ACCAF4法律的三种分类五种特征!
发布时间:2019-07-20
ACCA作为财会界的黄金证书,一直是很多小伙伴向往的考取的证书,但是因为其考试科目多,考试难度大的问题难倒了很多小伙伴,为此小编特地整理了关于ACCAF4的考试备考内容,具体内容如下。
一、三种分类方式
判例法(case law)指可作为先例据以决案的法院判决,是法官造法,也就是我们说的司法者造法,这点通常与成文法 (statute law) 相对,成文法是由议会制定法律。判例法和成文法都是英国法系法律的两个重要渊源 (source of law) ,也是重要的法律类型之一(types of law)。此时这种分类是按照法律制定的主体来区分的。
根据判例法制度,某一判决中的法律规则不仅适用于该案,而且往往作为一种先例(precedent)而适用于以后该法院或下级法院所管辖的案件。只要案件的基本事实相同或相似,就必须以判例所定规则处理。这就是所谓“遵循先例” (stare decisis) 原则。
此外,我们又可以通过法律规范的主体是否平等,将法律分为私法 (private law) 和公法(public law)。
私法 (private law) 主要是指调整普通公民,组织之间关系的法律,在社会层面上双方当事人的法律地位平等,私法关键在于调整公民个人的权利义务关系(right and obligation)。
公法(public law)主要是指调整国家与普通公民、组织之间关系的法律,从定义中可以看出双方当事人中必须至少有一方是公权力机关。在我们生活中的tax law,constituition law都是属于公法范畴的。
最后我们还可以依据法律规范的内容不同,将法律分为刑法(criminal law)和民法 (civil law)。民法属于私法的范畴,重点在于双方当事人之间权利与义务的分配,刑法属于公法的范畴,重点在于确定什么样的行为是犯罪行为,和对于犯罪行为给与怎么样的处罚(punishment),所以可以归纳为三个字罪与罚。考试中时常会考到两者的区别,需要同学们对该块内容加以重视。
二、五大必会特征
1. Burden of proof 举证责任
举证责任的一般原则是谁主张,这举证。在民事案件中由我们的原告(claimant)进行举证,在刑事案件中由国家提起公诉,这里的检察官(prosecution)就是代表国家。
2. Standard of proof 举证的标准
在民法中,举证的标准是看原告和被告谁的证据更占优势,即谁的证词可能性越高(balance of
probabilities),谁胜诉的概率就越高。
在刑事案件中,举证的标准会明显提高,需要排除一切合理的怀疑(beyond reasonable
doubt)。这是由于刑事案件的两方在法律地位上是不平等的,且刑事案件的判决结果对于被告人更为严重,所以公诉人想要胜诉,必须承担更高的举证标准,来证明被告有罪。
3. Decision 判决结果
在民事案件中,判决结果是被告是否有责任(liable / not liable),而在刑事案件中,判决结果往往是被告人是否有罪(guilty / not guilty)
4. Aim 法律目的
民法的目的是provide compensatory remedies,具有补偿性质,而并非惩罚。但在刑事案件中,法院对国家不允许或者不赞成的行为,给与惩罚(punishment)
5. Remedies 救济方式
在民事案件中,被告如果有责任,一般给到原告赔偿金(damages)作为救济方式,但是在刑事案件中,被告人如果有罪,就会受到收监关押(prinson)和罚金(fines)的惩罚。
综合以上就是关于ACCAF4的备考内容,希望对各位小伙伴有用,小编将持续更新相关内容。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) (i) Explain, by reference to Coral’s residence, ordinary residence and domicile position, how the rental
income arising in respect of the property in the country of Kalania will be taxed in the UK in the tax year
2007/08. State the strategy that Coral should adopt in order to minimise the total income tax suffered
on the rental income. (7 marks)
(b) (i) UK tax on the rental income
Coral is UK resident in 2007/08 because she is present in the UK for more than 182 days. Accordingly, she will be
subject to UK income tax on her Kalanian rental income.
Coral is ordinarily resident in the UK in 2007/08 as she is habitually resident in the UK.
Coral will have acquired a domicile of origin in Kalania from her father. She has not acquired a domicile of choice in the
UK as she has not severed her ties with Kalania and does not intend to make her permanent home in the UK.
Accordingly, the rental income will be taxed in the UK on the remittance basis.
Any rental income remitted to the UK will fall into the basic rate band and will be subject to income tax at 22% on the
gross amount (before deduction of Kalanian tax). Unilateral double tax relief will be available in respect of the 8% tax
suffered in Kalania such that the effective rate of tax suffered by Coral in the UK on the grossed up amount of income
remitted will be 14%.
In order to minimise the total income tax suffered on the rental income Coral should ensure that it is not brought into or
used in the UK such that it will not be subject to income tax in the UK.
Coral should retain evidence, for example bank statements, to show that the rental income has not been removed from
Kalania. Coral can use the money whilst she is on holiday in Kalania with no UK tax implications.
3 (a) Financial statements often contain material balances recognised at fair value. For auditors, this leads to additional
audit risk.
Required:
Discuss this statement. (7 marks)
3 Poppy Co
(a) Balances held at fair value are frequently recognised as material items in the statement of financial position. Sometimes it is
required by the financial reporting framework that the measurement of an asset or liability is at fair value, e.g. certain
categories of financial instruments, whereas it is sometimes the entity’s choice to measure an item using a fair value model
rather than a cost model, e.g. properties. It is certainly the case that many of these balances will be material, meaning that
the auditor must obtain sufficient appropriate evidence that the fair value measurement is in accordance with the
requirements of financial reporting standards. ISA 540 (Revised and Redrafted) Auditing Accounting Estimates Including Fair
Value Accounting Estimates and Related Disclosures and ISA 545 Auditing Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures
contain guidance in this area.
As part of the understanding of the entity and its environment, the auditor should gain an insight into balances that are stated
at fair value, and then assess the impact of this on the audit strategy. This will include an evaluation of the risk associated
with the balance(s) recognised at fair value.
Audit risk comprises three elements; each is discussed below in the context of whether material balances shown at fair value
will lead to increased risk for the auditor.
Inherent risk
Many measurements based on estimates, including fair value measurements, are inherently imprecise and subjective in
nature. The fair value assessment is likely to involve significant judgments, e.g. regarding market conditions, the timing of
cash flows, or the future intentions of the entity. In addition, there may be a deliberate attempt by management to manipulate
the fair value to achieve a desired aim within the financial statements, in other words to attempt some kind of window
dressing.
Many fair value estimation models are complicated, e.g. discounted cash flow techniques, or the actuarial calculations used
to determine the value of a pension fund. Any complicated calculations are relatively high risk, as difficult valuation techniques
are simply more likely to contain errors than simple valuation techniques. However, there will be some items shown at fair
value which have a low inherent risk, because the measurement of fair value may be relatively straightforward, e.g. assets
that are regularly bought and sold on open markets that provide readily available and reliable information on the market prices
at which actual exchanges occur.
In addition to the complexities discussed above, some fair value measurement techniques will contain significant
assumptions, e.g. the most appropriate discount factor to use, or judgments over the future use of an asset. Management
may not always have sufficient experience and knowledge in making these judgments.
Thus the auditor should approach some balances recognised at fair value as having a relatively high inherent risk, as their
subjective and complex nature means that the balance is prone to contain an error. However, the auditor should not just
assume that all fair value items contain high inherent risk – each balance recognised at fair value should be assessed for its
individual level of risk.
Control risk
The risk that the entity’s internal monitoring system fails to prevent and detect valuation errors needs to be assessed as part
of overall audit risk assessment. One problem is that the fair value assessment is likely to be performed once a year, outside
the normal accounting and management systems, especially where the valuation is performed by an external specialist.
Therefore, as a non-routine event, the assessment of fair value is likely not to have the same level of monitoring or controls
as a day-to-day business transaction.
However, due to the material impact of fair values on the statement of financial position, and in some circumstances on profit,
management may have made great effort to ensure that the assessment is highly monitored and controlled. It therefore could
be the case that there is extremely low control risk associated with the recognition of fair values.
Detection risk
The auditor should minimise detection risk via thorough planning and execution of audit procedures. The audit team may
lack experience in dealing with the fair value in question, and so would be unlikely to detect errors in the valuation techniques
used. Over-reliance on an external specialist could also lead to errors not being found.
Conclusion
It is true that the increasing recognition of items measured at fair value will in many cases cause the auditor to assess the
audit risk associated with the balance as high. However, it should not be assumed that every fair value item will be likely to
contain a material misstatement. The auditor must be careful to identify and respond to the level of risk for fair value items
on an individual basis to ensure that sufficient and appropriate evidence is gathered, thus reducing the audit risk to an
acceptable level.
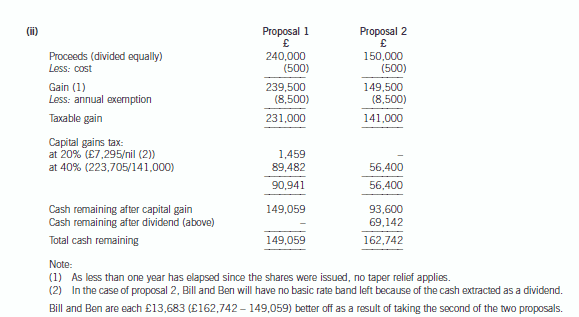
(ii) Following on from your answer to (i), evaluate the two purchase proposals, and advise Bill and Ben
which course of action will result in the highest amount of after tax cash being received by the
shareholders if the disposal takes place on 31 March 2006. (4 marks)
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-11
- 2021-04-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-04
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-05-21