2020年ACCA考试财务管理备考资料:知识点(11)
发布时间:2020-10-10
又到了每日分享小课堂,各位赶快集合。今天51题库考试学习网分享的内容是2020年ACCA考试财务管理备考资料:知识点(11),相关考点都清楚了吗?还未了解的小伙伴一起来看看吧。
【知识点】Aspects of factoring应收账款保理
Aspects of factoring
The main aspects of factoring include the
following:
(a) Administration of the client’s
invoicing, sales accounting and debt collection service.
(b) Credit protection for the client’s
debts, whereby the factor takes over the risk of loss from bad debts and so
‘insures’ the client against such losses. This is known as a non-recourse
service. However, if a non-recourse service is provided, the factor, not the
firm, will decide what action to take against non-payers.
(c) Making payments to the client in
advance of collecting the debts. This is sometimes referred to as ‘factor
finance’ because the factor is providing cash to the client against outstanding
debts.
【知识点】The symptoms of overtrading过量交易的特征
The symptoms of overtrading
(a) There is a rapid increase in sales
revenue.
(b) There is a rapid increase in the volume
of current assets and possibly also non-current assets. Inventory turnover and
accounts receivable turnover might slow down, in which case the rate of
increase in inventories and accounts receivable would be even greater than the
rate of increase in sales.
(c) There is only a small increase in
equity capital. Most of the increase in assets is financed by credit,
especially:
i. Trade accounts payable – the payment
period to accounts payable is likely to lengthen
ii. A bank overdraft, which often reaches
or even exceeds the limit of the facilities agreed by the bank.
(d) Some debt ratios and liquidity ratios
alter dramatically.
i. The proportion of total assets financed
by proprietor’s capital falls, and the proportion financed by credit sales.
ii. The current ratio and quick ratio fall.
iii. The business might have a liquid
deficit; that is, an excess of current liabilities over current assets.
以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的全部内容,相信小伙伴们都了解清楚。预祝12月份ACCA考试取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
Section A – This ONE question is compulsory and MUST be attempted
Hesket Nuclear (HN) is a nuclear power station in Ayland, a large European country. The HN plant is operated by Hesket Power Company (HPC), which in turn is wholly owned by the government of Ayland. Initially opened in the late 1950s, the power station grew in subsequent decades by the addition of several other facilities on the same site. HN now has the ability to generate 5% of Ayland’s entire electricity demand and is one of the largest nuclear stations in Europe. At each stage of its development from the 1950s to the present day, development on the site was welcomed by the relevant local government authorities, by the businesses that have supported it, by the trade union that represents the majority of employees (called Forward Together or FT for short) and also by the national Ayland government. A nuclear reprocessing facility was added in the 1980s. This is a valuable source of overseas income as nuclear power producers in many other parts of the world send material by sea to HN to be reprocessed. This includes nuclear producers in several developing countries that rely on the cheaper reprocessed fuel (compared to ‘virgin’ fuel) that HN produces.
HPC is loss-making and receives a substantial subsidy each year from the government of Ayland. HPC has proven itself uneconomic but is deemed politically and environmentally necessary as far as the government is concerned. The government of Ayland has reluctantly accepted that large subsidies to HPC will be necessary for many years but considers nuclear power to be a vital component of its energy portfolio (along with other energy sources such as oil, gas, coal, renewables and hydroelectric) and also as a key part of its ‘clean’ energy strategy. Unlike energy from fossil fuels (such as coal, gas and oil), nuclear power generates a negligible amount of polluting greenhouse gas. HN also provides much needed employment in an otherwise deprived part of the country. The HN power station underpins and dominates the economy of its local area and local government authorities say that the HN plant is vital to the regional economy.
Since it opened, however, the HN power station has been controversial. Whilst being welcomed by those who benefi t from it in terms of jobs, trade, reprocessing capacity and energy, a coalition has gradually built up against it comprising those sceptical about the safety and environmental impact of nuclear power. Some neighbouring countries believe themselves to be vulnerable to radioactive contamination from the HN plant. In particular, two countries, both of whom say their concerns about HN arise because of their geographical positions, are vocal opponents. They say that their geographical proximity forced them to be concerned as they are affected by the location of the HN plant which was not of their choosing.
The government of Beeland, whose capital city is 70 km across the sea from HN (which is situated on the coast), has consistently opposed HN and has frequently asked the government of Ayland to close HN down. The Beeland government claims that not only does ‘low-level’ emission from the site already contaminate the waters separating the two countries but it also claims that any future major nuclear ‘incident’ would have serious implications for the citizens of Beeland. There is some scientifi c support for this view although opinion is divided over whether Beeland is being irrational in its general opposition to HN.
The government of Ceeland is also a vocal opponent of HN. Ceeland is located to the north of Beeland and approximately 500 km away from Ayland. Some nuclear scientists have said that with such a large stretch of water between the HN plant and Ceeland, even a much-feared incident would be unlikely to seriously impact on Ceeland. Some commentators have gone further and said that Ceeland’s concerns are unfounded and ‘borne of ignorance’. FT, the trade union for HN employees, issued a statement saying that Ceeland had no reason to fear HN and that its fears were ‘entirely groundless’.
HN’s other vocal and persistent opponent is No Nuclear Now (NNN), a well-organised and well-funded campaigning group. Describing itself on its website as ‘passionate about the environment’, it describes HN’s social and environmental footprint as ‘very negative’. NNN has often pointed to an environmentally important colony of rare seals living near the HN plant. It says that the seals are dependent on a local natural ecosystem around the plant and are unable to move, arguing that the animals are at signifi cant risk from low-level contamination and would have ‘no chance’ of survival if a more serious radioactive leak ever occurred. NNN points to such a leak that occurred in the 1970s, saying that such a leak proves that HN has a poor safety record and that a leak could easily recur.
Each time an objection to the HN power station is raised, FT, the trade union, robustly defends the HN site in the media, and argues for further investment, based on the need to protect the jobs at the site. Furthermore, the radiation leak in the 1970s led to FT uniting with the HPC board to argue against those stakeholders that wanted to use the leak as a reason to close the HN site. The combination of union and HPC management was able to counter the arguments of those asking for closure.
HN places a great deal of emphasis on its risk management and often publicises the fact that it conducts continual risk assessments and is in full compliance with all relevant regulatory frameworks. Similarly, FT recently pointed out that HN has had an ‘impeccable’ safety record since the incident in the 1970s and says on its website that it is ‘proud’ that its members are involved in ensuring that the company is continually in full compliance with all of the regulatory requirements placed upon it.
The board of HPC, led by chairman Paul Gog, is under continual pressure from the government of Ayland to minimise the amount of government subsidy. Each year, the government places challenging targets on the HPC board requiring stringent cost controls at the HN power station. In seeking to reduce maintenance costs on the expiry of a prior maintenance contract last year, the board awarded the new contract to an overseas company that brought its own workers in from abroad rather than employing local people. The previous contract company was outraged to have lost the contract and the move also triggered an angry response from the local workforce and from FT, the representative trade union.
FT said that it was deplorable that HPC had awarded the contract to an overseas company when a domestic company in Ayland could have been awarded the work. The union convenor, Kate Allujah, said that especially in the nuclear industry where safety was so important, domestic workers were ‘more reliable’ than foreign workers who were brought in purely on the basis of cost and in whose countries safety standards in similar industries might not be so stringent. HPC said that it had done nothing illegal as the foreign workers were allowed to work in Ayland under international legal treaties. Furthermore, it argued that pressure by FT to raise wages over recent years had created, with the government’s subsidy targets, the cost pressure to re-tender the maintenance contract.
On HN’s 50th anniversary last year, NNN published what it called a ‘risk assessment’ for the HN power station. It said it had calculated the probabilities (P) and impacts (I) of three prominent risks.
Risk of major radioactive leak over the next 10 years: P = 10%, I = 20
Risk of nuclear explosion over the next 50 years: P = 20%, I = 100
Risk of major terrorist attack over next 10 years: P = 10%, I = 80
Impacts were on an arbitrary scale of 1–100 where 100 was defi ned by NNN as ‘total nuclear annihilation of the area and thousands of deaths’.
The governments of Beeland and Ceeland seized upon the report, saying that it proved that HN is a genuine threat to their security and should be immediately closed and decommissioned. HN’s risk manager, Keith Wan, vigorously disagreed with this assessment saying that the probabilities and the impacts were ‘ridiculous’, massively overstated and intended to unnecessarily alarm people. HN’s public relations offi ce was also angry about it and said it would issue a rebuttal statement.
Required:
(a) Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary stakeholders, identifying both types of stakeholders in Hesket Nuclear. Assess the claims of THREE of the involuntary ‘affected’ stakeholders identifi ed. (12 marks)
(b) The trade union, Forward Together, has had a long relationship with HN and represents not only the main workforce but also the employees of the maintenance company replaced by the foreign workers.
Required:
Explain the roles of employee representatives such as trade unions in corporate governance and critically evaluate, from the perspective of HPC’s board, the contribution of Forward Together in the governance of HPC. (10 marks)
(c) Explain what an agency relationship is and examine the board of HPC’s current agency relationship and objectives. Briefl y explain how these would differ if HPC was a company with private shareholders. (10 marks)
(d) As a part of HPC’s public relations effort, it has been proposed that a response statement should be prepared for the company’s website to help address two major challenges to their reputation.
Required:
Draft this statement to include the following:
(i) Referring to the NNN report, explain why accurate risk assessment is necessary at Hesket Nuclear. (8 marks)
(ii) Explain what a social and environmental ‘footprint’ is and construct the argument that HN’s overall social and environmental footprint is positive. (6 marks)
Professional marks will additionally be awarded in part (d) for drafting a statement that is clear, has a logical fl ow, is persuasive and is appropriately structured. (4 marks)
(a) Distinguish and identify
Voluntary stakeholders are those that engage with an organisation of their own choice and free will. They are ultimately (in the long term) able to detach and discontinue their stakeholding if they choose. Involuntary stakeholders have their stakeholding imposed and are unable to detach or withdraw of their own volition.
The voluntary stakeholders identifi ed in the case are: Forward Together (the trade union), Hesket Nuclear employees, the Ayland government, the board of HPC, local authorities, No Nuclear Now and other nuclear producers who use the reprocessing facility.
The involuntary stakeholders – those whose stakeholding is placed upon them by virtue of their physical position – are the governments of Beeland and Ceeland, the local community and the seal colony.
[Tutorial note: membership of these categories is contestable if time perspectives are introduced. In the short term, some voluntary stakeholders are involuntary in that their involvement cannot be quickly withdrawn. The case clearly identifi es the involuntary stakeholders.]
Assess the claims
The case identifi es three ‘affected’ stakeholders that are clearly involuntary. Both Beeland and Ceeland say that they are stakeholders because of their geographical position and the seals are unable to move because of local environmental conditions.
Beeland government’s claim is based on its position near to the Hesket plant. With the capital 70 km from the plant, it claims that it is already the ‘victim’ of low level radiation in the sea between the two countries. The case does not give the radius of damage if a major incident were to occur but it does say that there is ‘scientifi c support’ for the view that it could affect the capital of Beeland. Assuming that both of these statements are accurate then the Beeland government would appear to have a legitimate and reasonable claim that they are affected by the Hesket Nuclear plant and could be further affected in the future.
The government of Ceeland claims to be a potential ‘victim’ of nuclear contamination from the HN plant and has sought to have the plant closed as a result. The weakness of its claim rests upon the physical distance away from HN (500 km). If the threats to Ceeland are, as scientists have suggested, ‘unfounded and borne of ignorance’ then clearly Ceeland has a weak claim over Hesket Nuclear. It may have political reasons of its own to make protestations, perhaps to appease opinion in Ceeland or to be populist to manage dissent at home.
The case says that the local seal colony is unable to move away from the HN plant because of the local environmental conditions there and so it is unable to discontinue its stakeholding. It is thus involuntary. Low level emissions could potentially affect the seals and their food sources and any major incident would obviously impact it signifi cantly. Whilst their affectedness is therefore indisputable, the value of the colony’s claim rests in part upon the value placed upon sea life value against human and economic value. This assessment is therefore contestable.
The local community is another involuntary stakeholder albeit with a weaker involuntary element than the above three described. Whilst not structurally involuntary (they are able to move away if they do not like it), many local citizens may have lived near the HN plant for many years before it was built and may therefore have simply had to accept its development regardless of their views. The impacts on local communities can be positive or negative in that HN supports them through the provision of jobs but they would also be the fi rst and most affected if there ever was a major incident at the HN plant.
[Tutorial note: allow for other ‘affected’ stakeholders if coherently argued. It is possible to argue that the taxpayers of Ayland are affected involuntary stakeholders, for example.]
(b) Roles of employee representatives
Trade unions are the most usual example of employee representation in corporate governance. Trade unions represent employees in a work facility such as an offi ce or a plant. Membership is voluntary and the infl uence of the union is usually proportional to its proportion of membership.
Although a trade union is by default assumed to have an adversarial role with management, its ability to ‘deliver’ the compliance of a workforce can help signifi cantly in corporate governance. When an external threat is faced, such as with the reputation losses following the 1970s leak, then the coalition of workforce (via Forward Together) and management meant that it was more diffi cult for external critics to gain support.
A trade union is an actor in the checks and balances of power within a corporate governance structure. Where management abuses occur, it is often the trade union that is the fi rst and most effective reaction against it and this can often work to the advantage of shareholders or other owners, especially when the abuse has the ability to affect productivity.
Trade unions help to maintain and control one of the most valuable assets in an organisation (employees). Where a helpful and mutually constructive relationship is cultivated between union and employer then an optimally effi cient industrial relations climate exists, thus reinforcing the productivity of human resources in the organisation. In defending members’ interests and negotiating terms and conditions, the union helps to ensure that the workforce is content and able to work with maximum effi ciency and effectiveness.
Critically evaluate the contribution of Forward Together from HPC’s perspective
Helpful roles
The case describes Forward Together’s (FT) role as generally supportive of the development of the Hesket Nuclear site. Clearly, with a primary loyalty to its members, FT will always pursue causes that are going to maximise members’ job security. When the primary external stakeholder pressure is for the reduction of the HN site, the union and board are aligned in their objectives for the continuation of the facility.
FT’s statement over Ceeland’s concern was very helpful to the HPC board. FT has a clear interest in diffusing unfounded concern where it exists and its statement that Ceeland’s fears were ‘entirely groundless’ would reinforce the power of any similar such statement made by others. Similarly, FT provided support after the leakage incident in the 1970s. The helpful reinforcement was evident when FT pointed to the impeccable safety record and compliance. This may have meant more as a public relations exercise coming from the trade union rather than the HPC board as FT is independent of the company.
Unhelpful roles
FT’s wage pressure, over time, put a pressure on the company’s costs that had, according to the HPC board, created the need to bring in cheaper foreign workers to fulfi l the maintenance contract. From the board of HPC’s viewpoint, such pressure was ultimately self-defeating for the union and effectively meant that the previous maintenance contractor was priced out. The union had been short-sighted in its year-on-year wage demands.
We are not told whether the board agrees with Kate Allujah that workers from Ayland were ‘more reliable’ in such a risk sensitive industry, but her comment was possibly based on prejudice against foreign workers entering the country. She seemed to be unconcerned with the legal implications of her outrage. Given that the company was legally entitled to employ foreign workers in Ayland, she had no valid legal argument for her position. From an economic perspective, it is also unhelpful, from HPC’s perspective to have the union making high wage demands and then complaining about legitimate measures that the company takes to stay within its government subsidy such as cutting costs, including labour costs.
Conclusion
HPC’s relationship with FT has been positive and mutually benefi cial for the majority of the company’s history. Clearly seeing their destinies to be linked, FT has supported the company against external threats but has, at the same time, used its good relations to make wage demands that ultimately led to the award of a maintenance contract to the foreign workers. This would have broken an important relationship with experienced maintenance personnel and the foreign workers may or may not have had the same level of expertise as the previous workers.
(c) Explain agency relationship
An agency relationship is one of trust between an agent and a principal which obliges the agent to meet the objectives placed upon it by the principal. As one appointed by a principal to manage, oversee or further the principal’s specifi c interests, the primary purpose of agency is to discharge its fi duciary duty to the principal. In this case, there is an agency relationship between the government and the board of HPC.
Examine existing agency relationship
Although HPC is run by a conventional board, the company is wholly owned by the government of Ayland. This means that the company’s strategic objectives are determined by the government and these are likely to be different from purely commercial concerns. The nuclear operation is clearly not economic in terms of profi t and so the government’s objectives for the company must be other than that. The case describes this in terms of broadening its energy portfolio and meeting environmental objectives. The board’s objectives are likely to be predominantly fi nancial, due to the control by subsidy placed upon it, but the principal’s political and environmental concerns may also affect the objectives placed upon the HPC board (such as employment objectives in what is a deprived region of Ayland).
The principal is the government of Ayland and ultimately the board is accountable to the taxpayers of Ayland. This means that the development and even the existence of HN is ultimately under democratic control. The agency relationship means that the board of HPC has subsidy targets and also sees its role as fulfi lling an important role in Ayland’s energy portfolio.
HPC as a ‘conventional’ company owned by private shareholders
If HPC was a private company, its principals would be shareholders with very different objectives. Shareholders would be predominantly concerned with the economic performance of HP and the economies of the nuclear power industry. It would insist that the board pursued only those parts of the business that were profi table. This would necessitate a radical redesign of HPC’s business as we are told that in its present form. it is loss-making.
(d) (i)
Statement
Hesket Power Company’s response to the report produced by NNN
Importance of risk assessment at Hesket Power Company
Hesket Power Company was recently dismayed to have been made aware of a report conducted by an anti-nuclear pressure group purporting to be a risk assessment of selected risks to the Hesket Nuclear plant. The company would like to take this opportunity to inform. the public about the irresponsibility of the pressure group’s activity whilst comprehensively rejecting its arguments.
In all industries it is important to assess risks as accurately as possible but in the nuclear power industry, it is critical. It is because the pressure group misrepresented our risks that we feel it necessary to remind stakeholders about the importance of a correct risk assessment based on valid measurements.
In observing best practice, Hesket Nuclear carries out thorough and continual risk assessments in compliance with our regulatory frameworks. The information going into the process must be as accurate as possible because resources are allocated in part on the basis of our risk assessments. Clearly, a risk assessed as probable and of high impact would attract a signifi cant resource allocation and to have incorrect information could conceivably lead to the misallocation of company resources. This, in turn, would be a failure of our duty to the HPC company and ultimately to our owners, the government of Ayland and its taxpayers. The fact that there has not been a serious incident since the 1970s highlights the efforts that we take with risk assessment.
The ways in which we manage risk also depend upon the assessment. Once a risk, such as the risk of a nuclear leakage, is identifi ed and assessed, the company pursues a strategy for managing that risk, typically to transfer or share the risk, avoid the risk, reduce it or accept it. This has implications for the entire strategy of the organisation, especially where the assessed risks are strategic in nature. Inaccurate assessment might, for example, mean accepting a risk that should have been avoided or vice versa.
Our stakeholders expect us to be a responsible company in all matters but especially in matters of safety and the environment. We owe it to our local community, employees and others to ensure that all risks are fully but accurately understood. In addition to ensuring that we are fully compliant with all regulatory regimes applicable to us, we believe that accurate risk assessment is necessary to our valued reputation as an ethical and responsible employer and neighbour.
Finally, as we have seen in the case of this misguided report by the pressure group, inaccurate assessments can breed fear, distrust and unnecessary panic. HPC was disappointed to hear the report being used by critics when the information it contained was inaccurate and this leads us to the second matter.
(ii) HN’s social and environmental ‘footprint’
HPC is aware of some critics that have asserted that our overall footprint is negative. In responding to this, we feel it necessary to remind readers that the footprint of any organisation includes the sum total of its positive and negative interactions with the environment. Whilst this sometimes involves negative impacts such as carbon emissions and accidental pollution, it also takes into account the positive impacts such as social benefi t, through such things as job creation, and positive environmental impacts. Both ‘sides’ need to be taken into account before an overall evaluation of the social and environmental footprint can be established. To focus on only a small number of measures, as some of our critics have done, is to provide an unfair and biased account of our genuine overall footprint.
Social arguments
It is our belief that Hesket Nuclear makes a substantial positive contribution on both social and environmental measures. In terms of social contribution, HN makes a positive impact for several reasons. Whilst accepting that Hesket Nuclear has its critics, the company would like to remind the public both in Ayland and Beeland that the plant is a very large employer and vital to the economic well-being of the region, a fact recognised by a wide range of local and national stakeholders. Others have noted the importance of the jobs provided at Hesket Nuclear to the social and economic well-being of the region and HPC fully agrees with this analysis.
In addition to the jobs provided in Ayland, Hesket Nuclear also provides reprocessed fuel that is cheaper than virgin fuel. This provides support for nuclear power, and hence clean energy, in several developing countries that are our valued customers. Hesket Nuclear therefore indirectly supports employment and social development in those countries. Were our reprocessed fuel unavailable to them, rates of economic and social development growth may be slowed in those countries. We are therefore determined to continue to supply this vital input into those countries and to continue to support them.
Environmental arguments
In addition, as a non-fossil fuel industry, nuclear is relatively non-polluting and is an essential component of the government of Ayland’s clean energy strategy. Hesket Nuclear is proud to be a part of that strategy and will continue to be a dependable producer of nuclear power and reprocessing services. In so doing we will continue to carefully manage the risks of nuclear power supply whilst providing the jobs and clean energy for which Hesket Nuclear is corporately responsible. A likely alternative to nuclear is the burning of more polluting fossil fuels which would presumably be as unacceptable to our critics as it is to us.
Whilst conceding that all nuclear operations require a high level of safety and regulatory observance, we are pleased to be able to remind our stakeholders, including the governments of Beeland and Ceeland, of our very high performance in this area. As our colleagues in the Forward Together trade union recently said, Hesket Nuclear has had an impeccable safety record since the 1970s and is fully compliant with all relevant safety regulations. We fully intend to maintain this high level of performance.
[Tutorial note: allow latitude in responding to part (ii), especially rewarding answers referring to the specifi c case of nuclear]
(iii) State any disadvantages to the relief in (i) that Sharon should be aware of, and identify and describe
another relief that she might use. (4 marks)
(iii) There are several disadvantages to incorporation relief as follows:
1. The requirement to transfer all business assets to the company means that it will not be possible to leave behind
certain assets, such as the property. This might lead to a double tax charge (sale of the property, then extraction
of sale proceeds) at a future date.
2. Taper relief is lost on the transfer of the business. This means that any disposal of chargeable business assets (the
shares) within two years of the incorporation will lead to a higher chargeable gain, as the full rate of business asset
taper relief will not be available.
3. The relief does not eliminate the tax charge, it merely defers the payment of tax until some future event. The
deferred gain will become taxable when Sharon sells her shares in the company.
Gift relief could be used instead of incorporation relief. The assets would be gifted to the company for no consideration,
with the base cost of the assets to the company being reduced by the deferred gain arising. Unlike incorporation relief,
gift relief applies to individual assets used in a trade and not to an entire business. This is particularly useful if the
transferor wishes to retain some assets, such as property outside the company, as not all assets have to be transferred.
Note: If the business was non-trading, incorporation relief would still be available, but gift relief would not. However,
this restriction should not apply to Sharon and gift relief remains an option in this case.
5 Crusoe has contacted you following the death of his father, Noland. Crusoe has inherited the whole of his father’s
estate and is seeking advice on his father’s capital gains tax position and the payment of inheritance tax following his
death.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Crusoe.
Noland – personal information:
– Divorcee whose only other relatives are his sister, Avril, and two grandchildren.
– Died suddenly on 1 October 2007 without having made a will.
– Under the laws of intestacy, the whole of his estate passes to Crusoe.
Noland – income tax and capital gains tax:
– Has been a basic rate taxpayer since the tax year 2000/01.
– Sales of quoted shares resulted in:
– Chargeable gains of £7,100 and allowable losses of £17,800 in the tax year 2007/08.
– Chargeable gains of approximately £14,000 each tax year from 2000/01 to 2006/07.
– None of the shares were held for long enough to qualify for taper relief.
Noland – gifts made during lifetime:
– On 1 December 1999 Noland gave his house to Crusoe.
– Crusoe has allowed Noland to continue living in the house and has charged him rent of £120 per month
since 1 December 1999. The market rent for the house would be £740 per month.
– The house was worth £240,000 at the time of the gift and £310,000 on 1 October 2007.
– On 1 November 2004 Noland transferred quoted shares worth £232,000 to a discretionary trust for the benefit
of his grandchildren.
Noland – probate values of assets held at death: £
– Portfolio of quoted shares 370,000
Shares in Kurb Ltd 38,400
Chattels and cash 22,300
Domestic liabilities including income tax payable (1,900)
– It should be assumed that these values will not change for the foreseeable future.
Kurb Ltd:
– Unquoted trading company
– Noland purchased the shares on 1 December 2005.
Crusoe:
– Long-standing personal tax client of your firm.
– Married with two young children.
– Successful investment banker with very high net worth.
– Intends to gift the portfolio of quoted shares inherited from Noland to his aunt, Avril, who has very little personal
wealth.
Required:
(a) Prepare explanatory notes together with relevant supporting calculations in order to quantify the tax relief
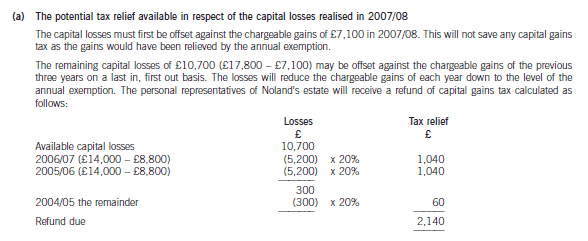
potentially available in respect of Noland’s capital losses realised in 2007/08. (4 marks)
One of your audit clients is Tye Co a company providing petrol, aviation fuel and similar oil based products to the government of the country it is based in. Although the company is not listed on any stock exchange, it does follow best practice regarding corporate governance regulations. The audit work for this year is complete, apart from the matter referred to below.
As part of Tye Co’s service contract with the government, it is required to hold an emergency inventory reserve of 6,000 barrels of aviation fuel. The inventory is to be used if the supply of aviation fuel is interrupted due to unforeseen events such as natural disaster or terrorist activity.
This fuel has in the past been valued at its cost price of $15 a barrel. The current value of aviation fuel is $120 a barrel. Although the audit work is complete, as noted above, the directors of Tye Co have now decided to show the ‘real’ value of this closing inventory in the financial statements by valuing closing inventory of fuel at market value, which does not comply with relevant accounting standards. The draft financial statements of Tye Co currently show a profit of approximately $500,000 with net assets of $170 million.
Required:
(a) List the audit procedures and actions that you should now take in respect of the above matter. (6 marks)
(b) For the purposes of this section assume from part (a) that the directors have agreed to value inventory at
$15/barrel.
Having investigated the matter in part (a) above, the directors present you with an amended set of financial
statements showing the emergency reserve stated not at 6,000 barrels, but reported as 60,000 barrels. The final financial statements now show a profit following the inclusion of another 54,000 barrels of oil in inventory. When queried about the change from 6,000 to 60,000 barrels of inventory, the finance director stated that this change was made to meet expected amendments to emergency reserve requirements to be published in about six months time. The inventory will be purchased this year, and no liability will be shown in the financial statements for this future purchase. The finance director also pointed out that part of Tye Co’s contract with the government requires Tye Co to disclose an annual profit and that a review of bank loans is due in three months. Finally the finance director stated that if your audit firm qualifies the financial statements in respect of the increase in inventory, they will not be recommended for re-appointment at the annual general meeting. The finance director refuses to amend the financial statements to remove this ‘fictitious’ inventory.
Required:
(i) State the external auditor’s responsibilities regarding the detection of fraud; (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss to which groups the auditors of Tye Co could report the ‘fictitious’ aviation fuel inventory;
(6 marks)
(iii) Discuss the safeguards that the auditors of Tye Co can use in an attempt to overcome the intimidation
threat from the directors of Tye Co. (4 marks)
(a)Valuationofaviationinventory–ReviewGAAPtoensurethattherearenoexceptionsforaviationfuelorinventoryheldforemergencypurposeswhichwouldsuggestamarketvaluationshouldbeused.–Calculatethedifferenceinvaluation.Theerrorininventoryvaluationis$105*6,000barrelsor$630k,whichisamaterialamountcomparedtoprofit.–Reviewprioryearworkingpaperstodeterminewhetherasimilarsituationoccurredlastyearandascertaintheoutcomeatthatstage.–Discussthematterwiththedirectorstoobtainreasonswhytheybelievethatmarketvalueshouldbeusedfortheinventorythisyear.–Warnthedirectorsthatinyouropinion,aviationfuelshouldbevaluedatthelowerofcostornetrealisablevalue(thatis$15/barrel)andthatusingmarketvaluewillresultinamodificationtotheauditreport.–Ifthedirectorsnowamendthefinancialstatementstoshowinventoryvaluedatcost,thenconsidermentioningtheissueintheweaknessletteranddonotmodifytheauditreportinrespectofthismatter.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,quantifytheeffectofthedisagreementinthevaluationmethod–thesumof$630,000ismaterialtothefinancialstatementsasTyeCo’sincomestatementfigureisdecreasedfromasmalllosstoalossof$130,000althoughnetassetsdecreasebyonlyabout0·3%.–ObtainamanagementrepresentationletterfromthedirectorsofTyeCoconfirmingthatmarketvalueistobeusedfortheemergencyinventoryofaviationfuel.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,drafttherelevantsectionsoftheauditreport,showingaqualificationonthegroundsofdisagreementwiththeaccountingpolicyforvaluationofinventory.(b)(i)ExternalauditorresponsibilitiesregardingdetectionoffraudOverallresponsibilityofauditorTheexternalauditorisprimarilyresponsiblefortheauditopiniononthefinancialstatementsfollowingtheinternationalauditingstandards(ISAs).ISA240(Redrafted)TheAuditor’sResponsibilitiesRelatingtoFraudinanAuditofFinancialStatementsisrelevanttoauditworkregardingfraud.Themainfocusofauditworkisthereforetoensurethatthefinancialstatementsshowatrueandfairview.Thedetectionoffraudisthereforenotthemainfocusoftheexternalauditor’swork.Anauditorisresponsibleforobtainingreasonableassurancethatthefinancialstatementsasawholearefreefrommaterialmisstatement,whethercausedbyfraudorerror.Theauditorisresponsibleformaintaininganattitudeofprofessionalscepticismthroughouttheaudit,consideringthepotentialformanagementoverrideofcontrolsandrecognisingthefactthatauditproceduresthatareeffectivefordetectingerrormaynotbeeffectivefordetectingfraud.MaterialityISA240statesthattheauditorshouldreduceauditrisktoanacceptablylowlevel.Therefore,inreachingtheauditopinionandperformingauditwork,theexternalauditortakesintoaccounttheconceptofmateriality.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorisnotresponsibleforcheckingallthetransactions.Auditproceduresareplannedtohaveareasonablelikelihoodofidentifyingmaterialfraud.DiscussionamongtheauditteamAdiscussionisrequiredamongtheengagementteamplacingparticularemphasisonhowandwheretheentity’sfinancialstatementsmaybesusceptibletomaterialmisstatementduetofaud,includinghowfraudmightoccur.IdentificationoffraudInsituationswheretheexternalauditordoesdetectfraud,thentheauditorwillneedtoconsidertheimplicationsfortheentireaudit.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorhasaresponsibilitytoextendtestingintootherareasbecausetheriskofprovidinganincorrectauditopinionwillhaveincreased.(ii)GroupstoreportfraudtoReporttoauditcommitteeDisclosethesituationtotheauditcommitteeastheyarechargedwithmaintainingahighstandardofgovernanceinthecompany.Thecommitteeshouldbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththedirectorsandrecommendthattheytakeappropriateactione.g.amendthefinancialstatements.ReporttogovernmentAsTyeCoisactingunderagovernmentcontract,andtheover-statementofinventorywillmeanTyeCobreachesthatcontract(thereportedprofitbecomingaloss),thentheauditormayhavetoreportthesituationdirectlytothegovernment.TheauditorofTyeConeedstoreviewthecontracttoconfirmthereportingrequiredunderthatcontract.ReporttomembersIfthefinancialstatementsdonotshowatrueandfairviewthentheauditorneedstoreportthisfacttothemembersofTyeCo.Theauditreportwillbequalifiedwithanexceptfororadverseopinion(dependingonmateriality)andinformationconcerningthereasonforthedisagreementgiven.Inthiscasetheauditorislikelytostatefactuallytheproblemofinventoryquantitiesbeingincorrect,ratherthanstatingorimplyingthatthedirectorsareinvolvedinfraud.ReporttoprofessionalbodyIftheauditorisuncertainastothecorrectcourseofaction,advicemaybeobtainedfromtheauditor’sprofessionalbody.Dependingontheadvicereceived,theauditormaysimplyreporttothemembersintheauditreport,althoughresignationandtheconveningofageneralmeetingisanotherreportingoption.(iii)Intimidationthreat–safeguardsInresponsetotheimpliedthreatofdismissaliftheauditreportismodifiedregardingthepotentialfraud/error,thefollowingsafeguardsareavailabletotheauditor.DiscusswithauditcommitteeThesituationcanbediscussedwiththeauditcommittee.Astheauditcommitteeshouldcomprisenon-executivedirectors,theywillbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththefinancedirectorandpointoutclearlytheauditor’sopinion.Theycanalsoremindthedirectorsasawholethattheappointmentoftheauditorrestswiththemembersontherecommendationoftheauditcommittee.Iftherecommendationoftheauditcommitteeisrejectedbytheboard,goodcorporategovernancerequiresdisclosureofthereasonforrejection.ObtainsecondpartnerreviewTheengagementpartnercanaskasecondpartnertoreviewtheworkingpapersandotherevidencerelatingtotheissueofpossiblefraud.Whilethisactiondoesnotresolvetheissue,itdoesprovideadditionalassurancethatthefindingsandactionsoftheengagementpartnerarevalid.ResignationIfthematterisserious,thentheauditorcanconsiderresignationratherthannotbeingre-appointed.Resignationhastheadditionalsafeguardthattheauditorcannormallyrequirethedirectorstoconveneageneralmeetingtoconsiderthecircumstancesoftheresignation.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2019-11-28
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2019-11-28
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2019-11-28
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18