ACCA考试报名时间已公布,报名前吉林省考生要这么备考!
发布时间:2020-01-10
早在2019年年末的时候就公布了ACCA考试报名时间,备考的你知道吗?同时,很多小伙伴来咨询51题库考试学习网,想问问ACCA考试那么多科目应该怎么样有效地、科学地复习呢?不用担心,51题库考试学习网帮大家整理了一些考试小技巧,帮助大家事半功倍地通过考试,早日脱坑:
可能有些初次备考ACCA考试的萌新不了解报名时间,51题库考试学习网再次提醒大家2020年ACCA考试的报名时间:
2020年3月ACCA考试报名时间报名周期
提前报名截止 2019年11月11日
常规报名截止 2020年1月27日
后期报名截止 2020年2月3日
2020年6月ACCA考试报名时间报名周期
提前报名截止 2020年2月10日
常规报名截止 2020年4月27日
后期报名截止 2020年5月4日
2020年9月ACCA考试报名时间报名周期
提前报名截止 2020年5月11日
常规报名截止: 2020年7月27日
后期报名截止 2020年8月3日
2020年12月ACCA考试报名时间报名周期
提前报名截止 2020年8月10日
常规报名截止 2020年10月26日
后期报名截止 2020年11月2日
AB(F1)
AB(F1)这门课,首先要从题型出发来分析:目前AB(F1)的题型主要是46个单选题+6个多任务题;因此,从题型上来看就可以分析得知大部分内容其实不需要考生去原封不动地去死记硬背知识点,更多的是要求考生理解性记忆,比如它会教大家用一些模型去分析企业所处的内部以及外部环境,所以考生所学的的是它如何分析这个模型的这种方法,活学活用才能以不变应万变。同时,它还会教一些关于职业道德,企业社会责任的简单介绍。
说到AB(F1),就不得不说SBL课程,其实它们两者是有重复的地方的,就比如SBL课程会把这些AB(F1)课程中的知识点做深入并细化地讲解,就好比分析内外部环境之后企业将如何面对环境的变化、企业在专业层面上的战略,以及在公司治理,财务从业人员的职业道德等做了更深入且全面的介绍。总而言之,AB(F1)是基础,而SBL课程就是延伸。
但考生需要注意的事情就是:因为国家对ACCA考试规则做了限制,你是没有办法同时报考AB(F1)与SBL两个科目的,因为中间还隔着F4-F9 6门技能课程。所以你能做的就是打好基础。对于备考SBL,AB(F1)的知识点是大量的基础知识,所以要注意在考过AB(F1)之后依然需要巩固和记忆相关的知识点,不要把所学的知识点给遗忘了,如果到时候重新来复习的话,就太浪费时间了。
文字类考试对考生的记忆力的要求是极高的,不光要求考生要记忆从中的知识点并且是要熟练记忆。因此51题库考试学习网建议在选择考试科目时要避免选择同时备考多科需要高强度记忆的考试科目,例如F4《Corporate and Business law》以及F8《Audit and Assurance》,如果这些同时备考的话,会增加记忆难度,间接地导致学习效果的下降,最后导致考试成绩的不理想,所以不建议在同一考季中备考多个文字类考试。但是,51题库考试学习网推荐在相邻两个考季中参加考试(比如2020年6月份准备F4,那么2020年6月份就准备F8),因为文字类考试的内容或多或少是有重叠的部分的,区别仅仅在于侧重点不同,识记内容有重叠部分;就比如F8学得很扎实的小伙伴对于后面的学习SBL或者选修高级审计与鉴证《Advanced Audit and Assurance(AAA)》是赢在了起跑线上的,优势是十分巨大的。这就是为什么有一些考神能一次性通过ACCA考试的原因:合理地、科学地、有目的性地、高效地去学习,巧用复习方法能让你的学习效果事半功倍。
F2《Management Accounting》、F5业绩管理《Performance Management》和F9选修高级业绩管理《Advanced Performance Management》
同理,对于F2《Management Accounting》、F5业绩管理《Performance Management》和F9选修高级业绩管理《Advanced Performance Management》。F2课程内容是F5和选修高级业绩管理的基础,三科课程内容都涉及管理会计与财务会计的区别,涵盖:管理会计,管理信息,成本会计,预算和标准成本,业绩衡量,短期决策方法。同样,差别也仅仅是在于侧重点以及研究深度和广度的不同而已。因此,51题库考试学习网建议学习能力强一点的考生将F2和F5考虑同时学习,而学习能力偏弱的考试就先学F2再学F5;在选择报考科目的时间上,建议将F2、F5以及选修高级业绩管理这三科在相邻考季中备考,因为F2中的variance,在F5中体现更加灵活、更加具体。先学F2,再看F5,F2比较简单,很多常识的知识,为F5打好基础,也加深对F2的理解。在这些学科中,ACCAer们将会学到:如何处理基本的成本信息,并能向管理层提供能用作预算和决策的信息。而与此同时,F9科目又是F5升级版,课程研究的更加具体化和形象化,但是RATIO部分是一样的,所以51题库考试学习网建议可以将F5和F9放在同一考季去考试。
F6和P6高级税务《Advanced Taxation》
如果你有选修学习P6高级税务《Advanced Taxation》的打算,可以建议把F6放在F阶段最后一门,在考完F6考试之后,就赶紧学习P6。因为,F6《Taxation》是P6《Advanced Taxation》的直接基础。这门课程涵盖:英国税收体制,个人所得税,企业所得税,资本利得税,增值税,遗产税这五大税种应交税额的计算以及基于个人收入缴纳的国民保险和养老金投资的计算。F6考试中以税负计算为主,而P6更偏向在熟悉税法规定后,帮客户做合理纳税筹划。为什么不将F6和P6在同一考季报考呢?也是由于国家的相关规定,禁止在同一考季报考的,因此在考完F6考试之后,就赶紧学习P6。可以安排在同一年度相邻考季考这两门是最好的,因为两个科目中的相关知识点,例如:税率不变也不用重新记;科目类别要选择一致的,例如F6选择了UK ,P6也就选择UK,但是这样选择存在一个弊端就是,由于在中国P6这门课程学习的人不多,学习资料与课程也很少,如果将F6和P6放在两个相邻,备考时间相对较紧凑,对于资料不好找的科目可能复习到的知识点可能存在不太全面的问题。因此,同学们应根据自身需求谨慎选择。
P2和F7
P2在2018年9月改革为新科目SBR(Strategic Business Reporting)。课程涵盖是十分广泛的,例如:财务会计,财务报表,公司合并报表,分析并解读财务报表。P2的核心就是:让你如何运用合理地会计准则和概念框架编制财务报表同时又能够分析并解读财务报表。不难发现的是:P2有一大部分是重复F7的内容,但是由于ACCA考试规则规定了必须F阶段考试全部通过完毕之后才能报考P阶段,所以51题库考试学习网建议考生在考完F阶段考试之后,可以在下一次考试先考P2,将F7的知识点灵活运用。
如果想要学习4选2的P4的话,可以再F9考完之后学习P4,P4《Advanced Financial Management》是F9《Financial Management》的延伸考查,与SBR也有一定的联系。
课程涵盖:高级投资评估,公司并购、重组,高级风险管理,跨国公司面临的经济环境,您将会学到作为一名高级财务人员进行与财务管理相关决策必备的知识、技巧和进行职业判断的能力。
F8《Audit Assurance》是P7《Advanced Audit Assurance》的直接基础,与F3,F7,SBL等课程都有一定的关系。
F8课程中涵盖:内部审计和外部审计以及设计建立及实施内控程序,重点学习审计师如何了解企业情况,对审计风险进行评估,制定审计计划,在国际审计准则下如何进行设计,建立并实施审计程序,以及各种审计报告和审计意见。
P7是F8的延伸,与p2也有一定的联系。从三个科目之间存在的共同点可以看出:F7和P2主要学习如何编制财务报表,F8和P7学习如何审计财务报表。
P7课程涵盖:监管环境与制度,职业道德,实务管理,历史财务信息的审计与报告,其它与审计相关的认证业务。
在这里要提醒各位小伙伴们,ACCA在P阶段从P4到P7是选修科目,学员们只要选择学习两门并通过考试就可以了。但这4门选修科目却基本通向不同的工作领域。
P4《Advanced Financial Management》更偏向金融方面,想去投行券商的小伙伴们可以考虑选择P4
P5《Advanced Performance Management》偏向财务管理方向,如果对分析公司财务状况以及咨询岗位感兴趣的小伙伴可以选择P5
P6《Advanced Taxation》及P7《Advanced Audit Assurance》可以让各位学员们对税法以及审计准则的知识熟练掌握,对于想在事务所工作的小伙伴们是不错的选择。
鲤鱼不跃,岂可成龙?大鹏驻足,焉能腾空?十年磨刀霍霍,只为今朝一搏。最后51题库考试学习网祝大家都能顺利通过ACCA,取得好成绩!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
2 Clifford and Amanda, currently aged 54 and 45 respectively, were married on 1 February 1998. Clifford is a higher
rate taxpayer who has realised taxable capital gains in 2007/08 in excess of his capital gains tax annual exemption.
Clifford moved into Amanda’s house in London on the day they were married. Clifford’s own house in Oxford, where
he had lived since acquiring it for £129,400 on 1 August 1996, has been empty since that date although he and
Amanda have used it when visiting friends. Clifford has been offered £284,950 for the Oxford house and has decided
that it is time to sell it. The house has a large garden such that Clifford is also considering an offer for the house and
a part only of the garden. He would then sell the remainder of the garden at a later date as a building plot. His total
sales proceeds will be higher if he sells the property in this way.
Amanda received the following income from quoted investments in 2006/07:
£
Dividends in respect of quoted trading company shares 1,395
Dividends paid by a Real Estate Investment Trust out of tax exempt property income 485
On 1 May 2006, Amanda was granted a 22 year lease of a commercial investment property. She paid the landlord
a premium of £6,900 and also pays rent of £2,100 per month. On 1 June 2006 Amanda granted a nine year
sub-lease of the property. She received a premium of £14,700 and receives rent of £2,100 per month.
On 1 September 2006 Amanda gave quoted shares with a value of £2,200 to a registered charity. She paid broker’s
fees of £115 in respect of the gift.
Amanda began working for Shearer plc, a quoted company, on 1 June 2006 having had a two year break from her
career. She earns an annual salary of £38,600 and was paid a bonus of £5,750 in August 2006 for agreeing to
come and work for the company. On 1 August 2006 Amanda was provided with a fully expensed company car,
including the provision of private petrol, which had a list price when new of £23,400 and a CO2 emissions rate of
187 grams per kilometre. Amanda is required to pay Shearer plc £22 per month in respect of the private use of the
car. In June and July 2006 Amanda used her own car whilst on company business. She drove 720 business miles
during this two month period and was paid 34 pence per mile. Amanda had PAYE of £6,785 deducted from her gross
salary in the tax year 2006/07.
After working for Shearer plc for a full year, Amanda becomes entitled to the following additional benefits:
– The opportunity to purchase a large number of shares in Shearer plc on 1 July 2007 for £3·30 per share. It is
anticipated that the share price on that day will be at least £7·50 per share. The company will make an interestfree
loan to Amanda equal to the cost of the shares to be repaid in two years.
– Exclusive free use of the company sailing boat for one week in August 2007. The sailing boat was purchased by
Shearer plc in January 2005 for use by its senior employees and costs the company £1,400 a week in respect
of its crew and other running expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate Clifford’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2007/08 on the assumption that the Oxford
house together with its entire garden is sold on 31 July 2007 for £284,950. Comment on the relevance
to your calculations of the size of the garden; (5 marks)
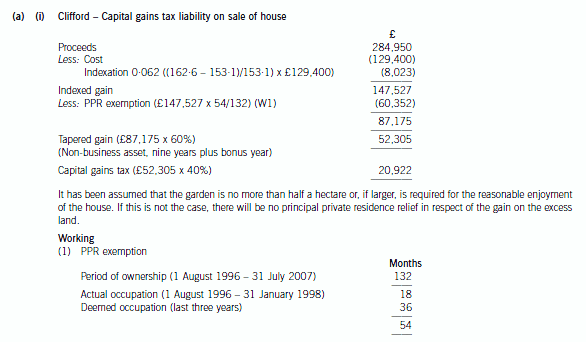
(c) At 1 June 2006, Router held a 25% shareholding in a film distribution company, Wireless, a public limited
company. On 1 January 2007, Router sold a 15% holding in Wireless thus reducing its investment to a 10%
holding. Router no longer exercises significant influence over Wireless. Before the sale of the shares the net asset
value of Wireless on 1 January 2007 was $200 million and goodwill relating to the acquisition of Wireless was
$5 million. Router received $40 million for its sale of the 15% holding in Wireless. At 1 January 2007, the fair
value of the remaining investment in Wireless was $23 million and at 31 May 2007 the fair value was
$26 million. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
(c) The investment in Wireless is currently accounted for using the equity method of accounting under IAS28 ‘Investments in
Associates’. On the sale of a 15% holding, the investment in Wireless will be accounted for in accordance with IAS39. Router
should recognise a gain on the sale of the holding in Wireless of $7 million (Working 1). The gain comprises the following:
(i) the difference between the sale proceeds and the proportion of the net assets sold and
(ii) the goodwill disposed of.
The total gain is shown in the income statement.
The remaining 10 per cent investment will be classified as an ‘available for sale’ financial asset or at ‘fair value through profit
or loss’ financial asset. Changes in fair value for these categories are reported in equity or in the income statement respectively.
At 1 January 2007, the investment will be recorded at fair value and a gain of $1 million $(23 – 22) recorded. At 31 May
2007 a further gain of $(26 – 23) million, i.e. $3 million will be recorded. In order for the investment to be categorised as
at fair value through profit or loss, certain conditions have to be fulfilled. An entity may use this designation when doing so
results in more relevant information by eliminating or significantly reducing a measurement or recognition inconsistency (an
‘accounting mismatch’) or where a group of financial assets and/or financial liabilities is managed and its performance is
evaluated on a fair value basis, in accordance with a documented risk management or investment strategy, and information
about the assets and/ or liabilities is provided internally to the entity’s key management personnel.
(b) Assess the benefits of the separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman that Alliya Yongvanich
argued for and explain her belief that ‘accountability to shareholders’ is increased by the separation of these
roles. (12 marks)
(b) Separation of the roles of CEO and chairman
Benefits of separation of roles
The separation of the roles of chief executive and chairman was first provided for in the UK by the 1992 Cadbury provisions
although it has been included in all codes since. Most relevant to the case is the terms of the ICGN clause s.11 and OECD
VI (E) both of which provide for the separation of these roles. In the UK it is covered in the combined code section A2.
The separation of roles offers the benefit that it frees up the chief executive to fully concentrate on the management of the
organisation without the necessity to report to shareholders or otherwise become distracted from his or her executive
responsibilities. The arrangement provides a position (that of chairman) that is expected to represent shareholders’ interests
and that is the point of contact into the company for shareholders. Some codes also require the chairman to represent the
interests of other stakeholders such as employees.
Having two people rather than one at the head of a large organisation removes the risks of ‘unfettered powers’ being
concentrated in a single individual and this is an important safeguard for investors concerned with excessive secrecy or
lack of transparency and accountability. The case of Robert Maxwell is a good illustration of a single dominating
executive chairman operating unchallenged and, in so doing, acting illegally. Having the two roles separated reduces
the risk of a conflict of interest in a single person being responsible for company performance whilst also reporting on
that performance to markets. Finally, the chairman provides a conduit for the concerns of non-executive directors who,
in turn, provide an important external representation of external concerns on boards of directors.
Tutorial note: Reference to codes other than the UK is also acceptable. In all cases, detailed (clause number) knowledge
of code provisions is not required.
Accountability and separation of roles
In terms of the separation of roles assisting in the accountability to shareholders, four points can be made.
The chairman scrutinises the chief executive’s management performance on behalf of the shareholders and will be
involved in approving the design of the chief executive’s reward package. It is the responsibility of the chairman to hold
the chief executive to account on shareholders’ behalfs.
Shareholders have an identified person (chairman) to hold accountable for the performance of their investment. Whilst
day-to-day contact will normally be with the investor relations department (or its equivalent) they can ultimately hold
the chairman to account.
The presence of a separate chairman ensures that a system is in place to ensure NEDs have a person to report to outside the
executive structure. This encourages the freedom of expression of NEDs to the chairman and this, in turn, enables issues to
be raised and acted upon when necessary.
The chairman is legally accountable and, in most cases, an experienced person. He/she can be independent and more
dispassionate because he or she is not intimately involved with day-to-day management issues.
(b) Using relevant evaluation criteria, assess how achievable and compatible these three strategic goals are over
the next five years. (20 marks)
(b) The three strategic goals are to become the leading premium ice cream brand in the UK; to increase sales to £25 million;
and to achieve a significant entry into the supermarket sector. On the basis of performance to date these goals will certainly
be stretching. All three strategies will involve significant growth in the company. Johnson and Scholes list three success criteria
against which the strategies can be assessed, namely suitability, acceptability and feasibility. Suitability is a test of whether a
strategy addresses the situation in which a company is operating. In Johnson and Scholes’ terms it is the firm’s ‘strategic
position’, an understanding of which comes from the analysis done in the answer to the question above. Acceptability is
concerned with the likely performance outcomes of the strategy and in particular whether the return and risk are in line with
the expectations of the stakeholders. Feasibility is the extent to which the strategy can be made to work and is determined
by the strategic capability of the company reflecting the resources available to implement the strategy. It is interesting to see
that the three growth related goals are compatible in that becoming the leading premium brand will involve increased market
penetration, product development and market development. If achieved it will increase sales and necessitate a successful
entry into the supermarket sector. Time will be an important influence on the success or otherwise of these growth goals –
five years seems to be a reasonable length of time to achieve these ambitious targets.
Suitability – Churchill is currently a small but significant player at the premium end of the market. This segment is becoming
more significant and is attractive because of the high prices and high margins attainable. This is leading to more intense
competition with global companies. One immediate question that springs to mind is what precisely does ‘leading brand’
mean? The most obvious test is that of market share and unless Churchill achieve the access to the supermarkets looked for
in the third strategic goal, seems difficult to achieve. If ‘leading brand’ implies brand recognition this again looks very
ambitious. On the positive side this segment of the ice cream market is showing significant growth and Churchill’s success
in gaining sponsorship rights to major sporting events is a step in the right direction. The combination of high price and high
quality should position the company where it wants to be. Achieving sales of £25 million represents a quantum shift in
performance in a company that has to date only achieved modest levels of sales growth.
Acceptability – as a family owned business the balance between risk and return is an important one. The family to date has
been ‘happy’ with a modest rate of growth and modest return in terms of profits. The other significant stakeholder group is
the professional managers headed up by Richard Smith. They seem much more growth orientated and may be happier with
the risks that the growth strategy entails. The family members seem more interested in the manufacturing side than the
retailing side of the business and their bad previous experiences with growing the business through international market
development may mean they are risk averse and less willing to invest the necessary resources.
Feasibility – again this is linked to how ‘leading brand’ is defined. If as seems likely the brand becomes more widely known
through increasing the number of company owned ice cream stores then a significant investment in retail outlets will be
necessary. Increasing the number of franchised outlets will reduce the financial resources required but may be at the expense
of the brand’s reputation. Certainly there would seem to be a need for increased levels of advertising and promotion –
particularly to gain access to the ice cream cabinets in the supermarket chains. This is likely to mean an increase in the
number of sales and marketing staff. Equally important will be the ability to develop and launch new products in a luxury
market shaped by impulse buying and customers looking to indulge themselves.
Overall, becoming the leading brand of premium ice cream may well be the key to achieving the desired presence in the
supermarket ice cream cabinets, which in turn is a pre-requisite for increasing company sales to £25 million. So the three
strategic goals may be regarded as consistent and compatible with one another. However each strategic goal will have to be
broken down into its key elements. For example in achieving sales of £25 million what proportion of sales will come from its
own ice cream stores and what proportion from other outlets including the supermarkets? Sales to date of Churchill ice cream
are dominated by impulse purchases but in achieving sales of £25 million penetrating the take home market will be essential.
Finally, what proportion of these take home sales will be under the supermarkets own label brands? Over reliance on own
label sales will seriously weaken Churchill’s desire to become the leading national brand of premium ice cream. It looks to
be an ambitious but attainable strategy but will require a significant planning effort to develop the necessary resources andcapabilities vital to successful implementation of the strategy.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-03-16
- 2020-01-14
- 2021-08-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-07-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-04-30
- 2021-06-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-05-09