2020年ACCA考试《业绩管理》科目辅导资料(4)
发布时间:2020-10-18
又到了每日分享小课堂,各位赶快集合。今天51题库考试学习网分享的内容是2020年ACCA考试《业绩管理》科目辅导资料(4),相关考点都清楚了吗?还未了解的小伙伴一起来看看吧。
周期成本处理 - LIFECYCLE COSTING
Within the context of environmental
accounting, lifecycle costing is a technique which
requires the full environmental consequences, and, therefore, costs, arising from
production of a product to be taken account across its whole lifecycle, literally ‘from cradle to grave’
识别环境成本 - IDENTIFYING ENVIRONMENTAL COSTS
Much of the information that is needed to
prepare environmental management accounts could actually be found in a business
‘general ledger. A close review of it should reveal the costs of materials, utilities and waste disposal, at the least.
The main problem is, however, that most of the costs will have to be found
within the category of ’general overheads ‘if they are to be accurately
identified. Identifying them could be a lengthy process, particularly in a large organization. The fact that environmental
costs are often ’hidden ‘in this way makes it difficult for management to
identify opportunities to cut environmental costs and yet it is crucial that
they do so in a world which is becoming increasingly regulated and where scarce
resources are becoming scarcer.
It is equally important to allocate
environmental costs to the processes or products, which give rise to them. Only
by doing this can an organization make well-informed business decisions? For
example, a pharmaceutical company may be deciding whether to continue with
the production of one of its drugs. In order to incorporate environmental
aspects into its decision, it needs to know exactly how many
products are input into the process compared to its outputs; How much waste is
created during the process; how much labor and fuel is used in making the drug;
how much packaging the drug uses and what percentage of that is recyclable etc.
Only by identifying these costs and allocating them to the product can an
informed decision be made about the environmental effects of continued
production.
In 2003,the UNDSD
identified four management accounting techniques for the identification and
allocation of environmental costs: input/outflow analysis,flow cost accounting, activity based costing and lifecycle
costing. These are referred to later under ‘different methods
of accounting for environmental costs’。
以上就是51题库考试学习网给大家带来的全部内容,相信小伙伴们都了解清楚。预祝大家在ACCA考试中取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
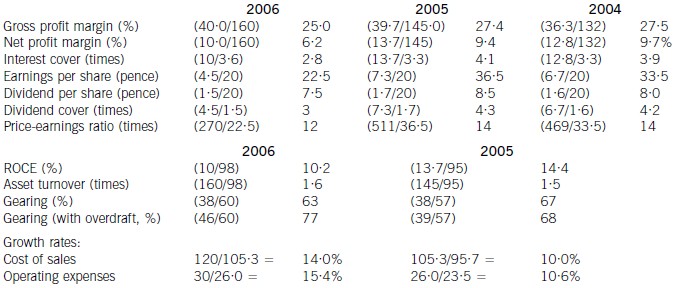
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
(c) Maxwell Co is audited by Lead & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Leo Sabat has enquired as to
whether your firm would be prepared to conduct a joint audit in cooperation with Lead & Co, on the future
financial statements of Maxwell Co if the acquisition goes ahead. Leo Sabat thinks that this would enable your
firm to improve group audit efficiency, without losing the cumulative experience that Lead & Co has built up while
acting as auditor to Maxwell Co.
Required:
Define ‘joint audit’, and assess the advantages and disadvantages of the audit of Maxwell Co being conducted
on a ‘joint basis’. (7 marks)
(c) A joint audit is when two or more audit firms are jointly responsible for giving the audit opinion. This is very common in a
group situation where the principal auditor is appointed jointly with the auditor of a subsidiary to provide a joint opinion on
the subsidiary’s financial statements. There are several advantages and disadvantages in a joint audit being performed.
Advantages
It can be beneficial in terms of audit efficiency for a joint audit to be conducted, especially in the case of a new subsidiary.
In this case, Lead & Co will have built up an understanding of Maxwell Co’s business, systems and controls, and financial
statement issues. It will be time efficient for the two firms of auditors to work together in order for Chien & Co to build up
knowledge of the new subsidiary. This is a key issue, as Chien & Co need to acquire a thorough understanding of the
subsidiary in order to assess any risks inherent in the company which could impact on the overall assessment of risk within
the group. Lead & Co will be able to provide a good insight into the company, and advise Chien & Co of the key risk areas
they have previously identified.
On the practical side, it seems that Maxwell Co is a significant addition to the group, as it is expected to increase operating
facilities by 40%. If Chien & Co were appointed as sole auditors to Maxwell Co it may be difficult for the audit firm to provide
adequate resources to conduct the audit at the same time as auditing the other group companies. A joint audit will allow
sufficient resources to be allocated to the audit of Maxwell Co, assuring the quality of the opinion provided.
If there is a tight deadline, as is common with the audit of subsidiaries, which should be completed before the group audit
commences, then having access to two firms’ resources should enable the audit to be completed in good time.
The audit should also benefit from an improvement in quality. The two audit firms may have different points of view, and
would be able to discuss contentious issues throughout the audit process. In particular, the newly appointed audit team will
have a ‘fresh pair of eyes’ and be able to offer new insight to matters identified. It should be easier to challenge management
and therefore ensure that the auditors’ position is taken seriously.
Tutorial note: Candidates may have referred to the recent debate over whether joint audits increase competition in the
profession. In particular, joint audits have been proposed as a way for ‘mid tier’ audit firms to break into the market of
auditing large companies and groups, which at the moment is monopolised by the ‘Big 4’. Although this does not answer
the specific question set, credit will be awarded for demonstration of awareness of this topical issue.
Disadvantages
For the client, it is likely to be more expensive to engage two audit firms than to have the audit opinion provided by one firm.
From a cost/benefit point of view there is clearly no point in paying twice for one opinion to be provided. Despite the audit
workload being shared, both firms will have a high cost for being involved in the audit in terms of senior manager and partner
time. These costs will be passed on to the client within the audit fee.
The two audit firms may use very different audit approaches and terminology. This could make it difficult for the audit firms
to work closely together, negating some of the efficiency and cost benefits discussed above. Problems could arise in deciding
which firm’s method to use, for example, to calculate materiality, design and pick samples for audit procedures, or evaluate
controls within the accounting system. It may be impossible to reconcile two different methods and one firm’s methods may
end up dominating the audit process, which then eliminates the benefit of a joint audit being conducted. It could be time
consuming to develop a ‘joint’ audit approach, based on elements of each of the two firms’ methodologies, time which
obviously would not have been spent if a single firm was providing the audit.
There may be problems for the two audit firms to work together harmoniously. Lead & Co may feel that ultimately they will
be replaced by Chien & Co as audit provider, and therefore could be unwilling to offer assistance and help.
Potentially, problems could arise in terms of liability. In the event of litigation, because both firms have provided the audit
opinion, it follows that the firms would be jointly liable. The firms could blame each other for any negligence which was
discovered, making the litigation process more complex than if a single audit firm had provided the opinion. However, it could
be argued that joint liability is not necessarily a drawback, as the firms should both be covered by professional indemnity
insurance.
1 Stuart is a self-employed business consultant aged 58. He is married to Rebecca, aged 55. They have one child,
Sam, who is aged 24 and single.
In November 2005 Stuart sold a house in Plymouth for £422,100. Stuart had inherited the house on the death of
his mother on 1 May 1994 when it had a probate value of £185,000. The subsequent pattern of occupation was as
follows:
1 May 1994 to 28 February 1995 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca as main residence
1 March 1995 to 31 December 1998 unoccupied
1 January 1999 to 31 March 2001 let out (unfurnished)
1 April 2001 to 30 November 2001 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca
1 December 2001 to 30 November 2005 used occasionally as second home
Both Stuart and Rebecca had lived in London from March 1995 onwards. On 1 March 2001 Stuart and Rebecca
bought a house in London in their joint names. On 1 January 2002 they elected for their London house to be their
principal private residence with effect from that date, up until that point the Plymouth property had been their principal
private residence.
No other capital disposals were made by Stuart in the tax year 2005/06. He has £29,500 of capital losses brought
forward from previous years.
Stuart intends to invest the gross sale proceeds from the sale of the Plymouth house, and is considering two
investment options, both of which he believes will provide equal risk and returns. These are as follows:
(1) acquiring shares in Omikron plc; or
(2) acquiring further shares in Omega plc.
Notes:
1. Omikron plc is a listed UK trading company, with 50,250,000 shares in issue. Its shares currently trade at 42p
per share.
2. Stuart and Rebecca helped start up the company, which was then Omega Ltd. The company was formed on
1 June 1990, when they each bought 24,000 shares for £1 per share. The company became listed on 1 May
1997. On this date their holding was subdivided, with each of them receiving 100 shares in Omega plc for each
share held in Omega Ltd. The issued share capital of Omega plc is currently 10,000,000 shares. The share price
is quoted at 208p – 216p with marked bargains at 207p, 211p, and 215p.
Stuart and Rebecca’s assets (following the sale of the Plymouth house but before any investment of the proceeds) are
as follows:
Assets Stuart Rebecca
£ £
Family house in London 450,000 450,000
Cash from property sale 422,100 –
Cash deposits 165,000 165,000
Portfolio of quoted investments – 250,000
Shares in Omega plc see above see above
Life insurance policy note 1 note 1
Note:
1. The life insurance policy will pay out a sum of £200,000 on the death of the first spouse to die.
Stuart has recently been diagnosed with a serious illness. He is expected to live for another two or three years only.
He is concerned about the possible inheritance tax that will arise on his death. Both he and Rebecca have wills whose
terms transfer all assets to the surviving spouse. Rebecca is in good health.
Neither Stuart nor Rebecca has made any previous chargeable lifetime transfers for the purposes of inheritance tax.
Required:
(a) Calculate the taxable capital gain on the sale of the Plymouth house in November 2005 (9 marks)
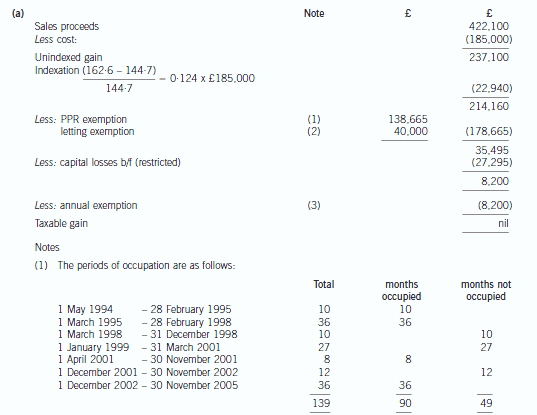
Note that the last 36 months count as deemed occupation, as the house was Stuart’s principal private residence (PPR)
at some point during his period of ownership.
The first 36 months of the period from 1 March 1995 to 31 March 2001 qualifies as a deemed occupation period as
Stuart and Rebecca returned to occupy the property on 1 April 2001. The remainder of the period will be treated as a
period of absence, although letting relief is available for part of the period (see below).
The exempt element of the gain is the proportion during which the property was occupied, real or deemed. This is
£138,665 (90/139 x £214,160).
(2) The chargeable gain is restricted for the period that the property was let out. This is restricted to the lowest of the
following:
(i) the gain attributable to the letting period (27/139 x 214,160) = £41,599
(ii) £40,000
(iii) the total exempt PPR gain = £138,665
i.e. £40,000.
(3) The taper relief is effectively wasted, having restricted losses b/f to preserve the annual exemption.
(b) Ambush loaned $200,000 to Bromwich on 1 December 2003. The effective and stated interest rate for this
loan was 8 per cent. Interest is payable by Bromwich at the end of each year and the loan is repayable on
30 November 2007. At 30 November 2005, the directors of Ambush have heard that Bromwich is in financial
difficulties and is undergoing a financial reorganisation. The directors feel that it is likely that they will only
receive $100,000 on 30 November 2007 and no future interest payment. Interest for the year ended
30 November 2005 had been received. The financial year end of Ambush is 30 November 2005.
Required:
(i) Outline the requirements of IAS 39 as regards the impairment of financial assets. (6 marks)
(b) (i) IAS 39 requires an entity to assess at each balance sheet date whether there is any objective evidence that financial
assets are impaired and whether the impairment impacts on future cash flows. Objective evidence that financial assets
are impaired includes the significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor and whether it becomes probable that the
borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganisation.
For investments in equity instruments that are classified as available for sale, a significant and prolonged decline in the
fair value below its cost is also objective evidence of impairment.
If any objective evidence of impairment exists, the entity recognises any associated impairment loss in profit or loss.
Only losses that have been incurred from past events can be reported as impairment losses. Therefore, losses expected
from future events, no matter how likely, are not recognised. A loss is incurred only if both of the following two
conditions are met:
(i) there is objective evidence of impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition
of the asset (a ‘loss event’), and
(ii) the loss event has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset or group of financial assets
that can be reliably estimated
The impairment requirements apply to all types of financial assets. The only category of financial asset that is not subject
to testing for impairment is a financial asset held at fair value through profit or loss, since any decline in value for such
assets are recognised immediately in profit or loss.
For loans and receivables and held-to-maturity investments, impaired assets are measured at the present value of the
estimated future cash flows discounted using the original effective interest rate of the financial assets. Any difference
between the carrying amount and the new value of the impaired asset is an impairment loss.
For investments in unquoted equity instruments that cannot be reliably measured at fair value, impaired assets are
measured at the present value of the estimated future cash flows discounted using the current market rate of return for
a similar financial asset. Any difference between the previous carrying amount and the new measurement of theimpaired asset is recognised as an impairment loss in profit or loss.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-10-17
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-18
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-10-17
- 2020-10-17