符合ACCA三年工作实践要求的经验有哪些?
发布时间:2020-02-19
最近,有小伙伴问,符合ACCA三年工作实践要求的经验有哪些?这是ACCA学员们在申请会员的时候的要求,那么,今天,51题库考试学习网来给大家普及一下吧!
根据2007年1月1日开始实行的新大纲,成为ACCA会员的必要条件是要完成“三个E”,具体指的是:
1. 通过ACCA专业资格大纲13门课程的考试;
2. 至少三年的相关工作经验;
3. 完成道德测试。
对在2007年1月1日之前注册的学员,完成在线职业操守训练课程不作为申请会员的必要条件,但ACCA鼓励学员完成这一课程。
ACCA开发了道德测试模块,以检验学员职业操守的价值观和行为。ACCA鼓励学员在报考课程战略阶段课程时就开始在网上学习职业操守的课程。学员可以自己灵活掌握学习时间,但是必须在申请会员之前完成课程的学习。
实践经验要求:
1. 具备工作经验是成为会员的一个非常重要的条件。在参加ACCA考试之前、考试期间、考试完成之后取得的工作经验ACCA都认可。
2. 成为ACCA会员必须具备相关的专业知识和能力,必须在职业道德、公司治理、绩效管理、沟通交流、财务报告、财务管理、审计、税务等方面达到相应的水平。
3. ACCA新大纲制定了20项有实践经验要求的绩效考核指标,要成为会员必须达到13项,其中9项是必须达到的关键要素,剩余4项从11个可选项中选择。
工作经验记录
:
1. ACCA设计了学员发展矩阵以便学员通过回答相关问题,记录自己在工作中达到的绩效考核指标。
2. TDM有在线和书面两种形式。当一项工作成绩记录被上司认可签字,ACCA将认可会员申请者满足了相应领域的绩效考核指标。该项纪录可以通过网络提交,也可以书面提交。
年度报告要求
:
1. 为了跟踪了解会员申请者的专业能力和职业发展,ACCA要求会员申请者在每年的最后一个季度提交年度报告。在报告中,申请者要阐明当年在哪个要素领域达到了绩效考核指标、在相关的岗位工作了多长时间。
2. 该报告可以通过网络提交,也可以书面提交。特别要说明的是,如果会员申请者所在的工作单位是ACCA的黄金或白金级认可雇主,申请者无须填写详细的TDM,只需在年度报告中声明这一点即可。
监督指导:会员申请者在工作中要有一名指导人对其在以下方面进行监督指导:
1. 选择绩效考核的领域;
2. 设定要达到的工作绩效的目标和时间;
3. 提供适当的条件和支持;
4. 定期进行审核评估。 指导人可以是申请人的直接上司、所在单位的部门经理或其他个人。
好了,看了上面的内容,相信大家对报考ACCA的三年工作实践经验的相关内容有了一定的了解。如果还想了解更多信息,欢迎来51题库考试学习网留言。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
1 The scientists in the research laboratories of Swan Hill Company (SHC, a public listed company) recently made a very
important discovery about the process that manufactured its major product. The scientific director, Dr Sonja Rainbow,
informed the board that the breakthrough was called the ‘sink method’. She explained that the sink method would
enable SHC to produce its major product at a lower unit cost and in much higher volumes than the current process.
It would also produce lower unit environmental emissions and would substantially improve product quality compared
to its current process and indeed compared to all of the other competitors in the industry.
SHC currently has 30% of the global market with its nearest competitor having 25% and the other twelve producers
sharing the remainder. The company, based in the town of Swan Hill, has a paternalistic management approach and
has always valued its relationship with the local community. Its website says that SHC has always sought to maximise
the benefit to the workforce and community in all of its business decisions and feels a great sense of loyalty to the
Swan Hill locality which is where it started in 1900 and has been based ever since.
As the board considered the implications of the discovery of the sink method, chief executive Nelson Cobar asked
whether Sonja Rainbow was certain that SHC was the only company in the industry that had made the discovery and
she said that she was. She also said that she was certain that the competitors were ‘some years’ behind SHC in their
research.
It quickly became clear that the discovery of the sink method was so important and far reaching that it had the
potential to give SHC an unassailable competitive advantage in its industry. Chief executive Nelson Cobar told board
colleagues that they should clearly understand that the discovery had the potential to put all of SHC’s competitors out
of business and make SHC the single global supplier. He said that as the board considered the options, members
should bear in mind the seriousness of the implications upon the rest of the industry.
Mr Cobar said there were two strategic options. Option one was to press ahead with the huge investment of new plant
necessary to introduce the sink method into the factory whilst, as far as possible, keeping the nature of the sink
technology secret from competitors (the ‘secrecy option’). A patent disclosing the nature of the technology would not
be filed so as to keep the technology secret within SHC. Option two was to file a patent and then offer the use of the
discovery to competitors under a licensing arrangement where SHC would receive substantial royalties for the twentyyear
legal lifetime of the patent (the ‘licensing option’). This would also involve new investment but at a slower pace
in line with competitors. The licence contract would, Mr Cobar explained, include an ‘improvement sharing’
requirement where licensees would be required to inform. SHC of any improvements discovered that made the sink
method more efficient or effective.
The sales director, Edwin Kiama, argued strongly in favour of the secrecy option. He said that the board owed it to
SHC’s shareholders to take the option that would maximise shareholder value. He argued that business strategy was
all about gaining competitive advantage and this was a chance to do exactly that. Accordingly, he argued, the sink
method should not be licensed to competitors and should be pursued as fast as possible. The operations director said
that to gain the full benefits of the sink method with either option would require a complete refitting of the factory and
the largest capital investment that SHC had ever undertaken.
The financial director, Sean Nyngan, advised the board that pressing ahead with investment under the secrecy option
was not without risks. First, he said, he would have to finance the investment, probably initially through debt, and
second, there were risks associated with any large investment. He also informed the board that the licensing option
would, over many years, involve the inflow of ‘massive’ funds in royalty payments from competitors using the SHC’s
patented sink method. By pursuing the licensing option, Sean Nyngan said that they could retain their market
leadership in the short term without incurring risk, whilst increasing their industry dominance in the future through
careful investment of the royalty payments.
The non-executive chairman, Alison Manilla, said that she was looking at the issue from an ethical perspective. She
asked whether SHC had the right, even if it had the ability, to put competitors out of business.
Required:
(a) Assess the secrecy option using Tucker’s model for decision-making. (10 marks)
(a) Tucker’s framework
Is the decision:
Profitable? For SHC, the answer to this question is yes. Profits would potentially be substantially increased by the loss of all
of its competitors and the emergence of SHC, in the short to medium term at least, as a near monopolist.
Legal? The secrecy option poses no legal problems as it is a part of normal competitive behaviour in industries. In some
jurisdictions, legislation forbids monopolies existing in some industries but there is no indication from the case that this
restriction applies to Swan Hill Company.
Fair? The fairness of the secrecy option is a moral judgment. It is probably fair when judged from the perspective of SHC’s
shareholders but the question is the extent to which it is fair to the employees and shareholders of SHC’s competitors.
Right? Again, a question of ethical perspective. Is it right to pursue the subjugation of competitors and the domination of an
industry regardless of the consequences to competitors? The secrecy option may be of the most benefit to the local community
of Swan Hill that the company has traditionally valued.
Sustainable or environmentally sound? The case says that the sink method emits at a lower rate per unit of output than the
existing process but this has little to do with the secrecy option as the rates of emissions would apply if SHC licensed the
process. This is also an argument for the licensing option, however, as environmental emissions would be lower if other
competitors switched to the sink method as well. There may be environmental implications in decommissioning the old plant
to make way for the new sink method investment.
Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:
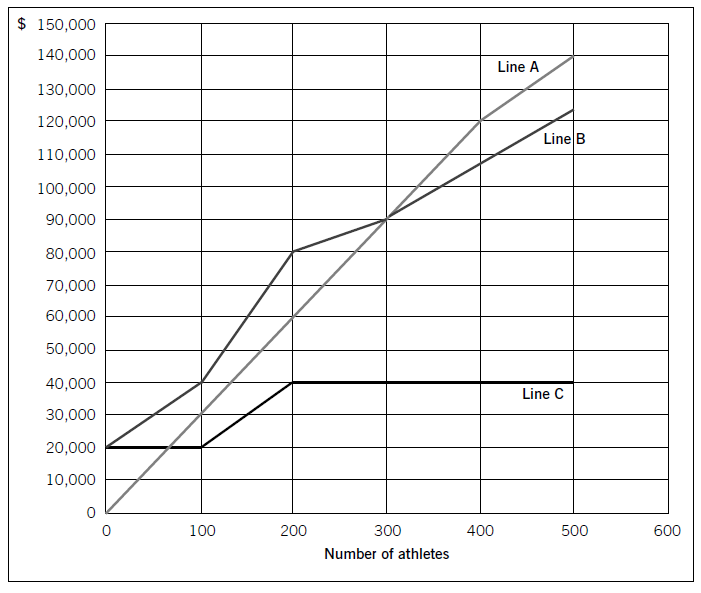
Required:
(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 marks)
(b) Using the chart above, explain the cost and revenue structure of the company. (8 marks)
(a)ThebreakevensalesrevenueforSwimCois$90,000.Thecompany’sprofit,tothenearest$10,000,if500athletesattendthecourseis$20,000($140,000–$120,000).(Fromthegraph,itisclearthatthepreciseamountwillbenearer$17,000,i.e.$140,000–approximately$123,000.)(b)CoststructureFromthechart,itisclearthatLineCrepresentsfixedcosts,LineBrepresentstotalcostsandLineArepresentstotalrevenue.LineCshowsthatinitially,fixedcostsare$20,000evenifnoathletesattendthecourse.Thisleveloffixedcostsremainsthesameif100athletesattendbutoncethenumberofattendeesincreasesabovethislevel,fixedcostsincreaseto$40,000.LineBrepresentstotalcosts.If100athletesattend,totalcostsare$40,000($400perathlete).Since$20,000ofthisrelatestofixedcosts,thevariablecostperathletemustbe$200.Whenfixedcostsstepupbeyondthispointatthelevelof200athletes,totalcostsobviouslyincreaseaswellandLineBconsequentlygetsmuchsteeper.However,sincetherearenow200athletestoabsorbthefixedcosts,thecostperathleteremainsthesameat$400perathlete($80,000/200),eventhoughfixedcostshavedoubled.If300athletesattendthecourse,totalcostperathletebecomes$300each($90,000/300).Sincefixedcostsaccountfor$40,000ofthistotalcost,variablecoststotal$50,000,i.e.$166·67perathlete.So,economiesofscaleariseatthislevel,asdemonstratedbythefactthatLineBbecomesflatter.At400athletes,thegradientofthetotalcostslineisunchangedfrom300athleteswhichindicatesthatthevariablecostshaveremainedthesame.Thereisnofurtherchangeat500athletes;fixedandvariablecostsremainsteady.RevenuestructureAsregardstherevenuestructure,itcanbeseenfromLineAthatfor100–400athletesthepriceremainsthesameat$300perathlete.However,if500athletesattend,thepricehasbeenreducedasthetotalrevenuelinebecomesflatter.$140,000/500meansthatthepricehasgonedownto$280perathlete.Thiswasobviouslynecessarytoincreasethenumberofattendeesandatthispoint,profitismaximised.1
(b) Using sensitivity analysis, estimate by what percentage each of the under-mentioned items, taken separately,
would need to change before the recommendation in (a) above is varied:
(i) Initial outlay;
(ii) Annual contribution. (4 marks)
25 What should the minority interest figure be in the group’s consolidated balance sheet at 31 December 2005?
A $240,000
B $80,000
C $180,000
D $140,000
20% x (400,000 + 800,000)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-04-23
- 2020-01-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-02-02
- 2019-12-28
- 2019-03-16
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-27