好消息来啦!四川省工薪阶层想要报考2020年ACCA考试的,你需要知道这些
发布时间:2020-01-09
随着ACCA考试逐年火爆起来,步入2020年预计报考的人数将会更多。近期不少准备报考ACCA考试的小伙伴听闻ACCA考试收费比较高,而打起了退堂鼓,51题库考试学习网有一个好消息想要告诉大家,当大家满足一些条件之后,有一些科目是可以免考的哟,同时也想告诉大家收获和付出是成正比的,尽管ACCA考试相比较其他考试而言收费偏高,但当你拿到证书的那一刻你就会明白自己的付出是值得的,那份喜悦是多少钱都买不来的。接下来,51题库考试学习网为大家讲解一下许多ACCAer关心的收费问题,建议收藏起来哦~
首先,考试收费的金额是不固定的,是根据科目、报考时间的不同,换句话来说越早报名所需要的费用也就越少,ACCA报考一门考试科目的费用从114英镑~350英镑不等,具体取决于你所报考的科目是什么,以及报考的时间是早期、中期还是晚期报名。
一般ACCA考下来的费用1-2万。ACCA考试费用约为:79+105+(AB-LW费用)+114*5(PM-FM)+188(SBL)+147*3(SBR+2门选修课)=1383+(AB-LW费用,费用是每科70-80英镑),这样下来,你所缴纳的ACCA官方报名费用约在人民币一万四到两万左右。有些同学有免考科目,但是温馨提示一下,虽然是免考,但仍然需要缴纳考试科目的费用的,因此建议大家可以在报名早期的时候缴纳就可以少支出一些费用了,因此,也算是变相的节约了教材费和培训费

注意:
ACCA学员可使用双币信用卡(支持人民币及英镑结算)或者支付宝完成费用支付,如果使用汇票方式交纳考试费用,您需等待收到总部的纸质考试报名表,填写完整的考试报名表及办理汇票后一起邮寄到英国进行考试报名。使用汇票进行考试报名只能申请常规时段的考试报名。
ACCA首次注册(或重新注册)费用:79英镑
ACCA年费:105英镑
ACCA免考费用:F阶段76英镑/科、P阶段103英镑/科
以上的这些信息希望对萌新们有所帮助,51题库考试学习网在这里真诚地告诉大家:“人生终有许多选择。每一步都要慎重。但是一次选择不能决定一切。不要犹豫,作出选择就不要后悔。只要我们能不屈不挠地奋斗,胜利就在前方。”ACCAer们,共勉~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
6 An important part of managing people in a professional organisation is to be able to distinguish between aggressiveness and assertiveness in an employee.
Required:
(a) Explain and give examples of aggressive behaviour. (8 marks)
6 To get the best out of people, managers need to have effective communication skills. Professional accountants as managers need to understand the difference between aggressive and assertive behaviour. Often an exchange of communication can be interpreted as a belligerent response from an employee. However, a slight difference in approach can communicate different feelings and achieve a more positive result.
(a) Aggressive behaviour is competitive and directed at defeating someone else. It is standing up for oneself at the expense of other people. It is defending one’s rights but doing so in such a way that violates the rights of other people. Aggressive behaviour ignores or dismisses the needs, wants, opinions, feelings or beliefs of others.
Characteristics of aggressive behaviour include excessive ‘I’ statements, boastfulness, and the individual’s opinions expressed as fact, threatening questions or postures from the individual, sarcasm and other throw-away remarks and a constant blaming of others.
Aggressive behaviour can be self defeating. It may cause such antagonism in the others in the organisation that they will refuse to co-operate or work with the person showing aggressive behaviour.
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
(a) Cate is an entity in the software industry. Cate had incurred substantial losses in the fi nancial years 31 May 2004 to 31 May 2009. In the fi nancial year to 31 May 2010 Cate made a small profi t before tax. This included signifi cant non-operating gains. In 2009, Cate recognised a material deferred tax asset in respect of carried forward losses, which will expire during 2012. Cate again recognised the deferred tax asset in 2010 on the basis of anticipated performance in the years from 2010 to 2012, based on budgets prepared in 2010. The budgets included high growth rates in profi tability. Cate argued that the budgets were realistic as there were positive indications from customers about future orders. Cate also had plans to expand sales to new markets and to sell new products whose development would be completed soon. Cate was taking measures to increase sales, implementing new programs to improve both productivity and profi tability. Deferred tax assets less deferred tax liabilities represent 25% of shareholders’ equity at 31 May 2010. There are no tax planning opportunities available to Cate that would create taxable profi t in the near future. (5 marks)
(b) At 31 May 2010 Cate held an investment in and had a signifi cant infl uence over Bates, a public limited company. Cate had carried out an impairment test in respect of its investment in accordance with the procedures prescribed in IAS 36, Impairment of assets. Cate argued that fair value was the only measure applicable in this case as value-in-use was not determinable as cash fl ow estimates had not been produced. Cate stated that there were no plans to dispose of the shareholding and hence there was no binding sale agreement. Cate also stated that the quoted share price was not an appropriate measure when considering the fair value of Cate’s signifi cant infl uence on Bates. Therefore, Cate estimated the fair value of its interest in Bates through application of two measurement techniques; one based on earnings multiples and the other based on an option–pricing model. Neither of these methods supported the existence of an impairment loss as of 31 May 2010. (5 marks)
(c) At 1 April 2009 Cate had a direct holding of shares giving 70% of the voting rights in Date. In May 2010, Date issued new shares, which were wholly subscribed for by a new investor. After the increase in capital, Cate retained an interest of 35% of the voting rights in its former subsidiary Date. At the same time, the shareholders of Date signed an agreement providing new governance rules for Date. Based on this new agreement, Cate was no longer to be represented on Date’s board or participate in its management. As a consequence Cate considered that its decision not to subscribe to the issue of new shares was equivalent to a decision to disinvest in Date. Cate argued that the decision not to invest clearly showed its new intention not to recover the investment in Date principally through continuing use of the asset and was considering selling the investment. Due to the fact that Date is a separate line of business (with separate cash fl ows, management and customers), Cate considered that the results of Date for the period to 31 May 2010 should be presented based on principles provided by IFRS 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations. (8 marks)
(d) In its 2010 fi nancial statements, Cate disclosed the existence of a voluntary fund established in order to provide a post-retirement benefi t plan (Plan) to employees. Cate considers its contributions to the Plan to be voluntary, and has not recorded any related liability in its consolidated fi nancial statements. Cate has a history of paying benefi ts to its former employees, even increasing them to keep pace with infl ation since the commencement of the Plan. The main characteristics of the Plan are as follows:
(i) the Plan is totally funded by Cate;
(ii) the contributions for the Plan are made periodically;
(iii) the post retirement benefi t is calculated based on a percentage of the fi nal salaries of Plan participants dependent on the years of service;
(iv) the annual contributions to the Plan are determined as a function of the fair value of the assets less the liability arising from past services.
Cate argues that it should not have to recognise the Plan because, according to the underlying contract, it can terminate its contributions to the Plan, if and when it wishes. The termination clauses of the contract establish that Cate must immediately purchase lifetime annuities from an insurance company for all the retired employees who are already receiving benefi t when the termination of the contribution is communicated. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss whether the accounting treatments proposed by the company are acceptable under International Financial Reporting Standards.
Professional marks will be awarded in this question for clarity and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
The mark allocation is shown against each of the four parts above.
(a) Deferred taxation
A deferred tax asset should be recognised for deductible temporary differences, unused tax losses and unused tax credits to the extent that it is probable that taxable profi t will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilised. The recognition of deferred tax assets on losses carried forward does not seem to be in accordance with IAS 12 Income Taxes. Cate is not able to provide convincing evidence that suffi cient taxable profi ts will be generated against which the unused tax losses can be offset. According to IAS 12 the existence of unused tax losses is strong evidence that future taxable profi t may not be available against which to offset the losses. Therefore when an entity has a history of recent losses, the entity recognises deferred tax assets arising from unused tax losses only to the extent that the entity has suffi cient taxable temporary differences or there is convincing other evidence that suffi cient taxable profi t will be available. As Cate has a history of recent losses and as it does not have suffi cient taxable temporary differences, Cate needs to provide convincing other evidence that suffi cient taxable profi t would be available against which the unused tax losses could be offset. The unused tax losses in question did not result from identifi able causes, which were unlikely to recur (IAS 12) as the losses are due to ordinary business activities. Additionally there are no tax planning opportunities available to Cate that would create taxable profi t in the period in which the unused tax losses could be offset (IAS 12).
Thus at 31 May 2010 it is unlikely that the entity would generate taxable profi ts before the unused tax losses expired. The improved performance in 2010 would not be indicative of future good performance as Cate would have suffered a net loss before tax had it not been for the non-operating gains.
Cate’s anticipation of improved future trading could not alone be regarded as meeting the requirement for strong evidence of future profi ts. When assessing the use of carry-forward tax losses, weight should be given to revenues from existing orders or confi rmed contracts rather than those that are merely expected from improved trading. Estimates of future taxable profi ts can rarely be objectively verifi ed. Thus the recognition of deferred tax assets on losses carried forward is not in accordance with IAS 12 as Cate is not able to provide convincing evidence that suffi cient taxable profi ts would be generated against which the unused tax losses could be offset.
(b) Investment
Cate’s position for an investment where the investor has signifi cant infl uence and its method of calculating fair value can be challenged.
An asset’s recoverable amount represents its greatest value to the business in terms of its cash fl ows that it can generate i.e. the higher of fair value less costs to sell (which is what the asset can be sold for less direct selling expenses) and value in use (the cash fl ows that are expected to be generated from its continued use including those from its ultimate disposal). The asset’s recoverable amount is compared with its carrying value to indicate any impairment. Both net selling price (NSP) and value in use can be diffi cult to determine. However it is not always necessary to calculate both measures, as if the NSP or value in use is greater than the carrying amount, there is no need to estimate the other amount.
It should be possible in this case to calculate a fi gure for the recoverable amount. Cate’s view that market price cannot refl ect the fair value of signifi cant holdings of equity such as an investment in an associate is incorrect as IAS 36 prescribes the method of conducting the impairment test in such circumstances by stating that if there is no binding sale agreement but an asset is traded in an active market, fair value less costs to sell is the asset’s market price less the costs of disposal. Further, the appropriate market price is usually the current bid price.
Additionally the compliance with IAS 28, Investments in associates is in doubt in terms of the non-applicability of value in use when considering impairment. IAS 28 explains that in determining the value in use of the investments, an entity estimates:
(i) its share of the present value of the estimated future cash fl ows expected to be generated by the associate, including the cash fl ows from the operations of the associate and the proceeds on the ultimate disposal of the investment; or
(ii) the present value of the estimated future cash fl ows expected to arise from dividends to be received from the investment and from its ultimate disposal.
Estimates of future cash fl ows should be produced. These cash fl ows are then discounted to present value hence giving value in use.
It seems as though Cate wishes to avoid an impairment charge on the investment.
(c) Disposal group ‘held for sale’
IAS 27 Revised Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements moved IFRS to the use of the economic entity model. The economic entity approach treats all providers of equity capital as shareholders of the entity, even when they are not shareholders in the parent company. IFRS 5 has been amended such that if there is an intention to dispose of a controlling interest in a subsidiary which meets the defi nition of ‘held for sale’, then the net assets are classifi ed as ‘held for sale’, irrespective of whether the parent was expected to retain an interest after the disposal. A partial disposal of an interest in a subsidiary in which the parent company loses control but retains an interest as an associate or trade investment creates the recognition of a gain or loss on the entire interest. A gain or loss is recognised on the part that has been disposed of and a further holding gain or loss is recognised on the interest retained, being the difference between the fair value of the interest and the book value of the interest. The gains are recognised in the statement of comprehensive income. Any prior gains or loss recognised in other components of equity would now become realised in the statement of comprehensive income.
In this case, Cate should stop consolidating Date on a line-by-line basis from the date that control was lost. Further investigation is required into whether the holding is treated as an associate or trade investment. The agreement that Cate is no longer represented on the board or able to participate in management would suggest loss of signifi cant infl uence despite the 35% of voting rights retained. The retained interest would be recognised at fair value.
An entity classifi es a disposal group as held for sale if its carrying amount will be recovered mainly through selling the asset rather than through usage and intends to dispose of it in a single transaction.
The conditions for a non-current asset or disposal group to be classifi ed as held for sale are as follows:
(i) The assets must be available for immediate sale in their present condition and its sale must be highly probable.
(ii) The asset must be currently marketed actively at a price that is reasonable in relational to its current fair value.
(iii) The sale should be completed or expected to be so, within a year from the date of the classifi cation.
(iv) The actions required to complete the planned sale will have been made and it is unlikely that the plan will be signifi cantly changed or withdrawn.
(v) management is committed to a plan to sell.
Cate has not met all of the conditions of IFRS 5 but it could be argued that the best presentation in the fi nancial statements was that set out in IFRS 5 for the following reasons.
The issue of dilution is not addressed by IFRS and the decision not to subscribe to the issue of new shares of Date is clearly a change in the strategy of Cate. Further, by deciding not to subscribe to the issue of new shares of Date, Cate agreed to the dilution and the loss of control which could be argued is similar to a decision to sell shares while retaining a continuing interest in the entity. Also Date represents a separate line of business, which is a determining factor in IFRS 5, and information disclosed on IFRS 5 principles highlights the impact of Date on Cate’s fi nancial statements. Finally, the agreement between Date’s shareholders confi rms that Cate has lost control over its former subsidiary.
Therefore, in the absence of a specifi c Standard or Interpretation applying to this situation, IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates and errors states that management should use its judgment and refer to other IFRS and the Framework.
Thus considering the requirements of IAS 27 (Para 32–37) and the above discussion, it could be concluded that the presentation based on IFRS 5 principles selected by the issuer was consistent with the accounting treatment required by IAS 27 when a parent company loses control of a subsidiary.
(d) Defi ned benefi t plan
The Plan is not a defi ned contribution plan because Cate has a legal or constructive obligation to pay further contributions if the fund does not have suffi cient assets to pay all employee benefi ts relating to employee service in the current and prior periods (IAS 19 Para 7). All other post-employment benefi t plans that do not qualify as a defi ned contribution plan are, by defi nition therefore defi ned benefi t plans. Defi ned benefi t plans may be unfunded, or they may be wholly or partly funded. Also IAS 19 (Para 26) indicates that Cate’s plan is a defi ned benefi t plan as IAS 19 provides examples where an entity’s obligation is not limited to the amount that it agrees to contribute to the fund. These examples include: (a) a plan benefi t formula that is not linked solely to the amount of contributions (which is the case in this instance); and (b) those informal practices that give rise to a constructive obligation. According to the terms of the Plan, if Cate opts to terminate, Cate is responsible for discharging the liability created by the plan. IAS 19 (Para 52) says that an entity should account not only for its legal obligation under the formal terms of a defi ned benefi t plan, but also for any constructive obligation that arises from the enterprise’s informal practices. Informal practices give rise to a constructive obligation where the enterprise has no realistic alternative but to pay employee benefi ts. Even if the Plan were not considered to be a defi ned benefi t plan under IAS 19, Cate would have a constructive obligation to provide the benefi t, having a history of paying benefi ts. The practice has created a valid expectation on the part of employees that the amounts will be paid in the future. Therefore Cate should account for the Plan as a defi ned benefi t plan in accordance with IAS 19. Cate has to recognise, at a minimum, its net present liability for the benefi ts to be paid under the Plan.
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
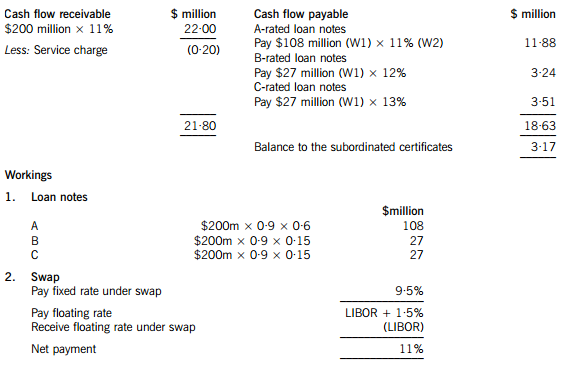
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-03-08
- 2019-08-01
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-08
- 2021-05-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-11
- 2021-05-14
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-02-15
- 2021-06-27
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-28