速看!ACCA注册报名流程!
发布时间:2021-04-24
随着ACCA在中国的认可度越来越高,报考ACCA也越来越多,如果你近期有报考ACCA的打算,那你是否熟悉ACCA报考流程呢?今天就给大家分享一下ACCA注册报名流程,让我们一起来看看吧!
首先来说说注册ACCA需要准备哪些资料:
在校学生需要准备的ACCA注册材料:1.中英文在校证明(原件),2.中英文成绩单(可复印加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章),3.中英文个人身份证件或护照(复印件加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章),4.2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,5.用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(建议使用Visa)
非在校学生所需准备的注册资料(符合学历要求):1.中英文个人身份证件或护照(复印件加盖第三方章),2.中英文学历证明(复印件加盖第三方章),3.2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,4.用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(推荐使用Visa)
如果不符合以上两个条件的,可通过FIA形式注册:1.中英文个人身份证件或护照(复印件加盖第三方章),2.2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,3.用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(建议使用Visa),之后在进入正题。
其次给大家说一下ACCA的注册流程:
ACCA的注册报名流程分为:1.准备注册所需材料,2.在全球官方网站进行注册,需要填写相关个人信息,学历信息,在线上传注册资料等,3.支付注册费,4.查询注册进度。
最后,再给大家说一下成功注册ACCA后,该如何缴纳年费?
关于年费的缴纳,请以ACCA英国总部发送给您的邮件为准,如有任何疑问,请及时联系英国总部。每年5月8日注册的学员需缴纳当年年费;5月8日之后注册的学员将从注册后次年一月份开始每年缴纳年费,以保持ACCA学员身份继续考试。可以登录英文官网在MY ACCA中查看自己是否有任何欠费并及时支付。确保用于注册ACCA学员的EMAIL地址真实有效。注册成为ACCA学员以后,ACCA英国总部将按照学员自行登记的联系方式,通过EMAIL与学员直接联系。中国代表处也将通过您在中文网站填写邮件地址进行通知,ACCA组织的各项活动详情会不定期的提供一些各大公司及事务所的职位空缺给学员。因此,登记的联系方式非常重要,如有手机号码、电子邮箱或通讯地址的任何变化,要及时登录ACCA英文官方网站MYACCA和中文官方网站更新信息,以便ACCA能联系到您。
以上就是关于ACCA报名的全部流程啦,希望能够帮助到大家,更多关于ACCA的资讯,可关注51题库考试学习网,51题库考试学习网将持续为你带来更多新内容。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
4 (a) Explain the auditor’s responsibilities in respect of subsequent events. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
4 JINACK CO
(a) Auditor’s responsibilities for subsequent events
■ Auditors must consider the effect of subsequent events on:
– the financial statements;
– the auditor’s report.
■ Subsequent events are all events occurring after a period end (i.e. reporting date) i.e.:
– events after the balance sheet date (as defined in IAS 10); and
– events after the financial statements have been authorised for issue.
Events occurring up to date of auditor’s report
■ The auditor is responsible for carrying out procedures designed to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that all
events up to the date of the auditor’s report that may require adjustment of, or disclosure in, the financial statements
have been identified.
■ These procedures are in addition to those applied to specific transactions occurring after the period end that provide
audit evidence of period-end account balances (e.g. inventory cut-off and receipts from trade receivables). Such
procedures should ordinarily include:
– reviewing minutes of board/audit committee meetings;
– scrutinising latest interim financial statements/budgets/cash flows, etc;
– making/extending inquiries to legal advisors on litigation matters;
– inquiring of management whether any subsequent events have occurred that might affect the financial statements
(e.g. commitments entered into).
■ When the auditor becomes aware of events that materially affect the financial statements, the auditor must consider
whether they have been properly accounted for and adequately disclosed in the financial statements.
Facts discovered after the date of the auditor’s report but before financial statements are issued
Tutorial note: After the date of the auditor’s report it is management’s responsibility to inform. the auditor of facts which
may affect the financial statements.
■ If the auditor becomes aware of such facts which may materially affect the financial statements, the auditor:
– considers whether the financial statements need amendment;
– discusses the matter with management; and
– takes appropriate action (e.g. audit any amendments to the financial statements and issue a new auditor’s report).
■ If management does not amend the financial statements (where the auditor believes they need to be amended) and the
auditor’s report has not been released to the entity, the auditor should express a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion
(as appropriate).
■ If the auditor’s report has been released to the entity, the auditor must notify those charged with governance not to issue
the financial statements (and the auditor’s report thereon) to third parties.
Tutorial note: The auditor would seek legal advice if the financial statements and auditor’s report were subsequently issued.
Facts discovered after the financial statements have been issued
■ The auditor has no obligation to make any inquiry regarding financial statements that have been issued.
■ However, if the auditor becomes aware of a fact which existed at the date of the auditor’s report and which, if known
at that date, may have caused the auditor’s report to be modified, the auditor should:
– consider whether the financial statements need revision;
– discuss the matter with management; and
– take appropriate action (e.g. issuing a new report on revised financial statements).
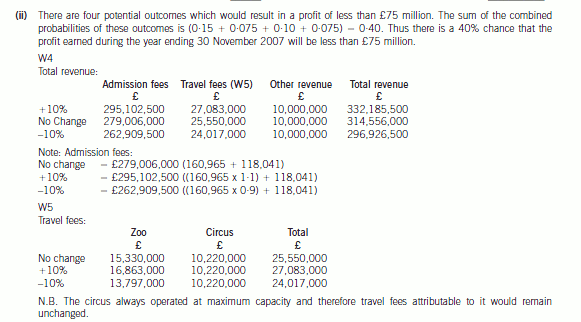
(ii) Calculate the probability of the net profit being less than £75 million. (2 marks)
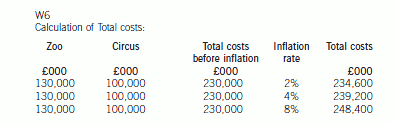
(c) Critically discuss the adoption of activity-based management (ABM) in companies such as TOC. (6 marks)
(c) Activity-based management (ABM) is a method of identifying and evaluating activities that a business performs using
activity-based costing to carry out a value chain analysis or a re-engineering initiative to improve strategic and operational
decisions in an organisation. Activity-based costing establishes relationships between overhead costs and activities so that
overhead costs can be more precisely allocated to products, services, or customer segments. Activity-based management
focuses on managing activities to reduce costs and improve customer value.
Kaplan and Cooper (1998) divide ABM into operational ABM and strategic ABM:
Operational ABM is about ‘doing things right’, using ABC information to improve efficiency. Those activities which add value
to the product can be identified and improved. Activities that don’t add value are the ones that need to be reduced to cut costs
without reducing product value.
Strategic ABM is about ‘doing the right things’, using ABC information to decide which products to develop and which
activities to use. This can also be used for customer profitability analysis, identifying which customers are the most profitable
and focusing on them more.
A risk with ABM is that some activities have an implicit value, not necessarily reflected in a financial value added to any
product. For instance a particularly pleasant workplace can help attract and retain the best staff, but may not be identified as
adding value in operational ABM. A customer that represents a loss based on committed activities, but that opens up leads
in a new market, may be identified as a low value customer by a strategic ABM process.
ABM can give middle managers an understanding of costs to other teams to help them make decisions that benefit the whole
organisation, not just their activities’ bottom line.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-07
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-04-15
- 2021-01-13
- 2021-04-24
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-05-07
- 2021-04-10
- 2021-04-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-12-31
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-04
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-24
- 2020-01-29