重庆市考生:2020年ACCA国际会计师考试时间是如何安排的?
发布时间:2020-01-10
众所周知,想要获得ACCA证书代价是十分巨大的,不仅仅要花费昂贵的报名费用,而且因为考试科目多的原因还需要大把大把的时间和精力去学习和理解知识点。尤其是对在职人员来说,更是一大挑战者,因此许多考生都因此望尘莫及,目前,ACCA国际会计师注册考试的报名时间和考试时间都依次发布了,51题库考试学习网替大家收集到了今年全部的考试报名时间信息和考试时间信息,希望对大家在了解到考试时间之后,能够合理地科学地备考考试。
首先是2020年ACCA考试报名时间:(建议收藏哦~)

了解完报名时间后,大家可以根据自己的学习能力和时间因素等情况依次可以开始备考了哟(学习能力强的考生可以优先从真题开始做起)
接下来,在认真复习、科学备考的同时,千万不要忘记了考试时间,所以这份是2020年ACCA考试时间表建议大家保存在相册里:


险夷原不滞胸中,何异浮云过太空!以上消息希望对正在准备备战3月份的ACCAer们有所帮助,51题库考试学习网预祝大家考试成功!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 Airtite was set up in 2000 as a low cost airline operating from a number of regional airports in Europe. Using these
less popular airports was a much cheaper alternative to the major city airports and supported Airtite’s low cost service,
modelled on existing low cost competitors. These providers had effectively transformed air travel in Europe and, in so
doing, contributed to an unparalleled expansion in airline travel by both business and leisure passengers. Airtite used
one type of aircraft, tightly controlled staffing levels and costs, relied entirely on online bookings and achieved high
levels of capacity utilisation and punctuality. Its route network had grown each year and included new routes to some
of the 15 countries that had joined the EU in 2004. Airtite’s founder and Chief Executive, John Sykes, was an
aggressive businessman ever willing to challenge governments and competitors wherever they impeded his airline and
looking to generate positive publicity whenever possible.
John is now looking to develop a strategy which will secure Airtite’s growth and development over the next 10 years.
He can see a number of environmental trends emerging which could significantly affect the success or otherwise of
any developed strategy. 2006 had seen fuel costs continue to rise reflecting the continuing uncertainty over global
fuel supplies. Fuel costs currently account for 25% of Airtite’s operating costs. Conversely, the improving efficiency of
aircraft engines and the next generation of larger aircraft are increasing the operating efficiency of newer aircraft and
reducing harmful emissions. Concern with fuel also extends to pollution effects on global warming and climate
change. Co-ordinated global action on aircraft emissions cannot be ruled out, either in the form. of higher taxes on
pollution or limits on the growth in air travel. On the positive side European governments are anxious to continue to
support increased competition in air travel and to encourage low cost operators competing against the over-staffed
and loss-making national flag carriers.
The signals for future passenger demand are also confused. Much of the increased demand for low cost air travel to
date has come from increased leisure travel by families and retired people. However families are predicted to become
smaller and the population increasingly aged. In addition there are concerns over the ability of countries to support
the increasing number of one-parent families with limited incomes and an ageing population dependent on state
pensions. There is a distinct possibility of the retirement age being increased and governments demanding a higher
level of personal contribution towards an individual’s retirement pension. Such a change will have a significant impact
on an individual’s disposable income and with people working longer reduce the numbers able to enjoy leisure travel.
Finally, air travel will continue to reflect global economic activity and associated economic booms and slumps together
with global political instability in the shape of wars, terrorism and natural disasters.
John is uncertain as to how to take account of these conflicting trends in the development of Airtite’s 10-year strategy
and has asked for your advice.
Required:
(a) Using models where appropriate, provide John with an environmental analysis of the conditions affecting the
low cost air travel industry. (12 marks)
(a) Environmental Analysis
Clearly, both the macro-environment and the industry environment facing Airtite are becoming more challenging and scanning
the environment and understanding the relative significance of the challenges is a key step in developing a future strategy to
deal with it. Many models and tools and techniques are available to assess the size of the competitive threats facing Airtite.
One of the earlier scanning models looks to measure whether the environment an organisation faces is becoming more
complex and more dynamic. Evidence from the scenario suggests both are occurring and this means it is becoming
increasingly difficult to predict the future nature of competition from what has happened in the past. Airtite’s future is linked
to an increasingly global environment and many conflicting and contradictory factors require the company to develop a
process through which these factors are considered on a regular and systematic basis.
Johnson and Scholes suggest there are five steps in terms of environmental analysis:
Step 1 Audit of environmental influences
Step 2 Assessment of the nature of the environment
Step 3 Identification of the key environmental forces
Step 4 Identification of competitive position
Step 5 Identification of the principal opportunities and threats
Systematic consideration of each of these steps leads to an understanding of the strategic position of the firm.
A PESTEL analysis is part of the process of environmental appraisal and it is important for John to recognise those parts of
its environment it can influence. All too often firms can regard themselves as ‘victims’ of the chosen environment, failing to
recognise that through their strategic decisions they can profoundly change the competitive environment for their current or
potential competitors. A good PESTEL analysis inevitably links into an informed SWOT analysis. In both instances it is
necessary to isolate the key forces causing environmental change – simply creating a long list of factors may simply convince
you of your inability to change the situation.
Once having decided which are the critical factors, it is then necessary to decide on the likelihood of a particular
environmental change occurring and the significance of its impact on the firm. Matching the competitive capability of the firm
against the attractiveness of the business sector Airtite is operating in will provide an understanding of the firm’s competitive
position and the options open to it. Many other models and tools and techniques are available, including Porter’s five forces,product life cycle analysis and scenario building to generate alternative strategic responses.
(ii) Comment briefly on how divisional managers might respond to the results achieved and ONE potential
problem that might be experienced by Our Timbers Ltd. (2 marks)
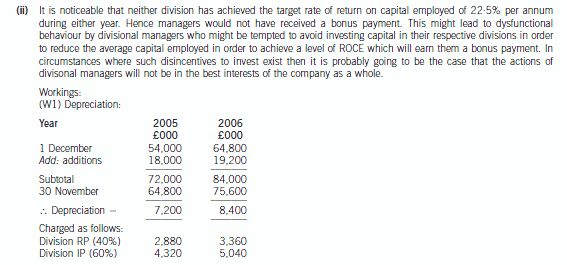
(b) Write a letter to Joanne setting out the value added tax (VAT) registration requirements and advising on
whether or not she should or could register for VAT and if registered if she could recover the VAT suffered on
the consultancy fees and computer purchased in October 2005. (7 marks)
(b) [Joanne’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Joanne 5 February 2006
I am writing to you in order to set out the value added tax (VAT) issues you face on registering your trade, together with some
other aspects of VAT that are relevant to you.
Registration
VAT registration is compulsory once taxable supplies exceed £58,000. This turnover figure is based on the value of your
cumulative taxable supplies in the previous 12 months. You have an obligation to inform. Customs within 30 days of the end
of the month in which the annual limit is exceeded. Registration will become effective on the first day of the following month.
VAT registration is also required if there are reasonable grounds for believing that the taxable supplies in the following 30 days
will exceed £58,000. In such cases, notification is required by the end of that 30 day period with registration being effective
from the start of that period.
Based on your estimates of taxable supplies, you will exceed the annual limit in October 2006 when your cumulative turnover
will be £62,000. You will therefore have to inform. Customs by the end of November. Your registration will be effective as of
1 December 2006.
You also have the option of voluntarily registering prior to then in which case you will normally become registered from the
date you applied. This is useful where your sales are to VAT registered customers for whom the extra VAT would not be a cost.
You would then be able to recover VAT on your attributable costs. However, you will have to comply with the VAT
administrative requirements.
Recovery of pre-registration VAT
It is possible to claim the recovery of VAT incurred prior to registering for VAT. There are some conditions, however. The costs
of the goods or services must have been incurred for the purpose of the business and there are time limits. You have three
years from the effective date of registration to recover the VAT on fixed assets (such as your computer) but only six months in
the case of purchased services (such as the consultancy fees).
As a result, I would recommend that you apply for voluntary registration as soon as possible, as registering after 1 April 2006
will mean that you will be unable to reclaim the VAT on your consultancy fees.
I hope the above information is useful to you.
Yours sincerely,
A. Consultant.
3 (a) Financial statements often contain material balances recognised at fair value. For auditors, this leads to additional
audit risk.
Required:
Discuss this statement. (7 marks)
3 Poppy Co
(a) Balances held at fair value are frequently recognised as material items in the statement of financial position. Sometimes it is
required by the financial reporting framework that the measurement of an asset or liability is at fair value, e.g. certain
categories of financial instruments, whereas it is sometimes the entity’s choice to measure an item using a fair value model
rather than a cost model, e.g. properties. It is certainly the case that many of these balances will be material, meaning that
the auditor must obtain sufficient appropriate evidence that the fair value measurement is in accordance with the
requirements of financial reporting standards. ISA 540 (Revised and Redrafted) Auditing Accounting Estimates Including Fair
Value Accounting Estimates and Related Disclosures and ISA 545 Auditing Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures
contain guidance in this area.
As part of the understanding of the entity and its environment, the auditor should gain an insight into balances that are stated
at fair value, and then assess the impact of this on the audit strategy. This will include an evaluation of the risk associated
with the balance(s) recognised at fair value.
Audit risk comprises three elements; each is discussed below in the context of whether material balances shown at fair value
will lead to increased risk for the auditor.
Inherent risk
Many measurements based on estimates, including fair value measurements, are inherently imprecise and subjective in
nature. The fair value assessment is likely to involve significant judgments, e.g. regarding market conditions, the timing of
cash flows, or the future intentions of the entity. In addition, there may be a deliberate attempt by management to manipulate
the fair value to achieve a desired aim within the financial statements, in other words to attempt some kind of window
dressing.
Many fair value estimation models are complicated, e.g. discounted cash flow techniques, or the actuarial calculations used
to determine the value of a pension fund. Any complicated calculations are relatively high risk, as difficult valuation techniques
are simply more likely to contain errors than simple valuation techniques. However, there will be some items shown at fair
value which have a low inherent risk, because the measurement of fair value may be relatively straightforward, e.g. assets
that are regularly bought and sold on open markets that provide readily available and reliable information on the market prices
at which actual exchanges occur.
In addition to the complexities discussed above, some fair value measurement techniques will contain significant
assumptions, e.g. the most appropriate discount factor to use, or judgments over the future use of an asset. Management
may not always have sufficient experience and knowledge in making these judgments.
Thus the auditor should approach some balances recognised at fair value as having a relatively high inherent risk, as their
subjective and complex nature means that the balance is prone to contain an error. However, the auditor should not just
assume that all fair value items contain high inherent risk – each balance recognised at fair value should be assessed for its
individual level of risk.
Control risk
The risk that the entity’s internal monitoring system fails to prevent and detect valuation errors needs to be assessed as part
of overall audit risk assessment. One problem is that the fair value assessment is likely to be performed once a year, outside
the normal accounting and management systems, especially where the valuation is performed by an external specialist.
Therefore, as a non-routine event, the assessment of fair value is likely not to have the same level of monitoring or controls
as a day-to-day business transaction.
However, due to the material impact of fair values on the statement of financial position, and in some circumstances on profit,
management may have made great effort to ensure that the assessment is highly monitored and controlled. It therefore could
be the case that there is extremely low control risk associated with the recognition of fair values.
Detection risk
The auditor should minimise detection risk via thorough planning and execution of audit procedures. The audit team may
lack experience in dealing with the fair value in question, and so would be unlikely to detect errors in the valuation techniques
used. Over-reliance on an external specialist could also lead to errors not being found.
Conclusion
It is true that the increasing recognition of items measured at fair value will in many cases cause the auditor to assess the
audit risk associated with the balance as high. However, it should not be assumed that every fair value item will be likely to
contain a material misstatement. The auditor must be careful to identify and respond to the level of risk for fair value items
on an individual basis to ensure that sufficient and appropriate evidence is gathered, thus reducing the audit risk to an
acceptable level.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-09-12
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-04-17
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-08-01
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-22