云南省考生:如何利用零散时间学习ACCA?
发布时间:2020-01-10
在我国职称会计师考试中,ACCA考试属于难度比较大的考试,由于严苛的报考条件,备考ACCA考试的朋友大多数都是工作比较忙碌的上班族,那么如何在繁忙的工作中合理安排备考时间对于考生来说就非常重要了。除去完整系统的备考时间外,生活中零散时间也是能够备考的,今天就来教大家如何高效利用零散时间学习ACCA考试,大家可以作为参考。
每天至少一道题
ACCA考试的类型有很多种,主要考察应试人员分析、解决财务工作的能力,同时对计算能力和语言能力也是极大的挑战。所以在平时的备考中是一定缺少不了习题的辅助的。建议大家每天至少要做一套ACCA真题训练,每道小问控制在8分钟左右,这就足够大家利用空闲时间进行做题。
生活空档看考点
在上班路上看新闻时间,午休后的看剧时间在备考期间大家都可以转换成“高会学习时间”,带上《轻松过关》辅导书,看里面的“考点精讲”,让你在短时间内了解学习内容。你可以选择将学过的知识点复习一遍,或者将要学习的知识点提前预习一遍,要知道只有多一份努力才能多一份胜算。
备考笔记随身带
很多考生在备考中有记笔记或者是记错题本的好习惯,将整理的内容随身携带,空闲时间可以随时拿出来进行学习也是不错的选择。选择自己整理的笔记可以加深学习的印象,在考试的过程中也能当成考试资料带入考场,寻找知识点也会更快。
用完整时间来学习,用零散时间来备考,两者结合高效备考!
以上就是为大家准备的备考方法,希望对大家有所帮助,预祝大家都能轻松过ACCA考试~加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) ‘opinion shopping’; (5 marks)
(b) ‘Opinion shopping’
Explanation of term
‘Opinion shopping’ occurs when management approach auditing firms (other than their incumbent auditors) to ask their views
on the application of accounting standards or principles to specific circumstances or transactions.
Ethical risks
The reasons for ‘opinion shopping’ may be:
■ to find alternative auditors; or
■ to get advice on a matter of contention with the incumbent auditor.
The member who is not the entity’s auditor must be alert to the possibility that their opinion – if it differs from that of the
incumbent auditor – may create undue pressure on the incumbent auditor’s judgement and so threaten the objectivity of the
audit.
Furthermore, by aligning with the interests of management when negotiating taking on an engagement, an incoming auditor
may compromise their objectivity even before the audit work commences. There is a risk that the audit fee might be seen to
be contingent upon a ‘favourable’ opinion (that is, the audit judgement coinciding with management’s preferences).
Employed professional accountants (accountants in industry) who support their company’s management in seeking second
opinions may call into question their integrity and professional behaviour.
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
Current ethical guidance requires that when asked to provide a ‘second opinion’ a member should seek to minimise the risk
of giving inappropriate guidance, by ensuring that they have access to all relevant information.
The member should therefore:
■ ascertain why their opinion is being sought;
■ contact the auditor to provide any relevant facts;
■ with the entity’s permission, provide the auditor with a copy of their opinion.
The member’s opinion is more likely to differ if it is based on information which is different (or incomplete) as compared with
that available to the incumbent auditor. The member should therefore decline to act if permission to communicate with the
auditor is not given.
‘Opinion shopping’ might be less prevalent if company directors had no say in the appointment and remuneration of auditors.
If audit appointments were made by an independent body ‘doubtful accounting practices’ would (arguably) be less of a
negotiating factor. However, to be able to appoint auditors to multi-national/global corporations, such measures would require
the backing of regulatory bodies worldwide.
Statutory requirements in this area could also be more stringent. For example, an auditor may be required to deposit a
‘statement of circumstances’ (or a statement of ‘no circumstances’) in the event that they are removed from office or resign.
However, disclosure could be made more public if, when a change in accounting policy coincides with a change of auditors,
the financial statements and auditor’s report highlight the change and the auditors state their concurrence (or otherwise) with
the change. This could be made a statutory requirement and International Standards on Auditing (ISAs) amended to give
guidance on how auditors should report on changes.
Further, if the incoming auditor were to have a statutory right of access to the files and working papers of the outgoing auditors
they would be able to make a better and informed assessment of the desirability of the client and also appreciate the validity
(or otherwise) of any ‘statement’ issued by the outgoing auditor.
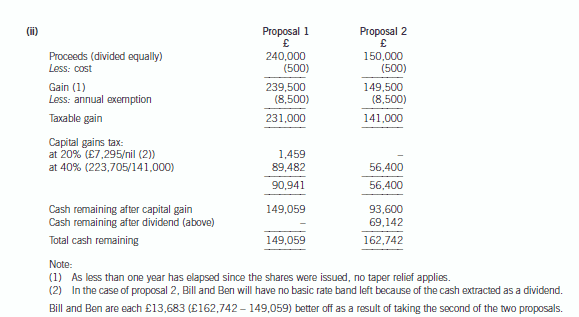
(ii) Following on from your answer to (i), evaluate the two purchase proposals, and advise Bill and Ben
which course of action will result in the highest amount of after tax cash being received by the
shareholders if the disposal takes place on 31 March 2006. (4 marks)
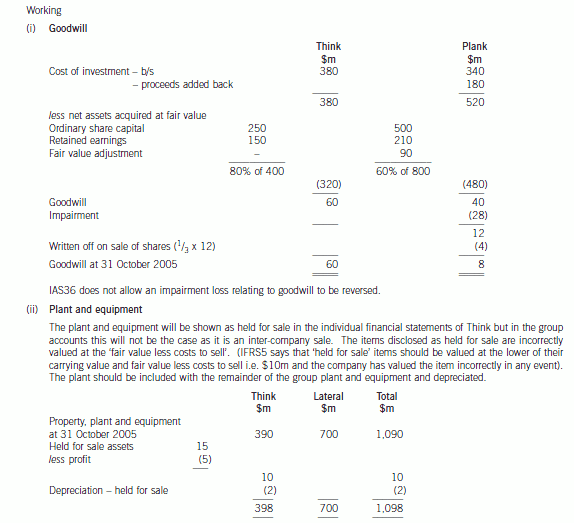
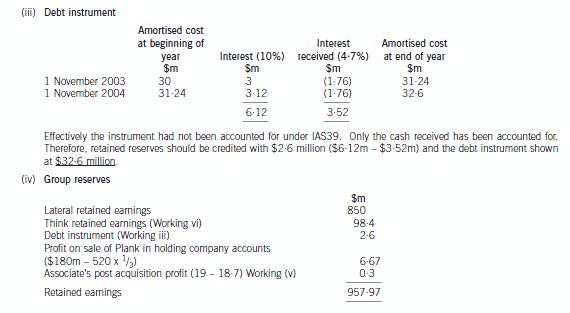
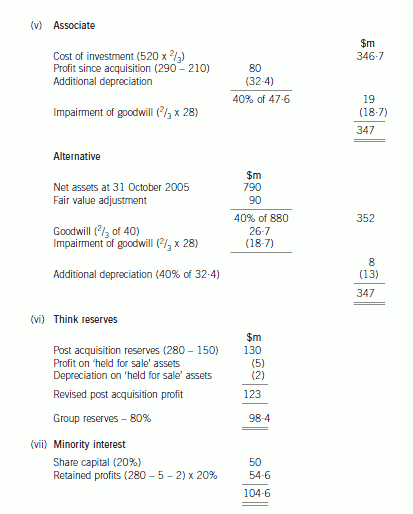
(b) Prepare a consolidated balance sheet as at 31 October 2005 for the Lateral Group in accordance with
International Financial Reporting Standards. (21 marks)
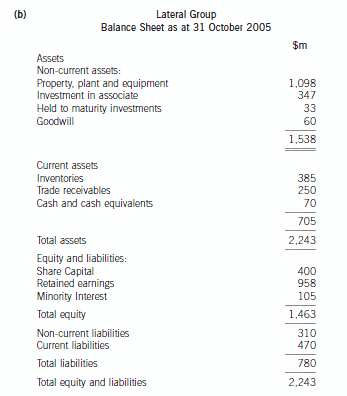
(b) International Standards on Auditing (ISAs); and (5 marks)
(b) International Standards on Auditing (ISAs)
The groundwork for an international set of auditing standards began in 1969 with a number of reports published by the
Accountants International Study Group that compared the situation in Canada, the UK, and US. The establishment of the
International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC), in 1973, generated calls for a similar body to be set up for auditing.
In the late 1970s the Council of International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) created the International Auditing Practices
Committee (IAPC) as a standing committee of the IFAC Council. (Subsequently the IFAC Board.)
Tutorial note: The IFAC Council was renamed the IFAC Board in May 2000.
The first ISA was issued in 1991. The codified core set released in 1994, which has remained the series to the present day,
has been increasingly accepted by national standard setters and auditors involved in global reporting and cross-border
financing transactions.
In July 2001, IFAC sought comment on the role of IASC3 and the future of ISAs. As a result of the review, in 2002, the IAPC
was renamed the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB). IAASB has made available, on its website,
the full text of ISAs since 2003.
Further, the growth of non-audit assurance services has led to the development of a new framework (‘The International
Framework for Assurance Engagements’) effective for assurance reports issued on or after 1 January 2005.
The hope that the take up of ISAs should follow the lead set by International Accounting Standards (IASs), following their
endorsement by IOSCO (the International Organization of Securities Commissions), has been expressed by many professional
bodies including ACCA and FEE (the Fédération des Experts Comptables Européens). FEE has been leading the debate on
the future of ISAs in Europe since 2001.
ISAs provide for the international harmonisation of national standards and the adoption of a global framework approach. As
a member of CCAB (the Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies) ACCA is committed to consulting its members on
the adoption of ISAs in the UK, and working with FEE, the European Commission (EC) and others.
In response to the move in the profession, away from the ‘traditional audit risk’ model, to a business risk model, IAASB issued
ISA 315 ‘Understanding the Entity and Its Environment and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement,’ ISA 330 ‘The
Auditor’s Procedures in Response to Assessed Risks’ and ISA 500 (Revised) ‘Audit Evidence’. These standards (and
conforming amendments) are effective for audits of financial statements for periods beginning on or after 15 December 2004.
That is, they will be applicable to financial statements for periods beginning on or after 1 January 2005 that in the European
Economic Area (EEA) and elsewhere will be adopting International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) for the first time.
The adoption of ISAs has been welcomed by professional bodies as providing a robust approach to risk, fraud and quality
control that is particularly important in the light of recent events (Enron/Worldcom/Parmalat). For example, ISA 315 provides
additional guidance on the assessment of risks of material misstatement at the financial statement level and at the assertion
level.
Tutorial note: Recent developments could validly be illustrated with reference to other standards. For example, ISA 240
(Revised) ‘The Auditor’s Responsibility to Consider Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’ that became effective from
1 January 2005 has raised auditor awareness of earnings management and the greater need for professional skepticism.
ISA 700 (Revised) ‘The Independent Auditor’s Report on a Complete Set of General Purpose Financial Statements’ is effective
for audits of financial statements for periods beginning on or after 15 December 2005. This proposed significant changes to
the auditor’s report to help promote consistency in reporting practices worldwide.
The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) is in discussion with IAASB about the possible
endorsement of ISAs (similar to its endorsement of IASs).
Practicing professionals must keep themselves up to date on auditing standards if they are to provide quality audits. Failure
to do so could result in negligence claims and/or disciplinary action (e.g. by ACCA’s disciplinary committee). A survey by FEE
has demonstrated that the European accountancy bodies broadly comply with ISAs. However, an earlier survey4 of IFAC
member bodies showed that 14% had some significant differences (usually relating to reporting). IFAC needs to require its
member bodies to act rather than merely encourage implementation. A set of global ethical requirements will help improve
the implementation of ISAs as well as reduce the expectation gap in performing audits of financial statements.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-01
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-07-23
- 2020-05-12
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-09-25
- 2021-08-29
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-01-05