ACCA考试常用公式汇总,值得新疆考生收藏!
发布时间:2020-01-10
距离2020年3月份的ACCA考试还有两个多月左右的时间,想必备考ACCA的同学们正在如火如荼地进行着复习。那么,今天这条“公式宝典”你一定要收好,或许会帮助你成功通过ACCA考试哦!接下来,51题库考试学习网将这份“公式宝典”分享给大家:
因为ACCA考试毕竟是国际性质的考试,因此一些题的计算可能就存在不同的计算方式,计算方式的不同也会导致结果的不同。
一、境内
1、税额=销项税-进项税
2、销项税=销售额×税率
3、视销征税无销额(1)当月类平均;(2)近类货平均,(3)组税价=成本×(1+成利率)
4、征增税及消税:
组税价=成本×(1+成润率)+消税
组税价=成本×(1+成润率)/(1-消率)
5、含税额换
不含税销额=含税销额/1+率(一般)
不含税销额=含税销额/1+征率(小规模)
6、购农销农品,或向小纳人购农品:
准扣的进税=买价×扣率(13%)
7、一般纳人外购货物付的运费
准扣的进税=运费×扣除率
*随运付的装卸、保费不扣
8、小纳人纳额=销项额×征率(6%或4%)
*不扣进额
9、小纳人不含税销额=含额/(1+征率)
10、自来水公司销水(6%)
不含税销额=发票额×(1+征率)
以上是国内物品的计算方式,接下来是国外进口的相关公式
二、进口货
1、组税价=关税完价+关税+消税
2、纳额=组税价×税率
三、出口货物退(免)税
1、"免、抵、退"计算方法(指生产企自营委外贸代出口自产)
(1)纳额=内销销税-(进税-免抵退税不免、抵税)
(2)免抵退税=FOB×外汇RMB牌价×退率-免抵退税抵减额
*FOB:出口货物离岸价。
*免抵退税抵减额=免税购原料价×退税率
免税购原料=国内购免原料+进料加工免税进料
进料加工免税进口料件组税价=到岸价+关、消税
(3)应退税和免抵税
A、如期末留抵税≤免抵退税,则:
应退税=期末留抵税
免抵税=免抵退税-应退税
B、期末留抵税>免抵退税,则:
应退税=免抵退税
免抵税=0
*期末留抵税额据《增值税纳税申报表》中"期末留抵税额"定。
(4)免抵退税不得免和抵税
免抵退税不免和抵税=FOB×外汇RMB牌价×(出口征率-出口退率)-免抵退税不免抵税抵减额
免抵退税不免和抵扣税抵减额=免税进原料价×(出口征率-出口货物退率)
2、先征后退
(1)外贸及外贸制度工贸企购货出口,出口增税免;出口后按收购成本与退税率算退税还外贸,征、退税差计企业成本
应退税额=外贸购不含增税购进金额×退税率
(2)外贸企购小纳人出货口增税退税规定:
A、从小纳人购并持普通发票准退税的抽纱、工艺品等12类出口货物,销售出口货入免,退还出口货进税
退税=[发票列(含税)销额]/(1+征率)×6%或5%
B、从小纳人购代开的增税发票的出口货:
退税=增税发票金额×6%或5%
C、外企托生企加工出口货的退税规定:
原辅料退税=国内原辅料增税发票进项×原辅料退税率
以上这些就是全部ACCA考试常用公式,希望对大家有所帮助!最后51题库考试学习网想告诉大家:“放弃可以找到一万个理由,但坚持只需一个信念!致敬那些在ACCA备考路上永不放弃的人,好结果只留给有毅力的人。”
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Discuss how the manipulation of financial statements by company accountants is inconsistent with their
responsibilities as members of the accounting profession setting out the distinguishing features of a
profession and the privileges that society gives to a profession. (Your answer should include reference to the
above scenario.) (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 marks for the quality of the discussion.
(c) Accounting and ethical implications of sale of inventory
Manipulation of financial statements often does not involve breaking laws but the purpose of financial statements is to present
a fair representation of the company’s position, and if the financial statements are misrepresented on purpose then this could
be deemed unethical. The financial statements in this case are being manipulated to show a certain outcome so that Hall
may be shown to be in a better financial position if the company is sold. The retained earnings of Hall will be increased by
$4 million, and the cash received would improve liquidity. Additionally this type of transaction was going to be carried out
again in the interim accounts if Hall was not sold. Accountants have the responsibility to issue financial statements that do
not mislead the public as the public assumes that such professionals are acting in an ethical capacity, thus giving the financial
statements credibility.
A profession is distinguished by having a:
(i) specialised body of knowledge
(ii) commitment to the social good
(iii) ability to regulate itself
(iv) high social status
Accountants should seek to promote or preserve the public interest. If the idea of a profession is to have any significance,
then it must make a bargain with society in which they promise conscientiously to serve the public interest. In return, society
allocates certain privileges. These might include one or more of the following:
– the right to engage in self-regulation
– the exclusive right to perform. particular functions
– special status
There is more to being an accountant than is captured by the definition of the professional. It can be argued that accountants
should have the presentation of truth, in a fair and accurate manner, as a goal.
(b) Advise Maureen on deregistration for the purposes of value added tax (VAT) and any possible alternative
strategy. (8 marks)
An additional mark will be awarded for the effectiveness with which the information is communicated.
(1 mark)
(b) Advice on Maureen’s VAT position
Deregistration
In order to voluntarily deregister for VAT you must satisfy HMRC that the value of your taxable supplies in the next twelve
months will not exceed £62,000. You will then be deregistered with effect from the date of your request or a later date as
agreed with HMRC.
On deregistering you are regarded as making a supply of all stocks and equipment in respect of which input tax has been
claimed. However, the VAT on this deemed supply need only be paid to HMRC if it exceeds £1,000.
Once you have deregistered, you must no longer charge VAT on your sales. You will also be unable to recover the input tax
on the costs incurred by your business. Instead, the VAT you pay on your costs will be allowable when computing your taxable
profits.
You should monitor your sales on a monthly basis; if your sales in a twelve-month period exceed £64,000 you must notify
HMRC within the 30 days following the end of the twelve-month period. You will be registered from the end of the month
following the end of the twelve-month period.
Flat rate scheme
Rather than deregistering you may wish to consider operating the flat rate scheme. This would reduce the amount of
administration as you would no longer need to record and claim input tax in respect of the costs incurred by your business.
Under the flat rate scheme you would continue to charge your customers VAT in the way that you do at the moment. You
would then pay HMRC a fixed percentage of your VAT inclusive turnover each quarter rather than calculating output tax less
input tax. This may be financially advantageous as compared with deregistering; I would be happy to prepare calculations for
you if you wish.
(ii) Briefly explain the extent to which the application of sensitivity analysis might be useful in deciding
which refrigeration system to purchase and discuss the limitations inherent in its use. (3 marks)
(ii) Sensitivity analysis could be used to assess how responsive the NPV calculated in part (a) in respect of each decision
option change is to changes in the variables used to calculate it. The application of sensitivity analysis requires that the
net present values are calculated under alternative assumptions in order to determine how sensitive they are to changing
conditions. In this particular example then a relatively small change in the forecast cash flows might lead to a change
in the investment decision. The application of sensitivity analysis can indicate those variables to which the NPV is most
sensitive and the extent to which these variables may change before an investment results in a negative NPV. Thus the
application of sensitivity analysis may provide management with an indication of why a particular project might fail. The
directors of Stay Cool Ltd should give consideration to the potential variations in the independent variables which feature
in the decision-making process such as:
– estimated revenues
– estimated operating costs
– estimated working lives
– estimated repair costs
– the estimated discount rate i.e. cost of capital of each alternative investment.
Sensitivity analysis has some serious limitations. The use of the method requires changes in each variable under
consideration are isolated. However management may be focused on what happens if changes occur in two or more
critical variables. Another problem relating to the use of sensitivity analysis to forecast outcomes lies in the fact that it
provides no indication of the likelihood of the occurrence of changes in critical variables.
(d) Wader has decided to close one of its overseas branches. A board meeting was held on 30 April 2007 when a
detailed formal plan was presented to the board. The plan was formalised and accepted at that meeting. Letters
were sent out to customers, suppliers and workers on 15 May 2007 and meetings were held prior to the year
end to determine the issues involved in the closure. The plan is to be implemented in June 2007. The company
wish to provide $8 million for the restructuring but are unsure as to whether this is permissible. Additionally there
was an issue raised at one of the meetings. The operations of the branch are to be moved to another country
from June 2007 but the operating lease on the present buildings of the branch is non-cancellable and runs for
another two years, until 31 May 2009. The annual rent of the buildings is $150,000 payable in arrears on
31 May and the lessor has offered to take a single payment of $270,000 on 31 May 2008 to settle the
outstanding amount owing and terminate the lease on that date. Wader has additionally obtained permission to
sublet the building at a rental of $100,000 per year, payable in advance on 1 June. The company needs advice
on how to treat the above under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
(d) A provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent assets’ can only be made in relation to the entity’s
restructuring plans where there is both a detailed formal plan in place and the plans have been announced to those affected.
The plan should identify areas of the business affected, the impact on employees and the likely cost of the restructuring and
the timescale for implementation. There should be a short timescale between communicating the plan and starting to
implement it. A provision should not be recognised until a plan is formalised.
A decision to restructure before the balance sheet date is not sufficient in itself for a provision to be recognised. A formal plan
should be announced prior to the balance sheet date. A constructive obligation should have arisen. It arises where there has
been a detailed formal plan and this has raised a valid expectation in the minds of those affected. The provision should only
include direct expenditure arising from the restructuring. Such amounts do not include costs associated with ongoing business
operations. Costs of retraining staff or relocating continuing staff or marketing or investment in new systems and distribution
networks, are excluded. It seems as though in this case a constructive obligation has arisen as there have been detailed formal
plans approved and communicated thus raising valid expectations. The provision can be allowed subject to the exclusion of
the costs outlined above.
Although executory contracts are outside IAS37, it is permissible to recognise a provision that is onerous. Onerous contracts
can result from restructuring plans or on a stand alone basis. A provision should be made for the best estimate of the excess
unavoidable costs under the onerous contract. This estimate should assess any likely level of future income from new sources.
Thus in this case, the rental income from sub-letting the building should be taken into account. The provision should be
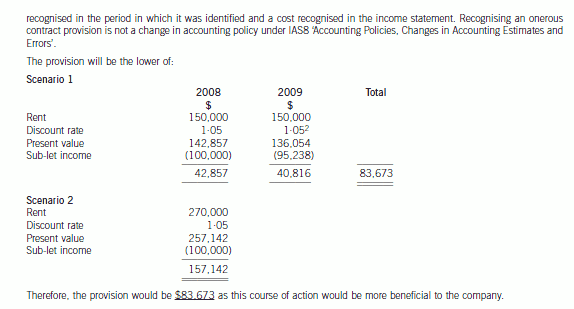
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-07
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-01-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-04
- 2019-12-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-18
- 2020-05-15