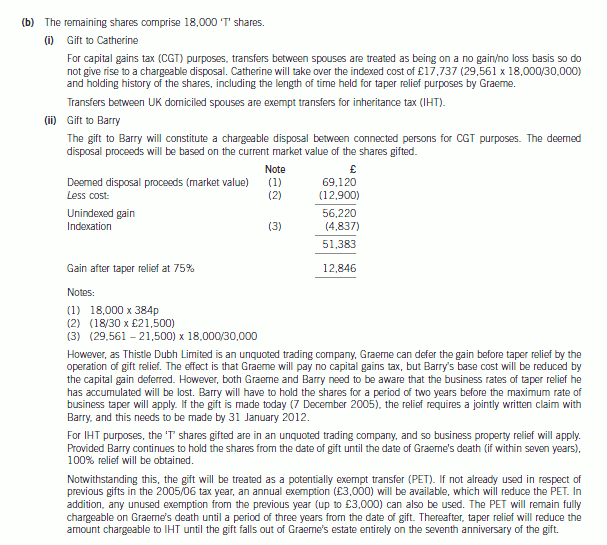
(b) Explain the capital gains tax (CGT) and inheritance tax (IHT) implications of Graeme gifting his remaining ‘T’
ordinary shares at their current value either:
(i) to his wife, Catherine; or
(ii) to his son, Barry.
Your answer should be supported by relevant calculations and clearly identify the availability and effect of
any reliefs (other than the CGT annual exemption) that might be used to reduce or defer any tax liabilities
arising. (9 marks)
(b) Examine how adopting a Six Sigma approach would help address the quality problems at UPC.
(10 marks)
(b) In many ways Six Sigma started out as a quality control methodology. It focused on measurement and the minimisation of
faults through pursuing Six Sigma as a statistical measure of some aspects of organisational performance. However, Six Sigma
has developed into something much more than a process control technique. It includes a problem-solving process called
DMAIC and a comprehensive toolkit ranging from brainstorming to balanced scorecards and process dashboards. It also has
defined team roles for managers and employees, often with martial arts names such as Black Belt, Green Belt and Master
Black Belt.
Six Sigma was first used in organisations in the early 1990s. However, it was its adoption and promotion by Jack Welch, the
CEO of GE that brought Six Sigma wider publicity. He announced that ‘Six Sigma is the most important initiative GE has ever
undertaken’. As Paul Harmon comments, ‘Welch’s popularity with the business press, and his dynamic style, guaranteed that
Six Sigma would become one of the hot management techniques of the late 1990s’.
Six Sigma uses an approach called DMAIC in its problem solving process. This stands for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve
and Control. Three aspects of this are considered below in the context of how they would address the problems at UPC.
Defining the problem
Part of defining the problem is the identification of the customer. It is important to understand what customers really want
and value and one of the main themes of Six Sigma is its focus on the customer. Six Sigma explicitly recognises the ‘voice of
the customer’ (VOC) in its approach. In the UPC situation quality requirements are currently defined by the physical condition
of the goods and by the alignment of the image. However, this may be a limiting view of quality because there is no evidence
of any systematic investigation of the requirements of the customer. Solving these problems may not lead to any significant
long-term gain; they may be quickly replaced by other ‘quality issues’. Furthermore, the customer is also perceived in a limited
way. These quality requirements are in the eye of the gift shop owner who is interested in saleable products. The end customer
– the consumer – who buys and uses the product may have other requirements which can also be addressed at this time.
By considering the VOC the problem and scope of the project becomes re-defined and the solution of the problems potentially
more valuable.
Measurement
Measurement is fundamental to Six Sigma. This includes the gathering of data to validate and quantify the problem. The
creation of the inspection team was based on initial evidence about an increase in breakages. This needs to be quantified.
The inaccurate printing of the image had been quantified as 500 units per month, out of the 250,000 shipped out of the
company. This equates to a failure rate of 0·2%, so that 99·8% of items are shipped with a correctly aligned image. This
sounds quite reasonable but it still raises issues and complaints that have to be dealt with, as well as creating wastage costs
of $10,000 per month. The problem is that even a relatively low percentage of defects can lead to a lot of unhappy customers.
Aiming for Six Sigma would reduce defects down to about one faulty item per month, reducing the wastage cost to $20.
Analysis
Analysis is concerned with understanding the process to find the root cause. Six Sigma focuses on processes and their
analysis. Analysis concerns methods, machines, materials, measures, Mother Nature and people. The alignment problem
needs investigation to find out what causes the imaging machine to irregularly produce misaligned images. Management
currently appear to blame the machine but it may be due to the way that certain people load the machine. The analysis of
the breakages is particularly important. It is unclear at present where these breakages occur (for example, are some of the
items broken before they leave UPC’s despatch facility) or are they all broken in transit? Neither is it understood why the
breakages occur. Management appear to blame the packers for packing incorrectly and not following the correct method.
However, it may be that the material is just not strong enough to withstand heavy handling by couriers who are outside the
control of UPC. Additionally, the breakages may be due to some manufacturing problem or raw material imperfection in the
items that break. Six Sigma stresses understanding the problem before solving it.
Although DMAIC has been selected as the framework for the sample answer, focusing on other aspects of Six Sigma would
be acceptable – as long as they are presented in the context of the UPC scenario.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-08
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-03-27
- 2021-08-29
- 2019-01-11
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-03-01