注意查看!2020年陕西省ACCA考试报名时间
发布时间:2020-09-03
ACCA在国内称为“国际注册会计师”,ACCA资格被认为是“国际财会界的通行证”。陕西的考生请注意,2020年ACCA考试报名时间已经公布了,51题库考试学习网为大家带来了报名相关事宜,让我们一起来看看吧!
一、报名时间及费用缴纳:
|
2020年12月ACCA考试报名时间、考试费用- |
|||
|
报名周期 |
报名(截止)日期 |
考试科目 |
考试费用 |
|
提前报名截止 |
2020年8月10日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
123英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
210英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
164英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
164英镑 |
||
|
常规报名截止 |
2020年11月2日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
130英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
222英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
173英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
173英镑 |
||
|
后期报名截止 |
2020年11月9日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
332英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
358英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
358英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
358英镑 |
||
二、ACCA报考条件:
1.凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2.教育部认可的高等院校在校生,顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3.未符合1、2项报名资格的16周岁以上的申请者,也可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成基础商业会计(FAB)、基础管理会计(FMA)、基础财务会计(FFA)3门课程,并完成ACCA基础职业模块,可获得ACCA商业会计师资格证书(Diploma in Accounting and Business),资格证书后可豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入技能课程的考试。
三、报名规则:
1.申请参加ACCA考试者,必须先注册成为ACCA学员。
2.学员必须按考试大纲设置的先后次序报考,即应用知识模块,应用技能模块,战略专业模块。同一个模块里的课程可以选择任意顺序报考,但建议在同一个模块中也按照课程顺序报考。
3.基础阶段的应用知识模块考试时间为两小时,基础阶段的应用技能模块和战略专业阶段的所有课程考试时间为三小时,及格成绩为50分(百分制)。从2016年起,ACCA实行4个考季,即学员可选择在3、6、9、12月考季在当地考点进行考试。学员每年最多可报考8门不相同的科目。
请注意:中国大陆地区自2018年3月考季开始将取消PM-FM的笔试。
4.基础阶段9门考试不设时限;专业阶段考试年限为7年,从通过第一门战略专业阶段考试之日算起。
5.考试的报名时间不同,考试资费标准就不同(该优惠政策仅限网上报名)。较早报名考试,费用会相对较少。报考时间分为提前报名时段,常规报名时段和后期报名时段。
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,各位小伙伴根据自己的情况进行查阅,希望本文对各位有所帮助,预祝各位取得满意的成绩,如需了解更多相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
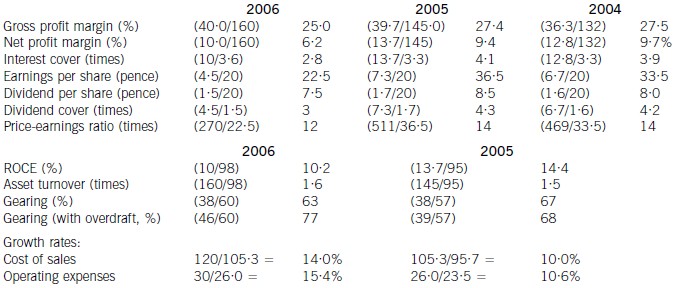
(ii) the recent financial performance of Merton plc from a shareholder perspective. Clearly identify any
issues that you consider should be brought to the attention of the ordinary shareholders. (15 marks)
(ii) Discussion of financial performance
It is clear that 2006 has been a difficult year for Merton plc. There are very few areas of interest to shareholders where
anything positive can be found to say.
Profitability
Return on capital employed has declined from 14·4% in 2005, which compared favourably with the sector average of
12%, to 10·2% in 2006. Since asset turnover has improved from 1·5 to 1·6 in the same period, the cause of the decline
is falling profitability. Gross profit margin has fallen each year from 27·5% in 2004 to 25% in 2006, equal to the sector
average, despite an overall increase in turnover during the period of 10% per year. Merton plc has been unable to keep
cost of sales increases (14% in 2006 and 10% in 2005) below the increases in turnover. Net profit margin has declined
over the same period from 9·7% to 6·2%, compared to the sector average of 8%, because of substantial increases in
operating expenses (15·4% in 2006 and 10·6% in 2005). There is a pressing need here for Merton plc to bring cost
of sales and operating costs under control in order to improve profitability.
Gearing and financial risk
Gearing as measured by debt/equity has fallen from 67% (2005) to 63% (2006) because of an increase in
shareholders’ funds through retained profits. Over the same period the overdraft has increased from £1m to £8m and
cash balances have fallen from £16m to £1m. This is a net movement of £22m. If the overdraft is included, gearing
has increased to 77% rather than falling to 63%.
None of these gearing levels compare favourably with the average gearing for the sector of 50%. If we consider the large
increase in the overdraft, financial risk has clearly increased during the period. This is also evidenced by the decline in
interest cover from 4·1 (2005) to 2·8 (2006) as operating profit has fallen and interest paid has increased. In each year
interest cover has been below the sector average of eight and the current level of 2·8 is dangerously low.
Share price
As the return required by equity investors increases with increasing financial risk, continued increases in the overdraft
will exert downward pressure on the company’s share price and further reductions may be expected.
Investor ratios
Earnings per share, dividend per share and dividend cover have all declined from 2005 to 2006. The cut in the dividend
per share from 8·5 pence per share to 7·5 pence per share is especially worrying. Although in its announcement the
company claimed that dividend growth and share price growth was expected, it could have chosen to maintain the
dividend, if it felt that the current poor performance was only temporary. By cutting the dividend it could be signalling
that it expects the poor performance to continue. Shareholders have no guarantee as to the level of future dividends.
This view could be shared by the market, which might explain why the price-earnings ratio has fallen from 14 times to
12 times.
Financing strategy
Merton plc has experienced an increase in fixed assets over the last period of £10m and an increase in stocks and
debtors of £21m. These increases have been financed by a decline in cash (£15m), an increase in the overdraft (£7m)
and an increase in trade credit (£6m). The company is following an aggressive strategy of financing long-term
investment from short-term sources. This is very risky, since if the overdraft needed to be repaid, the company would
have great difficulty in raising the funds required.
A further financing issue relates to redemption of the existing debentures. The 10% debentures are due to be redeemed
in two years’ time and Merton plc will need to find £13m in order to do this. It does not appear that this sum can be
raised internally. While it is possible that refinancing with debt paying a lower rate of interest may be possible, the low
level of interest cover may cause concern to potential providers of debt finance, resulting in a higher rate of interest. The
Finance Director of Merton plc needs to consider the redemption problem now, as thought is currently being given to
raising a substantial amount of new equity finance. This financing choice may not be available again in the near future,
forcing the company to look to debt finance as a way of effecting redemption.
Overtrading
The evidence produced by the financial analysis above is that Merton plc is showing some symptoms of overtrading
(undercapitalisation). The board are suggesting a rights issue as a way of financing an expansion of business, but it is
possible that a rights issue will be needed to deal with the overtrading problem. This is a further financing issue requiring
consideration in addition to the redemption of debentures mentioned earlier.
Conclusion
Ordinary shareholders need to be aware of the following issues.
1. Profitability has fallen over the last year due to poor cost control
2. A substantial increase in the overdraft over the last year has caused gearing to increase
3. It is possible that the share price will continue to fall
4. The dividend cut may warn of continuing poor performance in the future
5. A total of £13m of debentures need redeeming in two year’s time
6. A large amount of new finance is needed for working capital and debenture redemption
Appendix: Analysis of key ratios and financial information
(c) (i) Explain the inheritance tax (IHT) implications and benefits of Alvaro Pelorus varying the terms of his
father’s will such that part of Ray Pelorus’s estate is left to Vito and Sophie. State the date by which a
deed of variation would need to be made in order for it to be valid; (3 marks)
(c) (i) Variation of Ray’s will
The variation by Alvaro of Ray’s will, such that assets are left to Vito and Sophie, will not be regarded as a gift by Alvaro.
Instead, provided the deed states that it is intended to be effective for IHT purposes, it will be as if Ray had left the assets
to the children in his will.
This strategy, known as skipping a generation, will have no effect on the IHT due on Ray’s death but will reduce the
assets owned by Alvaro and thus his potential UK IHT liability. A deed of variation is more tax efficient than Alvaro
making gifts to the children as such gifts would be PETs and IHT may be due if Alvaro were to die within seven years.
The deed of variation must be entered into by 31 January 2009, i.e. within two years of the date of Ray’s death.
6 (a) Explain the term ‘money laundering’. (3 marks)
6 MONEY LAUNDERING
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) Meaning of the term
■ Money laundering is the process by which criminals attempt to conceal the true origin and ownership of the proceeds
of their criminal activity (‘dirty’ money) allowing them to maintain control over the proceeds and, ultimately, providing a
legitimate cover for their sources of income.
■ The term is widely defined to include:
– possessing; or
– in any way dealing with; or
– concealing
the proceeds of any crime (‘criminal property’).
■ It also includes:
– an attempt or conspiracy or incitement to commit such an offence; or
– aiding, abetting, counselling or procuring the commission of such an offence.
■ Further, it includes failure by an individual in a regulated sector to inform. the financial intelligence unit (FIU), as soon
as practicable, of knowledge or suspicion that another person is engaged in money laundering.
Tutorial note: The FIU serves as a national centre for receiving (and, as permitted, requesting), analysing and
disseminating suspicious transaction reports (STRs).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-27
- 2021-04-22
- 2021-04-02
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-04-08
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-05-01
- 2021-06-19
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-07-04
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-22
- 2021-04-24
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-23
- 2021-01-13
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-02-22
- 2021-10-23
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-27
- 2021-09-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-28