天津市考生注意:2020年ACCA考试,科目要这么选!
发布时间:2020-01-10
ACCA考试一共有13门考试科目,这对于一个刚学习ACCA的考生来说,多少有点难以下手的感觉。按照以往考霸学习经验,ACCA考试13门科目如何搭配比较合理呢?今天51题库考试学习网就给大家介绍一下吧!当然,51题库考试学习网推荐大家的报名顺序不一定是适用于每一个人的,仅供大家参考哟~大家一定要根据自己的学习能力和进度来调整报考顺序,毕竟适合自己的才是最好的。
ACCA考试科目共13科,分为四个大模块:知识模块(ACCA考试科目AB-FA)、技能模块(ACCA考试科目LW-FM)、核心模块(ACCA考试科目SBL&SBR)、选修模块(ACCA考试科目AFM-AAA)。学员只需要通过11门必修科目及2门选修科目共13门课程即可通过考试。
不过,总体来说,ACCA考试科目有两个部分:基础阶段和专业阶段。他们各自有哪些特点呢?
第一部分为基础阶段,主要分为知识课程和技能课程两个部分。知识课程主要涉及财务会计和管理会计方面的核心知识,也为接下去进行技能阶段的详细学习搭建了一个平台。技能课程共有六门课程,广泛的涵盖了一名会计师所涉及的知识领域及必须掌握的技能。
第二部分为专业阶段,主要分为核心课程和选修(四选二)课程。该阶段的课程相当于硕士阶段的课程难度,是对第一部分课程的引申和发展。该阶段课程引入了作为未来的高级会计师所必须的更高级的职业技能和知识技能。选修课程为从事高级管理咨询或顾问职业的学员,设计了解决更高级和更复杂的问题的技能。
对于ACCA考生来说,这必考的13门科目必须按模块顺序来报考,即知识模块-技能模块-核心模块-选修模块。必须按照这个顺序来报考,但是各个模块内部的科目是可以打乱顺序考的。例如:F1-F3,可以先考F3,再考F2,再考F1,后面的依此类推。
当然,ACCA每一次考试最多可以报满4科,那么可以把前面模块的都报上,报完以后还有剩余科目可以给后面模块的再报上后面模块的科目。
例如,可以一次把F1、F2、F3、F4都报上,考试结束后,F4、F3、F2都通过了,F1没通过,那么下次报F678等科目时,必须先把F1报上,如果考完了F4-F9的科目,F1还是没通过,报P阶段时,F1也必须先报上。就是说前一个模块没有考完的科目,必须在下一次报考下一个模块考试时都带上继续报考,直到通过。后面的依此类推。
F阶段的考试相对比较简单,P阶段考试科目是专业的阶段课程,相对于前面二部分是有难度的,对综合应用英语的能力和专业知识部分提出了新的挑战。ACCA考试科目P2、P4、P5偏向于计算,ACCA考试科目P1和P3的计算量较少。所以想一次性报考的话,ACCA考试科目P2、P4、P5偏向于计算,ACCA考试科目P1和P3的计算量较少,建议交叉考试分配,在告诉大家分配考试顺序之前,温馨提示一下大家:这里的可以随机顺序报考,指的是阶段内部的报考,譬如F阶段里面F1-F9你可以任意顺序报考,而硬性规定的一点就是F阶段的全部通过之后,才可以报考P阶段的考试。
这里给出的组合建议是:
1.毅力有精力有可以F6+F7+F9,然后F8+P1+P2,若是求稳,应该选择F6+F9,然后F7+F8
2.学习 F9 P2
3.学习 P1 P3
4.学习 P4 P5
为梦想孤注一掷,让努力苦尽甘来。以上信息希望可以帮助到你,最后51题库考试学习网祝你考试成功
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Provide an example that illustrates a structured application of the terms contained in the above statement in
respect of a profit-seeking organisation OR a not-for-profit organisation of your own choice. (6 marks)
(b) An illustration of the features detailed above, framed in the context of a University as an organisation in the not-for-profit sector
might be as follows:
The Overall objective might well be stated in the mission statement of a University. An example of such a mission statement
might be as follows:
‘To provide a quality educational environment in a range of undergraduate and post-graduate disciplines and a quality
educational focus for students and the business community.’
More specifically, objectives may be seen as the achievement of ‘value for money’ thereby ensuring effectiveness in areas such
as:
– The provision of high added value to students;
– The establishment of a reputation for recognised expertise in specific areas of research work within the wider community;
and
– The provision of a high quality service to industry and commerce.
Strategies may focus on aspects such as:
– The recruitment and retention of high quality academic staff;
– The development of IT equipment and skills within the institution;
– The mentoring of students in order to ensure high added value and low drop-out rates in intermediate years of study;
and
– The close liaison with employers as to qualities in graduate/post-graduate employees that they will value highly.
The determinants used to measure the results of strategies might include:
– Competitiveness – cost per graduate compared to other institutions; growth in student numbers; number of staff holding
a PhD qualification;
– Financial performance – average cost per graduate; income generation from consultancy work;
– Quality – range of awards (percentages of 1st class degrees); employer responses; measures of quality of delivery of
education, advice to students, etc;
– Flexibility – variable entry and exit points to courses; modular structure; the variety of full-time, part-time and distance
learning modes;
– Resource Utilisation – staff:student ratios; quotas met by each course; accommodation filled;
– Innovation – latest IT provision in linking lecture theatres to information databases; increased provision of flexilearning/
mixed mode course provision.
The application of business change techniques might include the following:
BPR with a focus on IT developments, flexible-learning or mixed mode course provision.
JIT with a focus on moves towards student-centred uptake of educational opportunities e.g. via intranet availability of lecture
and tutorial material linked to more flexible access to staff rather than a ‘push’ system of pre-structured times of
lectures/tutorials.
TQM with a focus on moves to improve quality in all aspects of the learning environment including delivery of lectures, access
to staff and pastoral care issues.
ABM with a focus on activities on a per student basis (both planned and actual) with a view to eliminating activities that do
not add value e.g. cost per lecture per student.
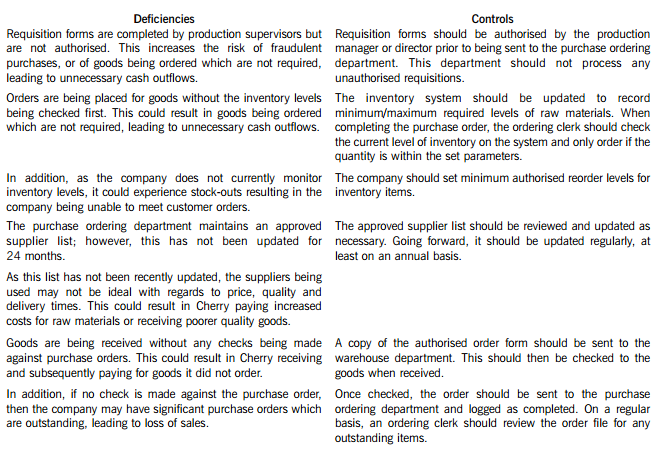
Cherry Blossom Co (Cherry) manufactures custom made furniture and its year end is 30 April. The company purchases its raw materials from a wide range of suppliers. Below is a description of Cherry’s purchasing system.
When production supervisors require raw materials, they complete a requisition form. and this is submitted to the purchase ordering department. Requisition forms do not require authorisation and no reference is made to the current inventory levels of the materials being requested. Staff in the purchase ordering department use the requisitions to raise sequentially numbered purchase orders based on the approved suppliers list, which was last updated 24 months ago. The purchasing director authorises the orders prior to these being sent to the suppliers.
When the goods are received, the warehouse department verifies the quantity to the suppliers despatch note and checks that the quality of the goods received are satisfactory. They complete a sequentially numbered goods received note (GRN) and send a copy of the GRN to the finance department.
Purchase invoices are sent directly to the purchase ledger clerk, who stores them in a manual file until the end of each week. He then inputs them into the purchase ledger using batch controls and gives each invoice a unique number based on the supplier code. The invoices are reviewed and authorised for payment by the finance director, but the actual payment is only made 60 days after the invoice is input into the system.
Required:
In respect of the purchasing system of Cherry Blossom Co:
(i) Identify and explain FIVE deficiencies; and
(ii) Recommend a control to address each of these deficiencies.
Note: The total marks will be split equally between each part.
Cherry Blossom Co’s (Cherry) purchasing system deficiencies and controls

2 John Dixon is the recently appointed Chief of Police for a major city in the UK. He has inherited a major problem in
that its residents are very concerned with various forms of antisocial behaviour and minor crimes carried out by a
small number of people, which makes living, working, travelling and socialising in the city centre unpleasant rather
than life threatening. The city’s residents have recently voted for it being one of the five worst cities in the UK in which
to live. There is little or no contact between the police and these residents.
The city is split into a number of police districts, each with its own senior officer in charge. Their focus is on the
response to emergency calls and solving serious crimes in their district rather than the less urgent crimes affecting
everyday living in the city. Response times and serious crime solution rates are the traditional measures by which their
performance is measured and leave them open to criticism of simply reacting to events. There is little sense of being
part of a city police force and, consequently, little sharing of information and experience between the different districts.
The failure in policing antisocial behaviour in the city is seen as being largely the result of a shortage of resources.
There are also important internal and external groups varying in their support or resistance to any necessary change
in policing strategy. Key players include the mayor of the city anxious to improve the reputation of the city, the city’s
press, traditionally used to highlighting police failures rather than successes and finally the courts of justice, which
are reluctant to take on the increased workload that any moves towards reducing antisocial behaviour would produce.
John is aware of the complexity of the problem he faces in changing the way the city is policed to improve the quality
of life of its citizens. He has, however, an impressive track record as a change agent in previous appointments and is
confident that he can bring about the necessary change.
Required:
(a) Using change management models where appropriate, provide John with a brief report on the nature of
change needed in the way the city is policed in order to improve the city’s quality of life. (12 marks)
(a) To: John Dixon
From: Change Management consultant
Changes to policing and impact on the city’s quality of life
This is a complex problem involving different stakeholders each of which is looking for different results from the policing
system. The recognition of the need to change is one of the most difficult parts of the change process. There will be
considerable commitment to the current ways of doing things reinforced by the ways in which performance is measured. The
various stakeholders involved will have different perceptions of the problem and the need for change. They will have different
levels of power and influence and different levels of interest in seeing the change happen. Mendelow’s model for mapping
may prove useful in understanding how to handle the expectations of the different groups. The key players would clearly be
the senior officers in charge of the city’s districts who will be responsible for implementing any change in the way the city is
policed. You will have to decide how to convince these officers that a change to the way they currently do things is needed.
One suggestion is that they actually get first-hand experience of the conditions being faced by the city’s residents. Another
group with significant power and interest are the courts because if they refuse to process the cases of antisocial behaviour
then the whole strategy will fail. However, the interest of the mayor and the media in the reputation the city has gained may
be used to counter the reluctance of the courts to take on the extra workload.
One of the most popular models for understanding change and likely resistance to it, is to carry out a forcefield analysis.
Johnson, Scholes and Whittington argue that such an analysis ‘provides an initial view of change problems that need to be
tackled, by identifying forces for and against change’. They ask three key questions:
What aspects of the current situation might aid change in the desired direction, and how might these be reinforced?
What aspects of the current situation would block such a change, and how can these be overcome?
What needs to be introduced or developed to aid change?
Forcefield analysis
Pushing Resisting
Residents’ desire for safer city Police commitment to serious crime
Mayor of city – city’s reputation District focus and not city concern
John Dixon’s desire for change Traditional performance measures
Courts fear of increased workload
Police resources over committed
Forcefield analysis was first developed by Kurt Lewin and linked to his 3-step model of change where to accomplish desired
change it is necessary to get the various stakeholders to recognise the need for change and unfreeze the situation. This will
require you to use some or all of the styles of managing change explained below. One of the real problems is that each
stakeholder will feel that they have an objective view of the situation. Getting a shared view may be very difficult to achieve
and require real leadership on your part.
Once the need to change is agreed there will need to be major changes in the way the city is policed to achieve the desired
goal of eliminating antisocial behaviour and improving the quality-of-life for the city’s residents. Real change will be needed
to the way in which police resources are deployed, the systems used to police on a city rather than on a district basis and
the way results are measured and publicised. There will be a need for ‘quick wins’ to show the potential positive results
achievable with the new strategy.
Finally, rewards and sanctions must be put in place to re-enforce the desired state of affairs and prevent behaviours slipping
back to the previous position. Here you will need to look at how to refreeze the situation and clearly show how the new
position means that the goals of the city and its stakeholders are really shared.
There are many available change models for a programme such as this such as the Gemini 4Rs framework and most will
look to assess the scope of change required and the timeframe. available to achieve it. Undoubtedly, you will require many ofthe skills associated with project management in a major change programme such as this.
Yours,
(b) Peter, one of Linden Limited’s non-executive directors, having lived and worked in the UK for most of his adult
life, sold his home near London on 22 March 2006 and, together with his wife (a French citizen), moved to live
in a villa which she owns in the south of France. Peter is now demanding that the tax deducted from his director’s
fees, for the board meetings held on 18 April and 16 May 2006, be refunded, on the grounds that, as he is no
longer resident in the UK, he is no longer liable to UK income tax. All of the company’s board meetings are held
at its offices in Cambridge.
Despite Peter’s assurance that none of the other companies of which he is a director has disputed his change of
tax status, Damian is uncertain whether he should make the refunds requested. However, as Peter is a friend of
the company’s founder, Linden Limited’s managing director is urging him to do so, stating that if the tax does
have to be paid, then Linden Limited could always bear the cost.
Required:
Advise Damian whether Peter is correct in his assertion regarding his tax position and in the case that there
is a UK tax liability the implications of the managing director’s suggestion. You are not required to consider
national insurance (NIC) issues. (4 marks)
(b) Peter will have been resident and ordinarily resident in the UK. When such individuals leave the UK for a purpose other than
to take up full time employment abroad, they normally continue to still be so regarded unless their absence spans a complete
tax year. But, where someone intends to live permanently abroad or to do so for a period of at least three tax years, they may
be treated as non-resident and non-ordinarily resident from the day after the date of their departure, if they can provide
evidence to HMRC of that intention. Selling a residence in the UK and setting up home abroad will normally constitute such
evidence. However to retain non-resident status the intention must actually be fulfilled, and visits to the UK must not exceed
182 days in any tax year or average more than 90 days per year over a period of four tax years. Given that Peter would appear
to have several company directorships in the UK, it is possible that he might fail to satisfy the 90 day average ‘substantial
visits’ rule.
Even if Peter is classed as non-resident, any remuneration earned in the UK will still be liable to UK income tax, and subject
to PAYE, unless it is for duties incidental to an overseas employment, which is unlikely to be the case for fees paid to a nonexecutive
director for attending board meetings. Thus, income tax should still be deducted from the fees under PAYE. Where
PAYE should have been deducted from a director’s emoluments and it has not been, but the tax is nevertheless accounted
for by the company to HMRC, then to the extent that the tax is not reimbursed by the director, he will be treated as receiving
a benefit equivalent to the amount of tax.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-08-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-10-09
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-03-04
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-03-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-03-04