可以不参与ACCA继续教育吗?
发布时间:2021-09-27
众所周知在取得ACCA会员资格的第二年,会正式要求ACCA会员遵守CPD(继续教育)的相关政策。那么,ACCA会员能够通过哪些途径完成ACCA“继续教育”呢?接下来51题库考试学习网就带大家去了解一下吧!
可以不参与ACCA继续教育吗?
ACCA要求所有会员通过完成相关的CPD而保持并更新知识和技能,以确保会员能在快速变化的竞争环境中胜出。继续教育计划不仅反映了会员的需要,还同时满足了企业雇主的需求。另外,刚刚获取会员资格的新会员需要从成为会员的第二年开始完成并提交CPD。
1.单位学时途径:
需要每年完成40个与专业相关的学时(一个学时即为一个小时)。其中21个学时的verifiable unit需要出示的相关证明材料(CPD evidence),其余的19个non-verifiable units学时则不需要出示任何证明。
2.单位学时兼职或半退休途径:
若会员全年工作时长低于770小时,则需要通过此途径,以工作时长+单位学时的组合完成CPD,只要有合理解释,该途径所需的单位学时通常是没有限定的。
3.ACCA认可雇主途径:
会员所在企业如果是ACCA CPD认可雇主,则只需保留就职于该公司的在职证明以及在每年年底提交当年的Annual CPD Declaration材料,在PART 1的OPTION A部分勾选“ACCA Approved Employer Route”即可。
4.其它“国际会计师联合会”成员途径:
会员如果同时隶属于其他国际财会专业团体,则ACCA官方承认会员在其他组织的继续教育有效性。
5.CPD豁免:
若会员处于离职状态,并且超过一个月,则可以申请豁免CPD。
报名注册ACCA学员,具备以下条件之一即可:
1、教育部认可的高等院校在校生(本科在校),顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2、凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3、未符合1、2项报名资格的申请者,年满16周岁的可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成FAB(基础商业会计)、FMA(基础管理会计)、FFA(基础财务会计)3门课程后,可以豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入ACCA技能课程的考试
以上就是51题库考试学习网给大家带来的关于ACCA考试继续教育的相关分享,还没有完成继续教育的考生赶紧行动起来吧!请大家持续关注51题库考试学习网,51题库考试学习网将会为大家持续更新最新、最热的考试资讯!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
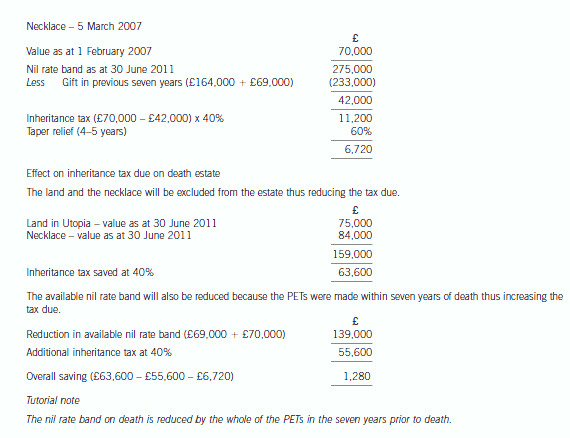
(b) Mabel has two objectives when making the gifts to Bruce and Padma:
(1) To pay no tax on any gift in her lifetime; and
(2) To reduce the eventual liability to inheritance tax on her death.
Advise Mabel which item to gift to Bruce and to Padma in order to satisfy her objectives. Give reasons for
your advice.
Your advice should include a computation of the inheritance tax saved as a result of the two gifts, on the
assumption that Mabel dies on 30 June 2011. (10 marks)

5 (a) Compare and contrast the responsibilities of management, and of auditors, in relation to the assessment of
going concern. You should include a description of the procedures used in this assessment where relevant.
(7 marks)
5 Dexter Co
(a) Responsibilities of management and auditors
Responsibilities
ISA 570 Going Concern provides a clear framework for the assessment of the going concern status of an entity, and
differentiates between the responsibilities of management and of auditors. Management should assess going concern in order
to decide on the most appropriate basis for the preparation of the financial statements. IAS 1 Presentation of Financial
Statements (revised) requires that where there is significant doubt over an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, the
uncertainties should be disclosed in a note to the financial statements. Where the directors intend to cease trading, or have
no realistic alternative but to do so, the financial statements should be prepared on a ‘break up’ basis.
Thus the main focus of the management’s assessment of going concern is to ensure that relevant disclosures are made where
necessary, and that the correct basis of preparation is used.
The auditor’s responsibility is to consider the appropriateness of the management’s use of the going concern assumption in
the preparation of the financial statements and to consider whether there are material uncertainties about the entity’s ability
to continue as a going concern that need to be disclosed in a note.
The auditor should also consider the length of the time period that management have looked at in their assessment of going
concern.
The auditor will therefore need to come to an opinion as to the going concern status of an entity but the focus of the auditor’s
evaluation of going concern is to see whether they agree with the assessment made by the management. Therefore whether
they agree with the basis of preparation of the financial statements, or the inclusion in a note to the financial statements, as
required by IAS 1, of any material uncertainty.
Evaluation techniques
In carrying out the going concern assessment, management will evaluate a wide variety of indicators, including operational
and financial. An entity employing good principles of corporate governance should be carrying out such an assessment as
part of the on-going management of the business.
Auditors will use a similar assessment technique in order to come to their own opinion as to the going concern status of an
entity. They will carry out an operational review of the business in order to confirm business understanding, and will conduct
a financial review as part of analytical procedures. Thus both management and auditors will use similar business risk
assessment techniques to discover any threats to the going concern status of the business.
Auditors should not see going concern as a ‘completion issue’, but be alert to issues affecting going concern throughout the
audit. In the same way that management should continually be managing risk (therefore minimising going concern risk),
auditors should be continually be alert to going concern problems throughout the duration of the audit.
However, one difference is that when going concern problems are discovered, the auditor is required by IAS 570 to carry out
additional procedures. Examples of such procedures would include:
– Analysing and discussing cash flow, profit and other relevant forecasts with management
– Analysing and discussing the entity’s latest available interim financial statements
– Reviewing events after the period end to identify those that either mitigate or otherwise affect the entity’s ability to
continue as a going concern, and
– Reading minutes of meetings of shareholders, those charged with governance and relevant committees for reference to
financing difficulties.
Management are not explicitly required to gather specific evidence about going concern, but as part of good governance would
be likely to investigate and react to problems discovered.
4 Hogg Products Company (HPC), based in a developing country, was recently wholly acquired by American Overseas
Investments (AOI), a North American holding company. The new owners took the opportunity to completely review
HPC’s management, culture and systems. One of the first things that AOI questioned was HPC’s longstanding
corporate code of ethics.
The board of AOI said that it had a general code of ethics that HPC, as an AOI subsidiary, should adopt. Simon Hogg,
the chief executive of HPC, disagreed however, and explained why HPC should retain its existing code. He said that
HPC had adopted its code of ethics in its home country which was often criticised for its unethical business behaviour.
Some other companies in the country were criticised for their ‘sweat shop’ conditions. HPC’s adoption of its code of
ethics, however, meant that it could always obtain orders from European customers on the guarantee that products
were made ethically and in compliance with its own highly regarded code of ethics. Mr Hogg explained that HPC had
an outstanding ethical reputation both locally and internationally and that reputation could be threatened if it was
forced to replace its existing code of ethics with AOI’s more general code.
When Ed Tanner, a senior director from AOI’s head office, visited Mr Hogg after the acquisition, he was shown HPC’s
operation in action. Mr Hogg pointed out that unlike some other employers in the industry, HPC didn’t employ child
labour. Mr Hogg explained that although it was allowed by law in the country, it was forbidden by HPC’s code of
ethics. Mr Hogg also explained that in his view, employing child labour was always ethically wrong. Mr Tanner asked
whether the money that children earned by working in the relatively safe conditions at HPC was an important source
of income for their families. Mr Hogg said that the money was important to them but even so, it was still wrong to
employ children, as it was exploitative and interfered with their education. He also said that it would alienate the
European customers who bought from HPC partly on the basis of the terms of its code of ethics.
Required:
(a) Describe the purposes and typical contents of a corporate code of ethics. (9 marks)
(a) Purposes of codes of ethics
To convey the ethical values of the company to interested audiences including employees, customers, communities and
shareholders.
To control unethical practice within the organisation by placing limits on behaviour and prescribing behaviour in given
situations.
To be a stimulant to improved ethical behaviour in the organisation by insisting on full compliance with the code.
[Tutorial note: other purposes, if relevant, will be rewarded]
Contents of a corporate code of ethics
The typical contents of a corporate code of ethics are as follows:
Values of the company. This might include notes on the strategic purpose of the organisation and any underlying beliefs,
values, assumptions or principles. Values may be expressed in terms of social and environmental perspectives, and
expressions of intent regarding compliance with best practice, etc.
Shareholders and suppliers of finance. In particular, how the company views the importance of sources of finances, how it
intends to communicate with them and any indications of how they will be treated in terms of transparency, truthfulness and
honesty.
Employees. Policies towards employees, which might include equal opportunities policies, training and development,
recruitment, retention and removal of staff. In the case of HPC, the policy on child labour will be covered by this part of the
code of ethics.
Customers. How the company intends to treat its customers, typically in terms of policy of customer satisfaction, product mix,
product quality, product information and complaints procedure.
Supply chain/suppliers. This is becoming an increasingly important part of ethical behaviour as stakeholders scrutinise where
and how companies source their products (e.g. farming practice, GM foods, fair trade issues, etc). Ethical policy on supply
chain might include undertakings to buy from certain approved suppliers only, to buy only above a certain level of quality, to
engage constructively with suppliers (e.g. for product development purposes) or not to buy from suppliers who do not meet
with their own ethical standards.
Community and wider society. This section concerns the manner in which the company aims to relate to a range of
stakeholders with whom it does not have a direct economic relationship (e.g. neighbours, opinion formers, pressure groups,
etc). It might include undertakings on consultation, ‘listening’, seeking consent, partnership arrangements (e.g. in community
relationships with local schools) and similar.
[Tutorial note: up to six points to be identified and described but similar valid general contents are acceptable]
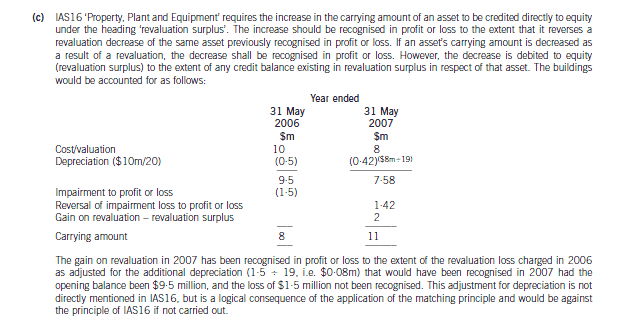
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09