ACCA还是USCPA?你pick哪一个
发布时间:2019-01-09
考证,提高自身实力,成了很多人谋求升职加薪的最佳选择。越来越多的国内企业谋求在海外上市融资,通晓国际财会准则的人才往往供不应求。可国际财会证书何其多,就拿ACCA和USCPA来说,有限的时间精力,到底应该先考哪张,往往让人伤透了脑筋。
USCPA:即美国注册会计师,是美国唯一正式的注册会计师国家资格。由全球最大的会计师协会——美国注册会计师协会颁发认证。堪称「八国通行证」,可换全球八个国家和地区的会计师资格认证,在国际上适用范围很广。
ACCA:在国内被称为「国际注册会计师」,在全球范围内获高度认可。ACCA全称英国特许公认会计师公会,该机构已有百年的历史,是当今国际上领先的专业会计师团体。在所有会计师组织中,ACCA也是学员最多,规模发展最快的。

美国CPA考试一年按照四个季度分为四个考试窗口(Test window)全年开放考试,其中3、6、9、12月只有前十天可以参加考试(2017年6月份不能考试)。考试内容分为4个部分,分别是:Auditing & Attestation(AUD)审计、 Financial Accounting & Reporting(FAR)财务会计与报告、Regulation(REG)法规、 Business Environment & Concepts(BEC)商业环境。
USCPA考试是机考,除了BEC有写作外,其他都是单选题,对于英语基础不好的考生来说相对便利。唯一的短板是,必须到美国的领土或属地,亚洲考生多数选择在关岛或夏威夷参加考试。
会计师事务所也很喜欢USCPA人才,尤其是在处理外企财务报告和审计外资资产的时候,想要赴美上市的企业,少不了USCPA人才的帮助。内部审计师、法规遵从经理、财务分析师、外部审计师、金融业务高级会计都是USCPA最好的职业方向。

ACCA考试有16个科目,共分3各阶段,全程学习可以获得3份不同等级的资格证书。每年考试4次,3、6、9、12月都有ACCA的考试。
基础知识阶段,主要涉及会计原理等基础内容,分别是:会计师与企业(F1)、管理会计(F2)、财务会计(F3)。
技能阶段,涉及财会人员应具备的核心专业技能,分别是:公司法与商法(F4)、业绩管理(F5)、税务(F6)、财务报告(F7)、审计与认证业务(F8)、财务管理(F9)。
专业阶段涉及企业战略管理中财务人员的实际工作技能,其中P4到P7通过其中任意两个科目即可,分别是:公司治理、风险管理与职业道德(P1)、公司报告(P2)、商务分析(P3)、高级财务管理(P4)、高级业绩管理(P5)、高级税务(P6)、高级审计与认证业务(P7)。
拥有ACCA人才最多的地方是会计师事务所,传统的四大会计师事务所,以及内资所都很喜欢招聘ACCA持证人。随着市场融合和业务开放,金融机构和企业也开始招揽ACCA人才,财务经理、税务经理、与基金有关的高级会计、企业估值分析、资产管理等岗位上出现了很多ACCA持证人。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Comment on the need for ethical guidance for accountants on money laundering. (4 marks)
(b) Need for ethical guidance
■ Accountants (firms and individuals) working in a country that criminalises money laundering are required to comply with
anti-money laundering legislation and failure to do so can lead to severe penalties. Guidance is needed because:
– legal requirements are onerous;
– money laundering is widely defined; and
– accountants may otherwise be used, unwittingly, to launder criminal funds.
■ Accountants need ethical guidance on matters where there is conflict between legal responsibilities and professional
responsibilities. In particular, professional accountants are bound by a duty of confidentiality to their clients. Guidance
is needed to explain:
– how statutory provisions give protection against criminal action for members in respect of their confidentiality
requirements;
– when client confidentiality over-ride provisions are available.
■ Further guidance is needed to explain the interaction between accountants’ responsibilities to report money laundering
offences and other reporting responsibilities, for example:
– reporting to regulators;
– auditor’s reports on financial statements (ISA 700);
– reports to those charged with governance (ISA 260);
– reporting misconduct by members of the same body.
■ Professional accountants are required to communicate with each other when there is a change in professional
appointment (i.e. ‘professional etiquette’). Additional ethical guidance is needed on how to respond to a ‘clearance’ letter
where a report of suspicion has been made (or is being contemplated) in respect of the client in question.
Tutorial note: Although the term ‘professional clearance’ is widely used, remember that there is no ‘clearance’ that the
incumbent accountant can give or withhold.
■ Ethical guidance is needed to make accountants working in countries that do not criminalise money laundering aware
of how anti-money laundering legislation may nevertheless affect them. Such accountants may commit an offence if,
for example, they conduct limited assignments or have meetings in a country having anti-money laundering legislation
(e.g. UK, Ireland, Singapore, Australia and the United States).
3 Fran?ois, Demetris, José and Giuseppe are a group of students from different Mediterranean countries, taking their
MBA in a large UK city. As part of their course requirements, the group has to come up with an innovative business
idea, research into the feasibility of that idea and then present their business plan to a panel. After considerable
brainstorming they have come up with the idea of a themed restaurant based around Mediterranean cooking, menus
and service provisionally called ‘Casa del Mediterraneo’ and located in the city centre.
Initial research has revealed suitable premises to rent, but also the severe competition they will face in a city that is
very cosmopolitan and well provided for with restaurants serving cuisine from many parts of the world. The city has
a student population of around 100,000 and this, together with a young working population, means that there is a
very vibrant social life and a real willingness to sample food from different parts of the world.
Required:
(a) Identify and evaluate the critical success factors and associated competences that the group should consider
in developing their business plan for the restaurant. (12 marks)
(a) New ventures are notoriously risky and it is vital that the group has a clear idea of the factors that will be critical to the
restaurant’s success and the capabilities and competences needed to achieve their critical success factors. Johnson, Scholes
and Whittington define critical success factors as ‘those product (or service) features that are particularly valued by a group
of customers, and, therefore where the organisation must excel to outperform. the competition’. The group have chosen to
enter a highly competitive market and one where it is very difficult to create a distinctive product or service for the customer.
It is important in establishing what factors are important that they know the features their potential customers will particularly
value in the restaurant business. All too often firms design products or services on the basis of what the ‘expert’ inside the
company thinks the customer wants. One of the major problems in setting up a new restaurant is that customers can easily
compare one restaurant with another. Often they are in close proximity making all aspects of the service, particularly price,
easily open to customer evaluation.
Clearly, service will be a critical factor but precisely how will it be defined? Does the customer look for fast food service with
an emphasis on being served quickly? This seems unlikely and a more likely requirement is that the table service replicates
the friendly ambience experienced at restaurants on the Mediterranean. Many of their customers will have experienced this
first-hand and this would reinforce the Mediterranean theme. To deliver this service the waiters/waitresses will need
appropriate training. The menu and quality of food will be key factors – they lie at the heart of the reason for setting up the
business. How is distinctiveness to be achieved? The quality of the chef and kitchen staff will determine the quality of the
food served. The design of the restaurant and its layout and seating are also features, which it is important to get right. Aboveall, there is the need to create a price/value combination that is difficult for competitors to beat.
The critical success factors will stem from using the restaurant’s resources in a distinctive way. In Hamel and Prahalad’s
terms, there are three tests that can identify core competences in a company. Firstly, the core competence has the potential
for transfer across a variety of markets – less likely in a small business. Secondly, a core competence should make a significant
contribution to the perceived customer benefits of the end product or service. Finally, the core competence will be difficult for
a competitor to imitate. In service businesses such as restaurants, imitation of less tangible factors such as the quality of tableservice may be much more difficult to copy than the features designed into a tangible product.
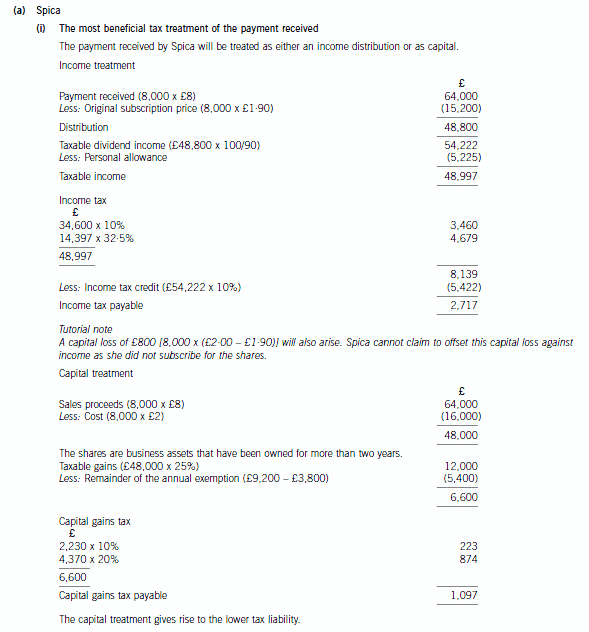
3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-02-18
- 2019-12-06
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-01
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-03-03
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2021-05-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-03
- 2019-01-09
- 2020-03-05