2020年第二考试季ACCA考试时间安排
发布时间:2020-03-07
由于2020年3月的ACCA考试取消,一些已经报考本次考试的学员不得不重新报名6月份的考试,并重新为考试做准备。于是,有网友就在询问2020年第二考试季ACCA考试时间安排。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来2020年ACCA考试报名时间的相关信息,以供参考。
2020年第二考试季的ACCA考试将在6月1日至5日举行,具体科目的考试时间还望考生在官网上查询详细信息。
ACCA考试每年举行四次,分别在每年的3月、6月、9月、12月。不同年份的具体考试时间略有差异,请考生注意ACCA官网发布的消息。每次考试报名时间都分为三个阶段:提前报名、常规报名、后期报名。不同年份的具体时间略有不同,通常而言,3月份考试的报名截止时间分别为上一年的11月、1月、2月;6月份考试的报名截止时间分别为当年的2月、4月以及5月;9月份考试的报名截止时间分别为当年的5月、7月、8月;12月份报名截止时间分别在当年的8月、10月、11月。注意,以上的报名时间均为截止日期。
以上就是关于2020年ACCA考试报名时间及考试时间的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:目前距离6月份的ACCA考试所剩时间已经不多,请各位考生注意合理安排复习计划。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Define ‘retirement by rotation’ and explain its importance in the context of Rosh and Company.
(5 marks)
(c) Retirement by rotation.
Definition
Retirement by rotation is an arrangement in a director’s contract that specifies his or her contract to be limited to a specific
period (typically three years) after which he or she must retire from the board or offer himself (being eligible) for re-election.
The director must be actively re-elected back onto the board to serve another term. The default is that the director retires
unless re-elected.
Importance of
Retirement by rotation reduces the cost of contract termination for underperforming directors. They can simply not be
re-elected after their term of office expires and they will be required to leave the service of the board as a retiree (depending
on contract terms).
It encourages directors’ performance (they know they are assessed by shareholders and reconsidered every three years) and
focuses their minds upon the importance of meeting objectives in line with shareholders’ aims.
It is an opportunity, over time, to replace the board membership whilst maintaining medium term stability of membership
(one or two at a time).
Applied to Rosh
Retirement by rotation would enable the board of Rosh to be changed over time. There is evidence that some directors may
have stayed longer than is ideal because of links with other board members going back many years.
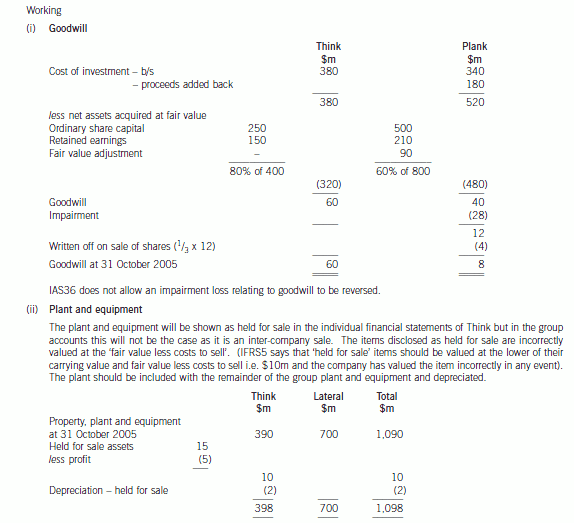
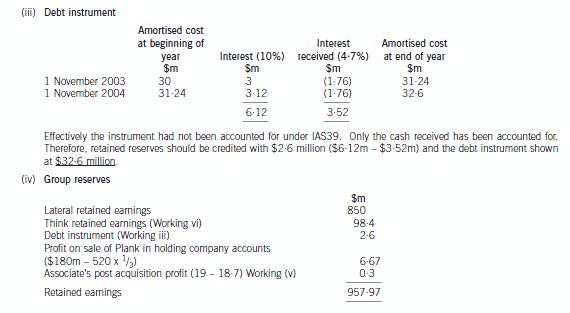
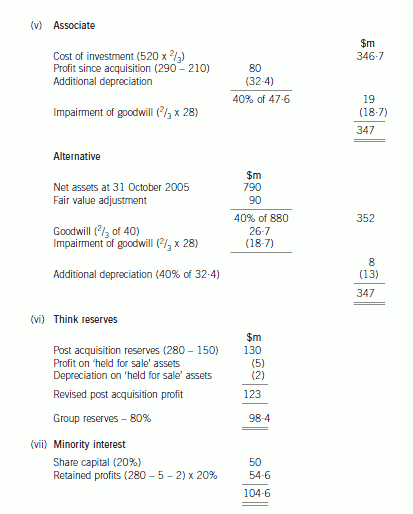
(b) Prepare a consolidated balance sheet as at 31 October 2005 for the Lateral Group in accordance with
International Financial Reporting Standards. (21 marks)
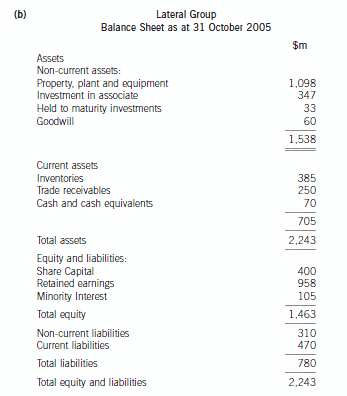
2 Plaza, a limited liability company, is a major food retailer. Further to the success of its national supermarkets in the
late 1990s it has extended its operations throughout Europe and most recently to Asia, where it is expanding rapidly.
You are a manager in Andando, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You have been approached by Duncan
Seymour, the chief finance officer of Plaza, to advise on a bid that Plaza is proposing to make for the purchase of
MCM. You have ascertained the following from a briefing note received from Duncan.
MCM provides training in management, communications and marketing to a wide range of corporate clients, including
multi-nationals. The ‘MCM’ name is well regarded in its areas of expertise. MCM is currently wholly-owned by
Frontiers, an international publisher of textbooks, whose shares are quoted on a recognised stock exchange. MCM
has a National and an International business.
The National business comprises 11 training centres. The audited financial statements show revenue of
$12·5 million and profit before taxation of $1·3 million for this geographic segment for the year to 31 December
2004. Most of the National business’s premises are owned or held on long leases. Trainers in the National business
are mainly full-time employees.
The International business has five training centres in Europe and Asia. For these segments, revenue amounted to
$6·3 million and profit before tax $2·4 million for the year to 31 December 2004. Most of the International business’s
premises are held on operating leases. International trade receivables at 31 December 2004 amounted to
$3·7 million. Although the International centres employ some full-time trainers, the majority of trainers provide their
services as freelance consultants.
Required:
(a) Define ‘due diligence’ and describe the nature and purpose of a due diligence review. (4 marks)
2 MCM
(a) Nature and purpose of a ‘due diligence’ review
■ ‘Due diligence’ may be defined as the process of systematically obtaining and assessing information in order to identify
and contain the risks associated with a transaction (e.g. buying a business) to an acceptable level.
■ The nature of such a review is therefore that it involves:
? an investigation (e.g. into a company whose equity may be sold); and
? disclosure (e.g. to a potential investor) of findings.
■ A due diligence assignment consists primarily of inquiry and analytical procedures.
Tutorial note: It will not, for example, routinely involve tests of control or substantive procedures.
* As the timescale for a due diligence review is often relatively short, but wider in scope than the financial statements
(e.g. business prospects, market valuation), there may be no expression of assurance.
■ Its purpose is to find all the facts that would be of material interest to an investor or acquirer of a business. It may not
uncover all such factors but should be designed with a reasonable expectation of so doing.
■ Professional accountants will not be held liable for non-disclosure of information that failed to be uncovered if their
review was conducted with ‘due diligence’.
(c) Construct the arguments in favour of Professor Leroi’s remark that external reporting requirements on internal
controls were ‘too ambitious’ for small and medium companies. (4 marks)
(c) The external reporting requirements (from the Sarbanes-Oxley section 404) being ‘too ambitious’ for small and medium
companies
There are several arguments to support Professor Leroi’s remark.
Fewer spare resources to carry out internal control. SMEs tend to operate with lower levels of spare resource than larger
businesses and conducting internal reviews would be more of a challenge for them.
The extra attestation fee (over and above normal audit fee) for the attestation of the internal control report could be a constraint
for many SMEs.
Lack of expertise from within existing employees (to internally audit/police as well as carry out internal activities) would be a
likely constraint.
SMEs will have fewer activities and less complexity, hence less need for shareholders to require the information (less to go
wrong).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-04-22
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-26
- 2021-07-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2019-11-27
- 2021-08-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-07