2020ACCA国际会计师考试山东省学霸是怎样计划备考的?
发布时间:2020-01-10
全科通过ACCA这件事,说起来容易做起来难。不过虽然难,每年通过全科考试的也大有人在。51题库考试学习网分析得出了一次性成功通过ACCA考试所需要的4大特质。
一:从不临时抱佛脚
3月考季刚结束时,考友群里一大波人表示:终于考完了,可以恢复到天天王者农药,晚晚吃鸡的生活了。初听起来没毛病,但仔细分析下就能看出,说出这些话的考生,在备考中采取的是突击的方式。即,平时尽情地玩,考试临头才忽然转换生活方式,将复习重新摆回首位,有时甚至为了复习修仙脱发。生动诠释了“人有多大胆,复习拖多晚”。看起来很励志,但用这种复习方式,生活和考证都会被影响,复习效果也会大打折扣。
在A考试上,考前突击的效果非常有限。进入大学之后,“考前突击”似乎成了大学生们应对考试的普遍方式。尤其是文科类专业,名词解释加选择题都能占去80分以上的内容,所以不少考生应对考试周的方法就是考前“刷夜”。约上三五好友,去图书馆狠狠背一晚上,将两张A4纸上的考试重点填鸭式地装进大脑,效果也是立竿见影,通常在考试里60分飘过问题不大。但这种方式比较适合记忆型科目,对于ACCA这样需要理解的内容较多的科目,就显得力不从心了。
A考试在内容上分为知识和原理两部分,前期打基础,需要记忆的知识点比较多,但越到后期,越考查考生的思维能力。偏偏在思维能力上,只有通过不断的练习来掌握,从来没有捷径可走。所以考前突击并非打开ACCA考试的正确方式。
那些成功的考生们,总是能保持一个平稳的复习进度,每天的学习时间和游戏时间互不侵占,学习生活两不误。
二:说到做到,有执行力
太多的备考经验在强调制定复习计划的重要性,然而,多少人在复习计划指定完第二天就起不来床?
每个人都会计划,但并不是每个人都有执行计划的能力。考试和人生中的大多数挑战一样,需要一份坚定不移,说到做到的气概才能终取得胜利。
前不久,在微博上看到了这么一条消息,一位外卖小哥利用每天下班后的一两个小时来学习,就为了准备一个证书考试。要说工作忙碌或是生活条件不允许,谁又有这位外卖小哥条件差呢?这位外卖小哥在面对记者询问时回答说,送外卖只是暂时的,考证是为了以后找新的工作。
许多考生们也一样,考证的 初动机就是为了摆脱现在的岗位和不满意的薪水,在职场走的更高。但即便有这样的动机,许多人却没有相应的执行力将自己的决定变为现实。
执行力差这件事, 大的坏处是会损害自信。一次计划未能成功执行,往往会导致对于自己能力的怀疑,次数多了之后,就更不敢再制定计划了,“随缘”“佛系”考生,就诞生了。
其实,在执行力上,不必非得逆着自己的生活习惯来制定计划。一个明明不习惯早起的人,就不必设定每天7点起床,假如将每天的计划定为起床之后学习两个小时,那么执行起来会容易很多。
三:善于总结归纳
一些对自己要求较高的考生在复习时,会设计类似高考那样的3轮复习方案。第一轮吃透课本,第二轮刷题为主,第三轮总结归纳。而事实上,在总结归纳上,很考验每个考生的能力。
在ACCA复习上流行一句话,客观题考的是点,主观题考的是面。ACCA考到 后会发现,如何形成这个面才是问题关键所在。而历年高分通过ACCA的那些考生们都有自己的总结归纳法宝。
去年在P2科目拿过全球第一的高顿财经何同学在谈到自己备考ACCA的经验时,曾反复强调一个词“自己的套路”。具体来说,在备考中的三个阶段,何同学都提到了归纳总结这一步骤。在听课和看书之后,何同学会给每一章的课堂笔记做一个汇总,从零散的语句中,画出一张清晰的,逻辑紧密的思维导图。这张图中文字的内容并不会很多,但非常切中肯,将每一章的内容全部囊括在内,形成一张有机的知识网络。
在刷习题集时也一样,何同学会将自己第一遍遭遇的难题,错题全部做上记号,过后再对照参考答案找出自己的遗漏的知识点,以及重要的,思路问题。用何同学的话说,千万不要记答案,而应该记思路。因为记答案后,假如考试时对部分内容没把握,那整个答案可能都会写错。而记下思路之后,即便忘记了参考答案的原文,用自己的语言来重新组织一遍,终也会拿到分数。甚至说,ACCA官方正是鼓励考生结合自己的经验来作答。而显然,根据自己经验作答的前提,也是对于自己经验的总结。
四:合理安排考试顺序
ACCA一共15门课程共分为两个阶段,分别是F阶段和P阶段,其中又分为几个部分,F1-F3属于知识课程部分,F4-F9属于技能课程部分,SBL-SBR属于核心课程部分,P4-P7(选修两门)属于选修课程部分。考生只需通过13门考试即可。
然后51题库考试学习网建议大家,ACCA在各阶段中确实是可以跳科目考试的,比如F阶段里,你可以先考F3,再考F1,这没有问题,P阶段你可以先考P3再考P1,这没有问题。所以,大家可以先报考自己擅长的或者说难度相对较容易的报考,根据自己的能力来定,也不用一个考季非要报满4个科目,报2个左右,给自己的复习压力也不算太大。
总而言之,俗话说滴水石穿,因此日常的积累和努力是成功通过考试的最有效的方法,没有任何途径可以走的。最后51题库考试学习网提前祝你成功通过ACCA考试。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue; and (4 marks)
(ii) Equipment used in the manufacture of Bachas Blue
Tutorial note: In the context of GVF, the principal issue to be addressed is whether or not the impairment loss previously
recognised should be reversed (by considering the determination of value in use). Marks will also be awarded for
consideration of depreciation, additions etc made specific to this equipment.
■ Agree cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses at the beginning of the year to prior year working
papers (and/or last year’s published financial statements).
■ Recalculate the current year depreciation charge based on the carrying amount (as reduced by the impairment
loss).
■ Calculate the carrying amount of the equipment as at 30 September 2005 without deduction of the impairment
loss.
Tutorial note: The equipment cannot be written back up to above this amount (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ Agree management’s schedule of future cash flows estimated to be attributable to the equipment for a period of up
to five years (unless a longer period can be justified) to approved budgets and forecasts.
■ Recalculate:
– on a sample basis, the make up of the cash flows included in the forecast;
– GVF’s weighted average cost of capital.
■ Review production records and sales orders for the year, as compared with the prior period, to confirm a ‘steady
increase’.
■ Compare sales volume at 30 September 2005 with the pre-‘scare’ level to assess how much of the previously
recognised impairment loss it would be prudent to write back (if any).
■ Scrutinize sales orders in the post balance sheet event period. Sales of such produce can be very volatile and
another ‘incident’ could have sales plummeting again – in which case the impairment loss should not be reversed.
(b) Explain how the use of SWOT analysis may be of assistance to the management of Diverse Holdings Plc.
(3 marks)
(b) The use of SWOT analysis will focus management attention on current strengths and weaknesses of each subsidiary company
which will be of assistance in the formulating of the business strategy of Diverse Holdings Plc. It will also enable management
to monitor trends and developments in the constantly changing environments of their subsidiaries. Each trend or development
may be classified as an opportunity or a threat that will provide a stimulus for an appropriate management response.
Management can make an assessment of the feasibility of required actions in order that the company may capitalise upon
opportunities whilst considering how best to negate or minimise the effect of any threats.
A SWOT analysis should assist the management of Diverse Holdings Plc as they must identify their strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities and threats. These may be classified as follows:
Strengths which appear to include both OFL and HTL.
Weaknesses which must include PSL and its limited outlets, which generate little growth and could collapse overnight. KAL
is also a weakness due to its declining profitability.
Opportunities where OFT, HTL and OPL are operating in growth markets.
Threats from which KAL is suffering.
If these four categories are identified and analysed then the group should be strengthened.
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
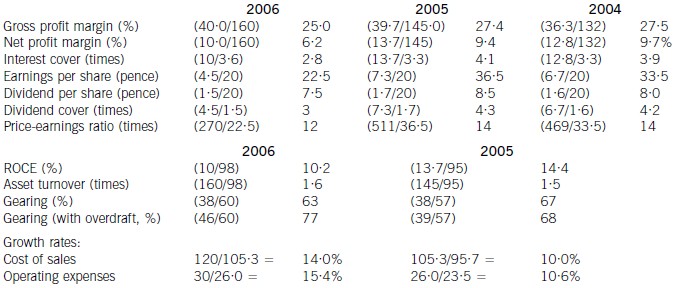
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-02
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-18
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-05-09
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-03-31
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-14
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-01-09