九月新挑战来了!ACCA考试机考流程你清楚吗?
发布时间:2019-08-04
参加ACCA考试的童鞋们都知道,ACCA考试每年都举行4次,分别是在3、6、9、12月考试,8月份一半的时间也要过去了,九月份也要到来了,童鞋们也要迎接9月份的考试了,那你知道ACCA机考流程吗?
1.考生在自己电脑上查询一下自己家乡是否有机考中心,如果没有,你需要到别的考区报名,你可以给机考中心打电话申请参加ACCA机考或者考生直接到机考中心缴纳考试费。
2.机考考试前,机考中心会公布具体的考试时间,考生可以根据时间来安排自己的考试报名。
3.到考试当天,考生须携带ACCA相关证件参加考试,不管是身份证、驾驶证还是护照都可以,它没有CFA考试那么严。
4.机考考试开始前,监考人员会宣读考场纪律;考生需要在电脑上输入个人信息,监考人员会核对考生的身份;身份核对后,电脑上会显示出3页考试操作指南,考生仔细阅读,得到监考人员的允许后才可点击考试科目,开始考试。
5.机考考试开始时,题目会直接在屏幕上显示,请直接在电脑上输入答案。
6.机考考试结束后,需要打印2份考试成绩通知单,自己保留一份,机考中心保留一份。
7.机考中心会在考试结束后上传考试成绩,72小时内成绩会上传到考生的MYACCA成绩记录中。
知道了ACCA考试流程,九月份的ACCA机考你是不是有点把握了,同时你的成绩在72小时就能出来,你也不会像等CFA成绩那么长时间哦。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) (i) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended
30 September 2005 should be submitted, and advise the company of the penalties that will be due if
the return is not submitted until 31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(ii) State the date by which Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005
should be paid, and advise the company of the interest that will be due if the liability is not paid until
31 May 2007. (3 marks)
(c) Self-assessment tax return
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s self-assessment corporation tax return for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be submitted by
30 September 2006.
(2) If the company does not submit its self-assessment tax return until 31 May 2007, then there will be an automatic fixed
penalty of £200 since the return is more than three months late.
(3) There will also be an additional corporation tax related penalty of £4,415 (44,150 × 10%) being 10% of the tax unpaid,
since the self-assessment tax return is more than six months late.
Corporation tax liability
(1) Thai Curry Ltd’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005 must be paid by 1 July 2006.
(2) If the company does not pay its corporation tax until 31 May 2007, then interest of £3,035 (44,150 at 7·5% = 3,311
× 11/12) will be charged by HM Revenue & Customs for the period 1 July 2006 to 31 May 2007.
6 Sergio and Gerard each inherited a half interest in a property, ‘Hilltop’, in October 2005. ‘Hilltop’ had a probate value
of £124,000, but in November 2005 it was badly damaged by fire. In January 2006 the insurance company made
a payment of £81,700 each to Sergio and Gerard. In February 2006 Sergio and Gerard each spent £55,500 of the
insurance proceeds on restoring the property. ‘Hilltop’ was worth £269,000 following the restoration work. In July
2006, Sergio and Gerard sold ‘Hilltop’ for £310,000.
Sergio is 69 years old and a widower with three adult children and seven grandchildren. His annual income consists
of a pension of £9,900 and interest of £300 on savings of £7,600 in a bank deposit account. Sergio owns his home
but no other significant assets. He plans to buy a domestic rental property with the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’,
such that on his death he will have a significant asset which can be sold and divided between the members of his
family.
Gerard is 34 years old. He is employed by Fizz plc on a salary of £66,500 per year together with a performance
related bonus. Gerard estimates that he will receive a bonus in December 2007 of £4,500, in line with previous
years, and that his taxable benefits in the tax year 2007/08 will amount to £7,140. He also expects to receive
dividends from UK companies of £1,935 and bank interest of £648 in the tax year 2007/08. Gerard intends to set
up a personal pension plan in August 2007. He has not made any pension contributions in the past and proposes to
use part of the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’ to make the maximum possible tax allowable contribution.
Fizz plc has announced that it intends to replace the performance related bonus scheme with a share incentive plan,
also linked to performance, with effect from 6 April 2008. Gerard estimates that Fizz plc will award him free shares
worth £2,100 each year. He will also purchase partnership shares worth £700 each year and, as a result, will be
awarded matching shares (further free shares) worth £1,400.
Required:
(a) Calculate the chargeable gains arising on the receipt of the insurance proceeds in January 2006 and the sale
of ‘Hilltop’ in July 2006. You should assume that any elections necessary to minimise the gain on the receipt
of the insurance proceeds have been submitted. (4 marks)
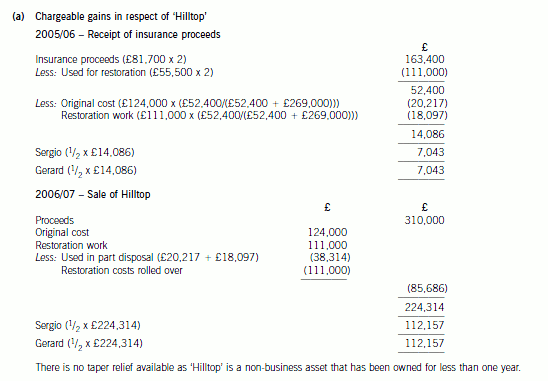
Discuss the principles and practices which should be used in the financial year to 30 November 2008 to account
for:(c) the purchase of handsets and the recognition of revenue from customers and dealers. (8 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
Handsets and revenue recognition
The inventory of handsets should be measured at the lower of cost and net realisable value (IAS2, ‘Inventories’, para 9). Johan
should recognise a provision at the point of purchase for the handsets to be sold at a loss. The inventory should be written down
to its net realisable value (NRV) of $149 per handset as they are sold both to prepaid customers and dealers. The NRV is $51
less than cost. Net realisable value is the estimated selling price in the normal course of business less the estimated selling costs.
IAS18, ‘Revenue’, requires the recognition of revenue by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the reporting
date. Revenue associated with the provision of services should be recognised as service as rendered. Johan should record the
receipt of $21 per call card as deferred revenue at the point of sale. Revenue of $18 should be recognised over the six month
period from the date of sale. The unused call credit of $3 would be recognised when the card expires as that is the point at which
the obligation of Johan ceases. Revenue is earned from the provision of services and not from the physical sale of the card.
IAS18 does not deal in detail with agency arrangements but says the gross inflows of economic benefits include amounts collected
on behalf of the principal and which do not result in increases in equity for the entity. The amounts collected on behalf of the
principal are not revenue. Revenue is the amount of the ‘commission’. Additionally where there are two or more transactions, they
should be taken together if the commercial effect cannot be understood without reference to the series of transactions as a whole.
As a result of the above, Johan should not recognise revenue when the handset is sold to the dealer, as the dealer is acting as an
agent for the sale of the handset and the service contract. Johan has retained the risk of the loss in value of the handset as they
can be returned by the dealer and the price set for the handset is under the control of Johan. The handset sale and the provision
of the service would have to be assessed as to their separability. However, the handset cannot be sold separately and is
commercially linked to the provision of the service. Johan would, therefore, recognise the net payment of $130 as a customer
acquisition cost which may qualify as an intangible asset under IAS38, and the revenue from the service contract will be recognised
as the service is rendered. The intangible asset would be amortised over the 12 month contract. The cost of the handset from the
manufacturer will be charged as cost of goods sold ($200).
1 The Great Western Cake Company (GWCC) is a well-established manufacturer of specialist flour confectionery
products, including cakes. GWCC sells its products to national supermarket chains. The company’s success during
recent years is largely attributable to its ability to develop innovative products which appeal to the food selectors within
national supermarket chains.
The marketing department of Superstores plc, a national supermarket chain has asked GWCC to manufacture a cake
known as the ‘Mighty Ben’. Mighty Ben is a character who has recently appeared in a film which was broadcast
around the world. The cake is expected to have a minimum market life of one year although the marketing department
consider that this might extend to eighteen months.
The management accountant of GWCC has collated the following estimated information in respect of the Mighty Ben
cake:
(1) Superstores plc has decided on a launch price of £20·25 for the Mighty Ben cake and it is expected that this
price will be maintained for the duration of the product’s life. Superstores plc will apply a 35% mark-up on the
purchase price of each cake from GWCC.
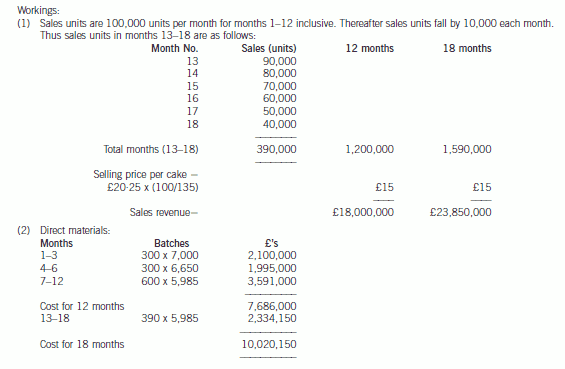
(2) Sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to be 100,000 units per month during the first twelve months.
Thereafter sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to decrease by 10,000 units in each subsequent month.
(3) Due to the relatively short shelf-life of the Mighty Ben cake, management has decided to manufacture the cakes
on a ‘just-in-time’ basis for delivery in accordance with agreed schedules. The cakes will be manufactured in
batches of 1,000. Direct materials input into the baking process will cost £7,000 per batch for each of the first
three months’ production. The material cost of the next three months’ production is expected to be 95% of the
cost of the first three months’ production. All batches manufactured thereafter will cost 90% of the cost of the
second three months’ production.
(4) Packaging costs will amount to £0·75 per cake. The original costs of the artwork and design of the packaging
will amount to £24,000. Superstores plc will reimburse GWCC £8,000 in the event that the product is
withdrawn from sale after twelve months.
(5) The design of the Mighty Ben cake is such that it is required to be hand-finished. A 75% learning curve will
apply to the total labour time requirement until the end of month five. Thereafter a steady state will apply with
labour time required per batch stabilising at that of the final batch in month five. The labour requirement for the
first batch of Mighty Ben cakes to be manufactured is expected to be 6,000 hours at £10 per hour.
(6) A royalty of 5% of sales revenue (subject to a maximum royalty of £1·1 million) will be payable by GWCC to the
owners of the Mighty Ben copyright.
(7) Variable overheads are estimated at £3·50 per direct labour hour.
(8) The manufacture of the Mighty Ben cake will increase fixed overheads by £75,000 per month.
(9) In order to provide a production facility dedicated to the Mighty Ben cake, an investment of £1,900,000 will be
required and this will be fully depreciated over twelve months.
(10) The directors of GWCC require an average annual return of 35% on their investment over 12 months and
18 months.
(11) Ignore taxation and the present value of cash flows.
Note: Learning curve formula:
y = axb
where y = average cost per batch
a = the cost of the initial batch
x = the total number of batches
b = learning index (= –0·415 for 75% learning rate)
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed calculations to show whether the manufacture of Mighty Ben cakes will provide the required
rate of return for GWCC over periods of twelve months and eighteen months. (20 marks)


声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-20
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-02-15
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-20
- 2019-01-09
- 2020-01-10