号外!号外!宁夏2020年ACCA考试准考证可以打印啦!这些打印流程你知道吗?
发布时间:2020-01-08
2020年已经过去了一个多周了,除去周末节假日和春节假日,留给大家备考ACCA考试的时间也不多了,相信现在有很多ACCAer们已经开始埋头苦读、认真备考了,但是51题库考试学习网在这里提醒大家:认真备考的同时千万不要忘了一个最最最重要的事情:打印准考证!“新手”ACCAer不知道打印的流程也不用担心,51题库考试学习网会把大家想要知道的咨询都分享给大家:
ACCA考试准考证打印是什么时候?
首先,ACCAer们需要注意的第一件事情就是:ACCA各科目的准考证必须学员自行通过ACCA全球官网下载,原则上不允许从第三方网站上下载相关准考证。2020年3月ACCA考试准考证目前尚未开放下载,请大家等待,ACCA考试准考证一般来说会在考试前2-3周时间开放,请各位ACCAer们注意时间,以免错过打印的时间。打印的步骤如下所示:
1、在ACCA官网主页http://www.accaglobal.com/en.html点击MYACCA,进入登录页面:
2、进入MYACCA账户后点击左侧的EXAM
ENTRY:
3、进入个人页面后点击左侧的“DOCKET”;
4、点击下方红色的“Access your
docket”进入准考证界面;
5、点击“Access your
docket” ,在随后出现的页面中选择学习方式及培训机构,培训机构选择“Beijing Champion Hi-Tech Co. Ltd.Dist...”(2019年3月考季起,ACCA全球统考准考证将不会再有个人照片!)
6、 在弹出的页面或者提示栏中选择“保存”(或是“下载”) ,准考证会以 pdf 格式显示。(一个考季内,第一次进入准考证界面时会出现以下“调查”,按实际情况填写并保存即可。)
7.下载好以后,打开文件,仔细核对准考证上的个人信息及考试信息,准考证共2页。(建议:以正反面的形式,打印在一张纸上)准考证会以 pdf 格式显示,打印完成后,考试时带上您的准考证、身份证/护照参加考试即可。
准考证打印相关注意事项有哪些?
参加笔试的考生,记得要带黑色圆珠笔。
不能用水笔的,一定是黑色圆珠笔。准考证打印好后一定要与其他考试物品(如:黑色圆珠笔,计算器等)放在一起。考试那天,把这些一并带上,另外,不要忘了带身份证(或护照)!
准考证是每位ACCA学员参加考试时必须的进场证明,所以我们要注意的准考证数量要与我们参加的考试科数相同,此外,还要仔细核对报考科目和考试地点有无错误。
需要注意的是:准考证打印没有要求彩色的,所以可以选择黑白也可选择彩色的打印。同时,准考证的要求双面打印的,这两点要尤其重视一下,提前做好准备,预防出现不必要的麻烦。
看完以上的这些信息之后,ACCAer们是不是顿时觉得打印准考证不是很难呀?51题库考试学习网在这里由衷地告诉大家:“只有一条路不能选择——那就是放弃的路;只有一条路不能拒绝——那就是成长的路。”加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
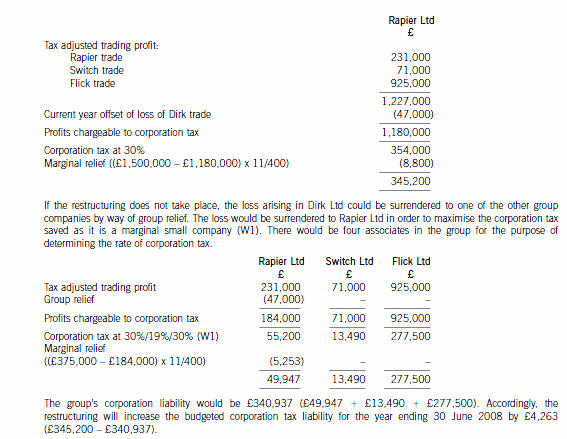
(ii) Any increase or decrease in the group’s budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June
2008 due to the restructuring on the assumption that trading losses will be used as efficiently as
possible. (8 marks)
(ii) The budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June 2008
Following the proposed restructuring, Rapier Ltd will be carrying on four separate trades. The current year loss arising
in the Dirk trade can be offset against its total profits. Its three subsidiaries will be dormant and will not be associates
for the purpose of determining the rate of corporation tax.
(c) Discuss the difficulties that may be experienced by a small company which is seeking to obtain additional
funding to finance an expansion of business operations. (8 marks)
(c) Small businesses face a number of well-documented problems when seeking to raise additional finance. These problems have
been extensively discussed and governments regularly make initiatives seeking to address these problems.
Risk and security
Investors are less willing to offer finance to small companies as they are seen as inherently more risky than large companies.
Small companies obtaining debt finance usually use overdrafts or loans from banks, which require security to reduce the level
of risk associated with the debt finance. Since small companies are likely to possess little by way of assets to offer as security,
banks usually require a personal guarantee instead, and this limits the amount of finance available.
Marketability of ordinary shares
The equity issued by small companies is difficult to buy and sell, and sales are usually on a matched bargain basis, which
means that a shareholder wishing to sell has to wait until an investor wishes to buy. There is no financial intermediary willing
to buy the shares and hold them until a buyer comes along, so selling shares in a small company can potentially take a long
time. This lack of marketability reduces the price that a buyer is willing to pay for the shares. Investors in small company
shares have traditionally looked to a flotation, for example on the UK Alternative Investment Market, as a way of realising their
investment, but this has become increasingly expensive. Small companies are likely to be very limited in their ability to offer
new equity to anyone other than family and friends.
Tax considerations
Individuals with cash to invest may be encouraged by the tax system to invest in large institutional investors rather than small
companies, for example by tax incentives offered on contributions to pension funds. These institutional investors themselves
usually invest in larger companies, such as stock-exchange listed companies, in order to maintain what they see as an
acceptable risk profile, and in order to ensure a steady stream of income to meet ongoing liabilities. This tax effect reduces
the potential flow of funds to small companies.
Cost
Since small companies are seen as riskier than large companies, the cost of the finance they are offered is proportionately
higher. Overdrafts and bank loans will be offered to them on less favourable terms and at more demanding interest rates than
debt offered to larger companies. Equity investors will expect higher returns, if not in the form. of dividends then in the form
of capital appreciation over the life of their investment.
(b) What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a balanced scorecard to better assess the overall
performance of Lawson Engineering? (8 marks)
(b) In many ways Lawson Engineering and its performance explains why Kaplan and Norton developed the balanced scorecard
to overcome the reliance on traditional, and they would argue flawed, financial measures of performance such as return on
capital employed (ROCE). Lawson Engineering as a privately owned company does not have the same pressure to maximise
shareholder wealth, which is the overarching long-term goal of publicly quoted companies. The intangible resources discussed
above – both internal and external – reflect the success of the company in meeting the expectations of the other key
stakeholders in the business, namely customers, employees and suppliers. In terms of the other measures of performance
used in the balanced scorecard the customer perspective seems to be very much a positive area of performance. Lawson
Engineering has developed a clear niche strategy based on the excellence of its products. Market share as a measure of
customer satisfaction is not too relevant as the company has chosen to develop its own markets and is not looking for large
volumes and a dominant market share. The growth of the company suggests that it is both retaining its existing customer
base and acquiring new ones. Clearly there need to be measures in place to show where its growth is coming from. Customer
acquisition is usually an expensive but necessary activity and cutomer retention a more positive route to profitability. Today
there is increasing emphasis on customer relationship management (CRM) and measures to show the share of a particular
customer’s business the company has, rather than the overall market share the company has achieved. Michael Porter has
drawn attention to the fact that having the biggest market share is not necessarily associated with being the most profitable
company in that market. Customer acquisition and retention are both useful indicators of customer satisfaction which many
companies have problems in measuring. Finally, knowing which customers are profitable ones is a key requirement.
Surprisingly there is a lot of evidence to suggest that many companies are unsure which of their products and which
customers actually contribute to their profits.
The third measure in the balanced scorecard is an internal one – the effectiveness or otherwise of the firm’s internal processes.
In turn there are three areas where performance should be measured – innovation, operational processes and after sales
service (where appropriate). Innovation itself is a result of effective internal processes and Lawson Engineering through its
patents and awards has tangible evidence of its success. Many firms are measuring the contribution of products introduced
in the last three or four years – 3M, a global manufacturer of consumer and industrial products looks to achieve 30% of its
sales from products that are less than four years old. Equally important in a company such as Lawson Engineering is the time
taken to develop and get new products to their customers. The strategy of being ‘first to market’ can be a very effective
competitive strategy.
Equally important for the customers are the operational processes that produce and deliver the inputs from their suppliers.
The introduction of JIT and the use of technology to shorten and simplify the links between supplier and customer are ways
of shortening lead times and increasing customer satisfaction. Lawson Engineering has looked to innovate its processes as
well as its products and can look to develop measures of key areas of operational performance. Finally it is worth stressing
that financial performance, customer satisfaction and effective internal processes are all dependent on the people who make
things happen in the firm. Employees and the way they learn and grow in their jobs will determine whether or not the firm
succeeds. Again there is evidence to suggest that Lawson Engineering’s employees are being trained and developed and as
a consequence are well motivated.
The balanced scorecard has been criticised on a number of accounts. Firstly, such a comprehensive set of performance
measures will take considerable time and commitment on the part of senior management to develop. There is a need to avoid
over-complexity and assess the costs and benefits of the process. Secondly, there is the question of whether all the key
stakeholders have shared goals and expectations and whether the measures are focused on short-, medium- or long-term
performance. Thirdly, its focus on internal and external processes may not come easily to firms that have organised themselves
on traditional lines. Most organisations have retained departments within which functional specialists are located, e.g.
production, marketing etc. Changing the way performance is measured may need a radical change in culture and meetsignificant resistance.
(c) Illustrate how:
(i) inquiry; and (4 marks)
(c) Due diligence review
(i) Inquiries
Tutorial note: These should be focussed on uncovering facts that may not be revealed by the audited financial
statements (e.g. off balance sheet finance, contingencies, commitments and contracts) especially where knowledge
may be confined to management.
■ Do any members of MCM’s senior/executive management have contractual terms that will result in significant
payouts to them (e.g. on change of ownership of the company or their being made redundant)?
■ What contracts with clients, if any, will lapse or be made void in the event that MCM is purchased from Frontiers?
■ What synergy or inter-company trading, if any, currently exists between MCM and Frontiers? For example, Frontiers
may publish MCM’s training materials.
■ Are there any major clients who are likely to be lost if MCM is purchased by Plaza (e.g. any competitor food
retailers)?
■ What are the principal terms of the operating leases relating to the International business’s premises?
■ What penalties should be expected to be incurred if operating leases and/or contracts with training consultants are
terminated?
■ Has MCM entered into any purchase commitments since 31 December 2004 (e.g. to buy or lease further
premises)?
■ Who are the best trainers that Plaza should seek to retain after the purchase of MCM?
■ What events since the audited financial statements to 31 December 2004 were published have made a significant
impact on MCM’s assets, liabilities, operating capability and/or cash flows? (For example, storm damage to
premises, major clients defaulting on payments, significant interest/foreign-exchange rate fluctuations, etc.)
■ Are there any unresolved tax issues which have not been provided for in full?
■ What effect will the purchase have on loan covenants? For example, term loans may be rendered repayable on a
change of ownership.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-17
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-01-10