ACCA考试F1有什么好的备考建议呢?
发布时间:2021-03-11
ACCA考试F1有什么好的备考建议呢?
最佳答案
F1书看过一遍确实都记不住什么的,通过的关键在于研究重点知识。
做练习册时,不光要做题,而且要看练习册里面的选项,把一道题当成四道题来做。ABCD每个选项都要知道它讲的是哪方面的知识点。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
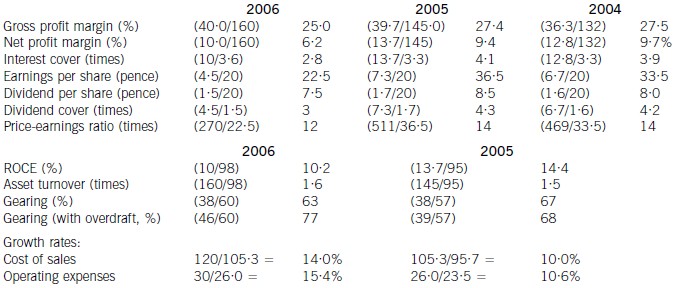
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
4 Assume today’s date is 5 February 2006.
Joanne is 37, she was born and until 2005 had lived all her life in Germany. She recently married Fraser, aged 38,
who is a UK resident, but who worked briefly in Germany. They have no children.
The couple moved to the UK to live permanently on 9 October 2005. Joanne was employed by an American company
in Germany, and she continued to work for them in the UK until the end of November 2005. Her earnings from the
American company were £5,000 per month. Joanne has not remitted any of the income she earned in Germany prior
to her arrival in the UK.
Joanne resigned from her job at the end of November 2005. The company did not hold her to the three months notice
stipulated in her contract, but still paid her for that period. In total, Joanne paid £4,200 in UK income tax under PAYE
for the tax tear 2005/06.
Joanne also wishes to sell the shares she holds in a German listed company. The shareholding cost the equivalent of
£3,500 in September 1986, and its current value is £21,500. She intends to sell the shares in March 2006 and to
invest the proceeds from the sale in the UK. Joanne has made no other capital disposals in the year.
Prior to her leaving employment, Joanne investigated the possibility of starting her own business providing a German
translation service for UK companies, and took some advice on the matter. She paid consultancy fees of £5,000
(excluding value added tax (VAT)) and bought a computer for £2,000 (excluding VAT), both on 23 October 2005.
Joanne started trading on 1 December 2005. She made sales of £2,000 in December, and estimates that her sales
will rise by £1,000 every month to a maximum of £7,000 per month. Joanne believes that her monthly expenses of
£400 (excluding VAT) will remain constant. Her year end will be 31 March, and the first accounts will be drawn up
to 31 March 2006.
Although Joanne has registered her business for tax purposes with the Revenue, she has not registered for VAT and
is unsure what is required of her in this respect.
Required:
(a) State, giving reasons, whether Joanne will be treated as resident or non-resident in the UK for the year of
assessment 2005/06, together with the basis on which her income and gains of that year will be subject to
UK taxation. (3 marks)
(a) Joanne will be treated as UK resident from the day she arrives in the UK, as she has stated her intention to move permanently
to the UK. Her income from this point will be taxable in the UK, although she will receive a full personal allowance
(unapportioned) for the year. Income earned in the UK will be taxable, but income earned abroad in Germany will not be
taxed unless it is remitted to the UK.
Although Joanne is UK resident, she is not UK domiciled. Thus, while capital gains on UK assets will be taxable, gains on
assets held overseas are taxable only to the extent that the proceeds of the sale are remitted to the UK. As Joanne intends to
remit the proceeds from selling her shares in Germany, the gain will be taxable in the UK.
4 You are an audit manager in Smith & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You have recently been made
responsible for reviewing invoices raised to clients and for monitoring your firm’s credit control procedures. Several
matters came to light during your most recent review of client invoice files:
Norman Co, a large private company, has not paid an invoice from Smith & Co dated 5 June 2007 for work in respect
of the financial statement audit for the year ended 28 February 2007. A file note dated 30 November 2007 states
that Norman Co is suffering poor cash flows and is unable to pay the balance. This is the only piece of information
in the file you are reviewing relating to the invoice. You are aware that the final audit work for the year ended
28 February 2008, which has not yet been invoiced, is nearly complete and the audit report is due to be issued
imminently.
Wallace Co, a private company whose business is the manufacture of industrial machinery, has paid all invoices
relating to the recently completed audit planning for the year ended 31 May 2008. However, in the invoice file you
notice an invoice received by your firm from Wallace Co. The invoice is addressed to Valerie Hobson, the manager
responsible for the audit of Wallace Co. The invoice relates to the rental of an area in Wallace Co’s empty warehouse,
with the following comment handwritten on the invoice: ‘rental space being used for storage of Ms Hobson’s
speedboat for six months – she is our auditor, so only charge a nominal sum of $100’. When asked about the invoice,
Valerie Hobson said that the invoice should have been sent to her private address. You are aware that Wallace Co
sometimes uses the empty warehouse for rental income, though this is not the main trading income of the company.
In the ‘miscellaneous invoices raised’ file, an invoice dated last week has been raised to Software Supply Co, not a
client of your firm. The comment box on the invoice contains the note ‘referral fee for recommending Software Supply
Co to several audit clients regarding the supply of bespoke accounting software’.
Required:
Identify and discuss the ethical and other professional issues raised by the invoice file review, and recommend
what action, if any, Smith & Co should now take in respect of:
(a) Norman Co; (8 marks)
4 Smith & Co
(a) Norman Co
The invoice is 12 months old and it appears doubtful whether the amount outstanding is recoverable. The fact that such an
old debt is unsettled indicates poor credit control by Smith & Co. Part of good practice management is to run a profitable,
cash generating audit function. The debt should not have been left outstanding for such a long period. It seems that little has
been done to secure payment since the file note was attached to the invoice in November 2007.
There is also a significant ethical issue raised. Overdue fees are a threat to objectivity and independence. Due to Norman Co
not yet paying for the 2007 year end audit, it could be perceived that the audit has been performed for free. Alternatively the
amount outstanding could be perceived as a loan to the client, creating a self-interest threat to independence.
The audit work for the year ended 28 February 2008 should not have been carried out without some investigation into the
unpaid invoice relating to the prior year audit. This also represents a self-interest threat – if fees are not collected before the
audit report is issued, an unmodified report could be seen as enhancing the prospect of securing payment. It seems that a
check has not been made to see if the prior year fee has been paid prior to the audit commencing.
It is also concerning that the audit report for the 2008 year end is about to be issued, but no invoice has been raised relating
to the work performed. To maximise cash inflow, the audit firm should invoice the client as soon as possible for work
performed.
Norman Co appears to be suffering financial distress. In this case there is a valid commercial reason why payment has not
been made – the client simply lacks cash. While this fact does not eliminate the problems noted above, it means that the
auditors can continue so long as adequate ethical safeguards are put in place, and after the monetary significance of the
amount outstanding has been evaluated.
It should also be considered whether Norman Co’s financial situation casts any doubt over the going concern of the company.
Continued cash flow problems are certainly a financial indicator of going concern problems, and if the company does not
resolve the cash flow problem then it may be unable to continue in operational existence.
Action to be taken:
– Discuss with the audit committee (if any) or those charged with governance of Norman Co:
The ethical problems raised by the non-payment of invoices, and a payment programme to secure cash payment in
stages if necessary, rather than demanding the total amount outstanding immediately.
– Notify the ethics partner of Smith & Co of the situation – the ethics partner should evaluate the ethical threat posed by
the situation and document the decision to continue to act for Norman Co.
– The documentation should include an evaluation of the monetary significance of the amount outstanding, as it will be
more difficult to justify the continuance of the audit appointment if the amount is significant.
– The ethics partner should ensure that a firm-wide policy is communicated to all audit managers requiring them to check
the payment of previous invoices before commencing new client work. This check should be documented.
– Consider an independent partner review of the working papers prepared for the 28 February 2008 audit.
– The audit working papers on going concern should be reviewed to ensure that sufficient evidence has been gathered to
support the audit opinion. Further procedures may be found to be necessary given the continued cash flow problems.
– Smith & Co have already acted to improve credit control by making a manager responsible for reviewing invoices and
monitoring subsequent cash collection. It is important that credit control procedures are quickly put into place to prevent
similar situations arising.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-06-03
- 2021-03-25
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-06-02
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-12-16
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-12-17
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-05-11
- 2021-01-05
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-03-25
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-04-15
- 2021-06-05
- 2021-04-21
- 2021-04-23
- 2021-07-01
- 2021-06-05