2020年ACCA考试财务会计(基础阶段)财经词汇汇总18
发布时间:2020-10-15
又到了每日分享小课堂,各位赶快集合。今天51题库考试学习网分享的内容是2020年ACCA考试财务会计(基础阶段)财经词汇汇总18,相关考点都清楚了吗?还未了解的小伙伴一起来看看吧。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Inventory
【English Terms】
Inventory
【中文翻译】
库存、存货
【详情解释/例子】
库存可以是原材料 、 可供出售制成品或制造中的半制成品 。库存是公司的资产负债表中的资产项。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:International
Bond
【English Terms】
International Bond
【中文翻译】
国际债券
【详情解释/例子】
指由非本土机构发行的债券。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:International
Fund
【English Terms】
International Fund
【中文翻译】
国际基金
【详情解释/例子】
可以在本土国家以外任何国家投资的共同基金。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Intrinsic
Value
【English Terms】
Intrinsic Value
【中文翻译】
内在价值
【详情解释/例子】
1.一家公司或一种资产根据隐含价值概念评估的价值。
2.对于买入期权,相等于相关股票价格与行使价格之间的差额。对于出售期权,相等于行使价格与相关股票价格之间的差额。若相关股票价格与行使价格的差额为负数,则内在价值为零,这适用于买回及出售期权。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Internal
Rate of Return(IRR)
【English Terms】
Internal Rate of Return(IRR)
【中文翻译】
内部回报率
【详情解释/例子】
在资本预算过程中常用的标准,是令所有现金流的净现值等于零的利率。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Internal
Growth Rate
【English Terms】
Internal Growth Rate
【中文翻译】
内部增长率
【详情解释/例子】
一项业务在没有外部融资的情况下可以实现的最高增长率。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Internal
Audit
【English Terms】
Internal Audit
【中文翻译】
内部审计
【详情解释/例子】
一家公司的内部人士对自己公司进行的审计。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Interim
Dividend
【English Terms】
Interim Dividend
【中文翻译】
中期股息
【详情解释/例子】
公司年度股东大会举行及公布全年财务报表前支付的股息。这项股息一般与公司的中期业绩一同公布。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Interest
Rate Ceiling
【English Terms】
Interest Rate Ceiling
【中文翻译】
最高利率
【详情解释/例子】
一家金融机构对任何可调整利率的房地产抵押或贷款可收取的最高利率,最高利率受到政府监管。
以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的全部内容,相信小伙伴们都了解清楚。预祝12月份ACCA考试取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
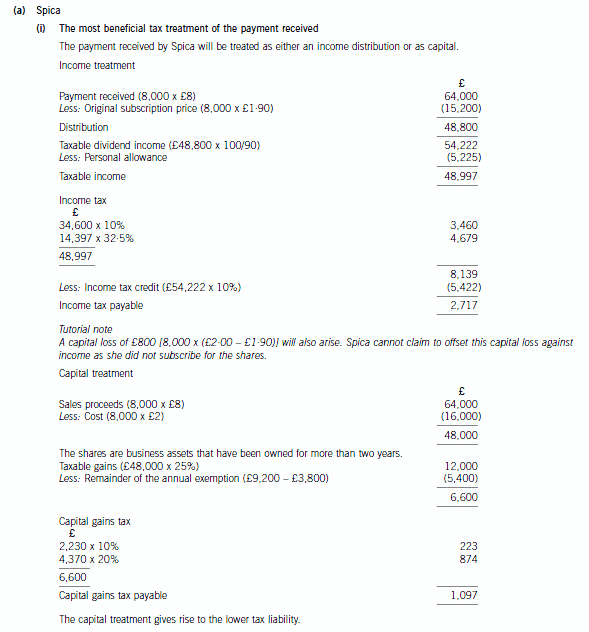
3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
Discuss the principles and practices which should be used in the financial year to 30 November 2008 to account
for:(c) the purchase of handsets and the recognition of revenue from customers and dealers. (8 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
Handsets and revenue recognition
The inventory of handsets should be measured at the lower of cost and net realisable value (IAS2, ‘Inventories’, para 9). Johan
should recognise a provision at the point of purchase for the handsets to be sold at a loss. The inventory should be written down
to its net realisable value (NRV) of $149 per handset as they are sold both to prepaid customers and dealers. The NRV is $51
less than cost. Net realisable value is the estimated selling price in the normal course of business less the estimated selling costs.
IAS18, ‘Revenue’, requires the recognition of revenue by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the reporting
date. Revenue associated with the provision of services should be recognised as service as rendered. Johan should record the
receipt of $21 per call card as deferred revenue at the point of sale. Revenue of $18 should be recognised over the six month
period from the date of sale. The unused call credit of $3 would be recognised when the card expires as that is the point at which
the obligation of Johan ceases. Revenue is earned from the provision of services and not from the physical sale of the card.
IAS18 does not deal in detail with agency arrangements but says the gross inflows of economic benefits include amounts collected
on behalf of the principal and which do not result in increases in equity for the entity. The amounts collected on behalf of the
principal are not revenue. Revenue is the amount of the ‘commission’. Additionally where there are two or more transactions, they
should be taken together if the commercial effect cannot be understood without reference to the series of transactions as a whole.
As a result of the above, Johan should not recognise revenue when the handset is sold to the dealer, as the dealer is acting as an
agent for the sale of the handset and the service contract. Johan has retained the risk of the loss in value of the handset as they
can be returned by the dealer and the price set for the handset is under the control of Johan. The handset sale and the provision
of the service would have to be assessed as to their separability. However, the handset cannot be sold separately and is
commercially linked to the provision of the service. Johan would, therefore, recognise the net payment of $130 as a customer
acquisition cost which may qualify as an intangible asset under IAS38, and the revenue from the service contract will be recognised
as the service is rendered. The intangible asset would be amortised over the 12 month contract. The cost of the handset from the
manufacturer will be charged as cost of goods sold ($200).
10 What would the company’s profit become after the correction of the above errors?
A $634,760
B $624,760
C $624,440
D $625,240
630,000 – 4,320 – 440
(c) Assess the likely criteria which would need to be satisfied for software to be regarded as ‘quality software’.
(4 marks)
(c) The following are important considerations regarding the quality of the business software:
– The software is error-free as this will improve its reliability. Whilst in practice this might not always be achievable the
directors of SSH must recognise the dangers involved in supplying bespoke software which may prove damaging to their
clients’ businesses with the resulting loss of client goodwill.
– The software should meet quality control standards such as those specified by the ISO (International Standards
Organisation).
– The software must be delivered on time. Late delivery of business software will prove problematic since clients may rely
on updated software to meet new customer needs or to fulfil revised business objectives.
– The software must meet the initial specification of the customer. In meeting the specification SSH will be demonstrating
that the software has been produced correctly with an appropriate focus on the requirements of end users.
– The software must be usable i.e. as well as being able to do what it is supposed to do it is important that it is easy to
use.
– The software should be capable of being updated in the light of future changes that occur in the clients’ requirements.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-15
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-03-05
- 2019-03-17
- 2019-06-29
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-04-02
- 2021-04-04
- 2021-04-08
- 2021-02-14
- 2021-04-08
- 2020-10-11
- 2021-03-05
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-15
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-11
- 2020-10-11
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-10-18