acca考试费用一共要花多少钱?
发布时间:2021-04-24
acca考试费用一共要花多少钱?
最佳答案
ACCA费用主要包括:注册费,年费,报名费,教材费,培训费。
1、注册费:79英镑
2、年费:105英镑,每年。
大部分ACCA学员学习ACCA一般都需要三到四年,就按照四年年费来计算
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
4 (a) For this part, assume today’s date is 1 March 2006.
Bill and Ben each own 50% of the ordinary share capital in Flower Limited, an unquoted UK trading company
that makes electronic toys. Flower Limited was incorporated on 1 August 2005 with 1,000 £1 ordinary shares,
and commenced trading on the same day. The business has been successful, and the company has accumulated
a large cash balance of £180,000, which is to be used to purchase a new factory. However, Bill and Ben have
received an offer from a rival company, which they are considering. The offer provides Bill and Ben with two
alternative methods of payment for the purchase of their shares:
(i) £480,000 for the company, inclusive of the £180,000 cash balance.
(ii) £300,000 for the company assuming the cash available for the factory purchase is extracted prior to sale.
Bill and Ben each currently receive a gross salary of £3,750 per month from Flower Limited. Part of the offer
terms is that Bill and Ben would be retained as employees of the company on the same salary.
Neither Bill nor Ben has used any of their capital gains tax annual exemption for the tax year 2005/06.
Required:
(i) Calculate which of the following means of extracting the £180,000 from Flower Limited on 31 March
2006 will result in the highest after tax cash amount for Bill and Ben:
(1) payment of a dividend, or
(2) payment of a salary bonus.
You are not required to consider the corporation tax (CT) implications for Flower Limited in your
answer. (5 marks)
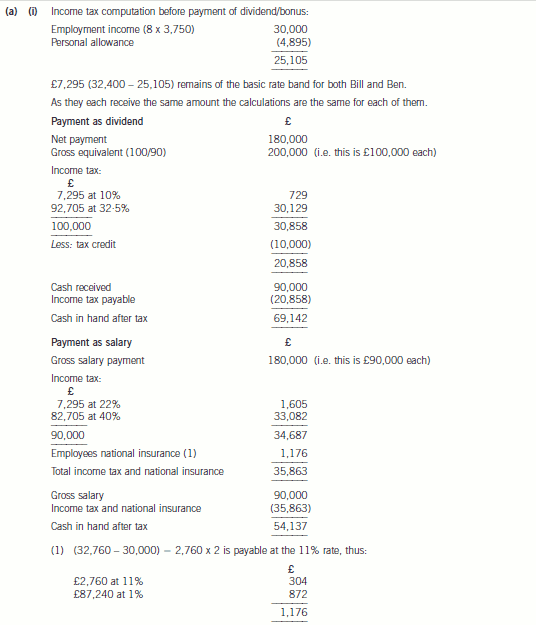
As a result, Bill and Ben would each be better off by £15,005 (69,142 – 54,137). If the cash were extracted by way
of dividend.
Tutorial note: In this answer the employers’ national insurance liability on the salary has been ignored. Credit would be
given to a candidate who recognised this issue.
(b) International Standards on Auditing (ISAs); and (5 marks)
(b) International Standards on Auditing (ISAs)
The groundwork for an international set of auditing standards began in 1969 with a number of reports published by the
Accountants International Study Group that compared the situation in Canada, the UK, and US. The establishment of the
International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC), in 1973, generated calls for a similar body to be set up for auditing.
In the late 1970s the Council of International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) created the International Auditing Practices
Committee (IAPC) as a standing committee of the IFAC Council. (Subsequently the IFAC Board.)
Tutorial note: The IFAC Council was renamed the IFAC Board in May 2000.
The first ISA was issued in 1991. The codified core set released in 1994, which has remained the series to the present day,
has been increasingly accepted by national standard setters and auditors involved in global reporting and cross-border
financing transactions.
In July 2001, IFAC sought comment on the role of IASC3 and the future of ISAs. As a result of the review, in 2002, the IAPC
was renamed the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB). IAASB has made available, on its website,
the full text of ISAs since 2003.
Further, the growth of non-audit assurance services has led to the development of a new framework (‘The International
Framework for Assurance Engagements’) effective for assurance reports issued on or after 1 January 2005.
The hope that the take up of ISAs should follow the lead set by International Accounting Standards (IASs), following their
endorsement by IOSCO (the International Organization of Securities Commissions), has been expressed by many professional
bodies including ACCA and FEE (the Fédération des Experts Comptables Européens). FEE has been leading the debate on
the future of ISAs in Europe since 2001.
ISAs provide for the international harmonisation of national standards and the adoption of a global framework approach. As
a member of CCAB (the Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies) ACCA is committed to consulting its members on
the adoption of ISAs in the UK, and working with FEE, the European Commission (EC) and others.
In response to the move in the profession, away from the ‘traditional audit risk’ model, to a business risk model, IAASB issued
ISA 315 ‘Understanding the Entity and Its Environment and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement,’ ISA 330 ‘The
Auditor’s Procedures in Response to Assessed Risks’ and ISA 500 (Revised) ‘Audit Evidence’. These standards (and
conforming amendments) are effective for audits of financial statements for periods beginning on or after 15 December 2004.
That is, they will be applicable to financial statements for periods beginning on or after 1 January 2005 that in the European
Economic Area (EEA) and elsewhere will be adopting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) for the first time.
The adoption of ISAs has been welcomed by professional bodies as providing a robust approach to risk, fraud and quality
control that is particularly important in the light of recent events (Enron/Worldcom/Parmalat). For example, ISA 315 provides
additional guidance on the assessment of risks of material misstatement at the financial statement level and at the assertion
level.
Tutorial note: Recent developments could validly be illustrated with reference to other standards. For example, ISA 240
(Revised) ‘The Auditor’s Responsibility to Consider Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’ that became effective from
1 January 2005 has raised auditor awareness of earnings management and the greater need for professional skepticism.
ISA 700 (Revised) ‘The Independent Auditor’s Report on a Complete Set of General Purpose Financial Statements’ is effective
for audits of financial statements for periods beginning on or after 15 December 2005. This proposed significant changes to
the auditor’s report to help promote consistency in reporting practices worldwide.
The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) is in discussion with IAASB about the possible
endorsement of ISAs (similar to its endorsement of IASs).
Practicing professionals must keep themselves up to date on auditing standards if they are to provide quality audits. Failure
to do so could result in negligence claims and/or disciplinary action (e.g. by ACCA’s disciplinary committee). A survey by FEE
has demonstrated that the European accountancy bodies broadly comply with ISAs. However, an earlier survey4 of IFAC
member bodies showed that 14% had some significant differences (usually relating to reporting). IFAC needs to require its
member bodies to act rather than merely encourage implementation. A set of global ethical requirements will help improve
the implementation of ISAs as well as reduce the expectation gap in performing audits of financial statements.
(c) Describe the main stages of a formal grievance procedure that Oliver should now pursue. (10 marks)
Part (c):
Grievance procedures must be accessible to all employees of Hoopers and Henderson at any level of the organisation and
regardless of their status. Managers must have suitable training in procedures and be provided with background as to how
grievances can occur in the first place. Grievance procedures must be regarded as beneficial and not threatening.
If an employee has a grievance, he or she should be able to pursue it and have the problem which has led to the grievance resolved.
A formal grievance procedure must be available, set out in writing and accessible to all employees. The procedure should consist
of five formal stages.
The first stage states the grade of employee or employees and their rights for each type of grievance.
The second stage details the actual procedures for pursuing a grievance, and is in four parts:
– The employee must discuss the grievance with his or her immediate supervisor or line manager.
– If the grievance can not be resolved at the first level, then the employee’s manager must become involved.
– The interview between the employee and manager takes place with the employee being allowed a representative if desired.
– If the grievance remains unresolved then the matter must be referred to a higher manager.
The third stage (referral to a higher manager) requires that the Human Resources Department or, in the case of Hoopers and
Henderson the partner responsible, must be informed.
The fourth stage is that written records must be kept and be available to all employees.
Finally, the procedure must be time limited.
Allowance must be made for the involvement of a trade union, staff association or individual support (if desired) at an appropriate
stage in the procedure.
At Hoopers and Henderson, Oliver has attempted to discuss the issue with his immediate manager (David Morgan) but without
success. He has therefore followed the procedure, but to continue correctly, Oliver must have taken up his grievance with the
manager next in seniority to David Morgan, who in this case is the partner responsible for human resources.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-11-17
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-04-14
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-12-31
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-10
- 2021-06-24
- 2021-01-04
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-17
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-02-15
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-06-08
- 2021-03-13
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-05-11
- 2021-05-11
- 2021-06-12