2020年湖南12月ACCA考试报名时间,速围观!
发布时间:2020-08-13
2020年湖南ACCA考试9月报名时间已经结束,想要报考的小伙伴现在只能报考ACCA12月的考试,那么ACCA12月考试报名时间是什么时候呢?下面51题库考试学习网就带领大家一起来看看,想要了解的小伙伴赶紧来围观吧。
12月ACCA考试报名截止时间:
提前报名截止:2020年8月10日
常规报名截止:2020年10月26日
后期报名截止:2020年11月02日
参加ACCA考试,需要先注册ACCA学员。
ACCA考试注册流程
注册报名:
1、准备注册所需材料
2、在全球官方网站进行注册
–2.1在线上传注册资料扫描文件
–2.2采用纸质材料将注册资料递交ACCA代表处
3、支付注册费用
注:采用在线上传资料方式的必须在线支付
4、查询注册进度
–4.1线上完成全部注册的约2周
–4.2纸质注册约6周
在校学生所需准备的注册材料:
中英文在校证明(原件必须为彩色扫描件)
中英文成绩单(均需为加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件)
中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件)
2寸彩色护照用证件照一张
用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(推荐使用Visa)
非在校学生所需准备的注册资料(符合学历要求):
中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章的彩色扫描件)
中英文学历证明(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章的彩色扫描件MPAcc专业,需提供中英文成绩单*国外学历均需提供成绩单)
2寸彩色护照证件照一张
用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(推荐使用Visa)
非在校学生所需准备的注册资料(不符合学历要求-FIA形式):
中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章或者学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件)
2寸彩色护照证件照一张
用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票(推荐使用Visa)
如何进行ACCA考位预约?
1、进入ACCA官网登录myACCA账号;
2、选择 EXAM
ENTRY 然后进入报名页面;
3、选择下方的机考栏目中的 China,点击Book a session CBE ,进入到后续报名页面;
4、然后在后续页面中选择科目等信息,机考报名的操作流程非常简单清晰,一般不会弄错;
5、点击下方考试科目自动弹出考试地点的选择,填写合适的城市就会自动生成考试报名信息,只要添加到考试计划中缴费确认即可报名成功。
以上是本次51题库考试学习网带给大家的内容,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
The following financial information relates to HGR Co:
Statement of financial position at the current date (extracts)
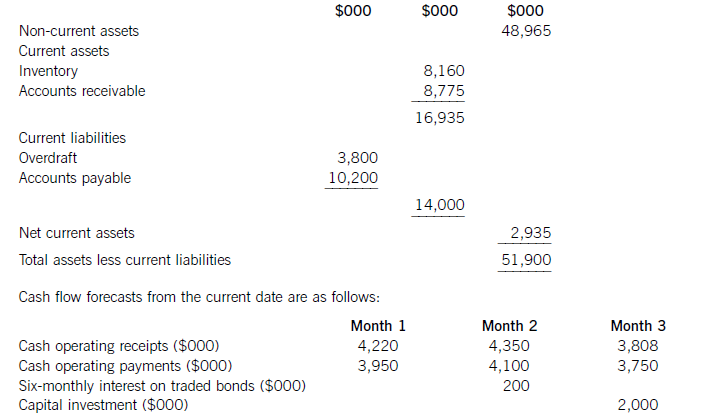
The finance director has completed a review of accounts receivable management and has proposed staff training and operating procedure improvements, which he believes will reduce accounts receivable days to the average sector value of 53 days. This reduction would take six months to achieve from the current date, with an equal reduction in each month. He has also proposed changes to inventory management methods, which he hopes will reduce inventory days by two days per month each month over a three-month period from the current date. He does not expect any change in the current level of accounts payable.
HGR Co has an overdraft limit of $4,000,000. Overdraft interest is payable at an annual rate of 6·17% per year, with payments being made each month based on the opening balance at the start of that month. Credit sales for the year to the current date were $49,275,000 and cost of sales was $37,230,000. These levels of credit sales and cost of sales are expected to be maintained in the coming year. Assume that there are 365 working days in each year.
Required:
(a) Discuss the working capital financing strategy of HGR Co. (7 marks)
(b) For HGR Co, calculate:
(i) the bank balance in three months’ time if no action is taken; and
(ii) the bank balance in three months’ time if the finance director’s proposals are implemented.
Comment on the forecast cash flow position of HGR Co and recommend a suitable course of action.
(10 marks)
(c) Discuss how risks arising from granting credit to foreign customers can be managed and reduced.
(8 marks)
(a)Whenconsideringthefinancingofworkingcapital,itisusefultodividecurrentassetsintofluctuatingcurrentassetsandpermanentcurrentassets.Fluctuatingcurrentassetsrepresentchangesinthelevelofcurrentassetsduetotheunpredictabilityofbusinessactivity.Permanentcurrentassetsrepresentthecorelevelofinvestmentincurrentassetsneededtosupportagivenlevelofturnoverorbusinessactivity.Asturnoverorlevelofbusinessactivityincreases,thelevelofpermanentcurrentassetswillalsoincrease.Thisrelationshipcanbemeasuredbytheratioofturnovertonetcurrentassets.Thefinancingchoiceasfarasworkingcapitalisconcernedisbetweenshort-termandlong-termfinance.Short-termfinanceismoreflexiblethanlong-termfinance:anoverdraft,forexample,isusedbyabusinessorganisationastheneedarisesandvariableinterestischargedontheoutstandingbalance.Short-termfinanceisalsomoreriskythanlong-termfinance:anoverdraftfacilitymaybewithdrawn,orashort-termloanmayberenewedonlessfavourableterms.Intermsofcost,thetermstructureofinterestratessuggeststhatshort-termdebtfinancehasalowercostthanlong-termdebtfinance.Thematchingprinciplesuggeststhatlong-termfinanceshouldbeusedforlong-terminvestment.Applyingthisprincipletoworkingcapitalfinancing,long-termfinanceshouldbematchedwithpermanentcurrentassetsandnon-currentassets.Afinancingpolicywiththisobjectiveiscalleda‘matchingpolicy’.HGRCoisnotusingthisfinancingpolicy,sinceofthe$16,935,000ofcurrentassets,$14,000,000or83%isfinancedfromshort-termsources(overdraftandtradepayables)andonly$2,935,000or17%isfinancedfromalong-termsource,inthiscaseequityfinance(shareholders’funds)ortradedbonds.ThefinancingpolicyorapproachtakenbyHGRCotowardsthefinancingofworkingcapital,whereshort-termfinanceispreferred,iscalledanaggressivepolicy.Relianceonshort-termfinancemakesthisriskierthanamatchingapproach,butalsomoreprofitableduetothelowercostofshort-termfinance.Followinganaggressiveapproachtofinancingcanleadtoovertrading(undercapitalisation)andthepossibilityofliquidityproblems.(b)Bankbalanceinthreemonths’timeifnoactionistaken:Workings:ReductioninaccountsreceivabledaysCurrentaccountsreceivabledays=(8,775/49,275)x365=65daysReductionindaysoversixmonths=65–53=12daysMonthlyreduction=12/6=2daysEachreceivablesdayisequivalentto8,775,000/65=$135,000(Alternatively,eachreceivablesdayisequivalentto49,275,000/365=$135,000)Monthlyreductioninaccountsreceivable=2x135,000=$270,000ReductionininventorydaysCurrentinventorydays=(8,160/37,230)x365=80daysEachinventorydayisequivalentto8,160,000/80=$102,000(Alternatively,eachinventoryday=37,230,000/365=$102,000)Monthlyreductionininventory=102,000x2=$204,000OverdraftinterestcalculationsMonthlyoverdraftinterestrate=1·06171/12=1·005or0·5%Ifnoactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0·005=$19,000Period2interest=3,549,000x0·005=$17,745or$18,000Period3interest=3,517,000x0·005=$17,585or$18,000Ifactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0.005=$19,000Period2interest=3,075,000x0.005=$15,375or$15,000Period3interest=2,566,000x0.005=$12,830or$13,000DiscussionIfnoactionistaken,thecashflowforecastshowsthatHGRCowillexceeditsoverdraftlimitof$4millionby$1·48millioninthreemonths’time.Ifthefinancedirector’sproposalsareimplemented,thereisapositiveeffectonthebankbalance,buttheoverdraftlimitisstillexceededinthreemonths’time,althoughonlyby$47,000ratherthanby$1·47million.Ineachofthethreemonthsfollowingthat,thecontinuingreductioninaccountsreceivabledayswillimprovethebankbalanceby$270,000permonth.Withoutfurtherinformationonoperatingreceiptsandpayments,itcannotbeforecastwhetherthebankbalancewillreturntolessthanthelimit,orevencontinuetoimprove.Themainreasonfortheproblemwiththebankbalanceisthe$2millioncapitalexpenditure.Purchaseofnon-currentassetsshouldnotbefinancedbyanoverdraft,butalong-termsourceoffinancesuchasequityorbonds.Ifthecapitalexpenditurewereremovedfromtheareaofworkingcapitalmanagement,theoverdraftbalanceattheendofthreemonthswouldbe$3·48millionifnoactionweretakenand$2·05millionifthefinancedirector’sproposalswereimplemented.GiventhatHGRCohasalmost$50millionofnon-currentassetsthatcouldpossiblybeusedassecurity,raisinglong-termdebtthrougheitherabankloanorabondissueappearstobesensible.Assumingabondinterestrateof10%peryear,currentlong-termdebtintheform.oftradedbondsisapproximately($200mx2)/0·1=$4m,whichismuchlessthantheamountofnoncurrentassets.AsuitablecourseofactionforHGRCotofollowwouldthereforebe,firstly,toimplementthefinancedirector’sproposalsand,secondly,tofinancethecapitalexpenditurefromalong-termsource.Considerationcouldalsobegiventousingsomelong-termdebtfinancetoreducetheoverdraftandtoreducethelevelofaccountspayable,currentlystandingat100days.(c)Whencreditisgrantedtoforeigncustomers,twoproblemsmaybecomeespeciallysignificant.First,thelongerdistancesoverwhichtradetakesplaceandthemorecomplexnatureoftradetransactionsandtheirelementsmeansforeignaccountsreceivableneedmoreinvestmentthantheirdomesticcounterparts.Longertransactiontimesincreaseaccountsreceivablebalancesandhencetheleveloffinancingandfinancingcosts.Second,theriskofbaddebtsishigherwithforeignaccountsreceivablethanwiththeirdomesticcounterparts.Inordertomanageandreducecreditrisks,therefore,exportersseektoreducetheriskofbaddebtandtoreducethelevelofinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivable.Manyforeigntransactionsareon‘openaccount’,whichisanagreementtosettletheamountoutstandingonapredetermineddate.Openaccountreflectsagoodbusinessrelationshipbetweenimporterandexporter.Italsocarriesthehighestriskofnon-payment.Onewaytoreduceinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableistoagreeearlypaymentwithanimporter,forexamplebypaymentinadvance,paymentonshipment,orcashondelivery.Thesetermsoftradeareunlikelytobecompetitive,however,anditismorelikelythatanexporterwillseektoreceivecashinadvanceofpaymentbeingmadebythecustomer.Onewaytoacceleratecashreceiptsistousebillfinance.Billsofexchangewithasignedagreementtopaytheexporteronanagreedfuturedate,supportedbyadocumentaryletterofcredit,canbediscountedbyabanktogiveimmediatefunds.Thisdiscountingiswithoutrecourseifbillsofexchangehavebeencountersignedbytheimporter’sbank.Documentarylettersofcreditareapaymentguaranteebackedbyoneormorebanks.Theycarryalmostnorisk,providedtheexportercomplieswiththetermsandconditionscontainedintheletterofcredit.Theexportermustpresentthedocumentsstatedintheletter,suchasbillsoflading,shippingdocuments,billsofexchange,andsoon,whenseekingpayment.Aseachsupportingdocumentrelatestoakeyaspectoftheoveralltransaction,lettersofcreditgivesecuritytotheimporteraswellastheexporter.Companiescanalsomanageandreduceriskbygatheringappropriateinformationwithwhichtoassessthecreditworthinessofnewcustomers,suchasbankreferencesandcreditreports.Insurancecanalsobeusedtocoversomeoftherisksassociatedwithgivingcredittoforeigncustomers.Thiswouldavoidthecostofseekingtorecovercashduefromforeignaccountsreceivablethroughaforeignlegalsystem,wheretheexportercouldbeatadisadvantageduetoalackoflocalorspecialistknowledge.Exportfactoringcanalsobeconsidered,wheretheexporterpaysforthespecialistexpertiseofthefactorasawayofreducinginvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableandreducingtheincidenceofbaddebts.
Assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2004 apply throughout.
(b) Explain the corporation tax (CT) and value added tax (VAT) issues that Irroy should be aware of, if she
proceeds with her proposal for the Irish subsidiary, Green Limited. Your answer should clearly identify those
factors which will determine whether or not Green Limited is considered UK resident or Irish resident and
the tax implications of each alternative situation.
You need not repeat points that are common to each situation. (16 marks)
(b) There are several matters that Irroy will need to be aware of in relation to value added tax and corporation tax. These are set
out below.
Residence of subsidiary
Irroy will want to ensure that the subsidiary is treated as being resident in the Republic of Ireland. It will then pay corporation
tax on its profits at lower rates than in the UK. The country of incorporation usually claims taxing rights, but this is not by
itself sufficient. Irroy needs to be aware that a company can be treated as UK resident by virtue of the location of its central
management and control. This is usually defined as being where the board of directors meets to make strategic decisions. As
a result, Irroy needs to ensure that board meetings are conducted outside the UK.
If Green Limited is treated as being UK resident, it will be taxed in the UK on its worldwide income, including that arising in
the Republic of Ireland. However, as it will be conducting trading activities in the Republic of Ireland, Green Limited will also
be treated as being Irish resident as its activities in that country are likely to constitute a permanent establishment. Thus it
may also suffer tax in the Republic of Ireland as a consequence, although double tax relief will be available (see later).
A permanent establishment is broadly defined as a fixed place of business through which a business is wholly or partly carried
on. Examples of a permanent establishment include an office, factory or workshop, although certain activities (such as storage
or ancillary activities) can be excluded from the definition.
If Green Limited is treated as being an Irish resident company, any dividends paid to Aqua Limited will be taxed under
Schedule D Case V in the UK. Despite being non resident, Green Limited will still count as an associate of the existing UK
companies, and may affect the rates of tax paid by Aqua Limited and Aria Limited in the UK. However, as a non UK resident
company, Green Limited will not be able to claim losses from the UK companies by way of group relief.
Double tax relief
If Green Limited is treated as UK resident, corporation tax at UK rates will be payable on all profits earned. However, income
arising in the Republic of Ireland is likely to have been taxed in that country also by virtue of having a permanent
establishment located there. As the same profits have been taxed twice, double tax relief is available, either by reference to
the tax treaty between the UK and the Republic of Ireland, or on a unilateral basis, where the UK will give relief for the foreign
tax suffered.
If Green Limited is treated as an Irish resident company, it will pay tax in the Republic of Ireland, based on its worldwide
taxable profits. However, any repatriation of profits to the UK by dividend will be taxed on a receipts basis in the UK. Again,
double tax relief will be available as set out above.
Double tax relief is available against two types of tax. For payments made by Green Limited to Aqua Limited on which
withholding tax has been levied, credit will be given for the tax withheld. In addition, relief is available for the underlying tax
where a dividend is received from a foreign company in which Aqua Limited owns at least 10% of the voting power. The
underlying tax is the tax attributable to the relevant profits from which the dividend was paid.
Double tax relief is given at the lower rate of the UK tax and the foreign tax (withholding and underlying taxes) suffered.
Transfer pricing
Where groups have subsidiaries in other countries, they may be tempted to divert profits to subsidiaries which pay tax at lower
rates. This can be achieved by artificially changing the prices charged (known as the transfer price) between the group
companies. While they can do this commercially through common control, anti avoidance legislation seeks to correct this by
ensuring that for taxation purposes, profits on such intra-group transactions are calculated as if the transactions were carried
out on an arms length basis. Since 1 April 2004, this legislation can also be applied to transactions between UK group
companies.
If Green Limited is treated as a UK resident company, the group’s status as a small or medium sized enterprise means that
transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Limited and the other UK group companies.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, transfer pricing issues will not apply to transactions between Green Ltd and the
UK resident companies because of the group’s status as a small or medium-sized enterprise and the existence of a double
tax treaty, based on the OECD model, between the UK and the Republic of Ireland.
Controlled foreign companies
Tax legislation exists to stop a UK company accumulating profits in a foreign subsidiary which is subject to a low tax rate.
Such a subsidiary is referred to as a controlled foreign company (CFC), and exists where:
(1) the company is resident outside the UK, and
(2) is controlled by a UK resident entity or persons, and
(3) pays a ‘lower level of tax’ in its country of residence.
A lower level of tax is taken to be less than 75% of the tax that would have been payable had the company been UK resident.
If Green Limited is an Irish resident company, it will be paying corporation tax at 12·5% so would appear to be caught by
the above rules and is therefore likely to be treated as a CFC.
Where a company is treated as a CFC, its profits are apportioned to UK resident companies entitled to at least 25% of its
profits. For Aqua Limited, which would own 100% of the shares in Green Limited, any profits made by Green Limited would
be apportioned to Aqua Limited as a deemed distribution. Aqua Limited would be required to self-assess this apportionment
on its tax return and pay UK tax on the deemed distribution (with credit being given for the Irish tax suffered).
There are some exemptions which if applicable the CFC legislation does not apply and no apportionments of profits will be
made. These include where chargeable profits of the CFC do not exceed £50,000 in an accounting period, or where the CFC
follows an acceptable distribution policy (distributing at least 90% of its chargeable profits within 18 months of the relevant
period).
Value added tax (VAT)
Green Limited will be making taxable supplies in the Republic of Ireland and thus (subject to exceeding the Irish registration
limit) liable to register for VAT there. If Green Limited is registered for VAT in the Republic of Ireland, then supplies of goods
made from the UK will be zero rated. VAT on the goods will be levied in the Republic of Ireland at a rate of 21%. Aqua Limited
will need to have proof of supply in order to apply the zero rate, and will have to issue an invoice showing Green Limited’s
Irish VAT registration number as well as its own. In the absence of such evidence/registration, Aqua Limited will have to treat
its transactions with Green Limited as domestic sales and levy VAT at the UK standard rate of 17·5%.
In addition to making its normal VAT returns, Aqua Limited will also be required to complete an EU Sales List (ESL) statement
each quarter. This provides details of the sales made to customers in the return period – in this case, Green Limited. Penalties
can be applied for inaccuracies or non-compliance.
4 (a) Explain the meaning of the term ‘working capital cycle’ for a trading company. (4 marks)
(a) The working capital cycle illustrates the changing make-up of working capital in the course of the trading operations of a
business:
1 Purchases are made on credit and the goods go into inventory.
2 Inventory is sold and converted into receivables
3 Credit customers pay their accounts
4 Cash is used to pay suppliers.
(c) Discuss the difficulties that may be experienced by a small company which is seeking to obtain additional
funding to finance an expansion of business operations. (8 marks)
(c) Small businesses face a number of well-documented problems when seeking to raise additional finance. These problems have
been extensively discussed and governments regularly make initiatives seeking to address these problems.
Risk and security
Investors are less willing to offer finance to small companies as they are seen as inherently more risky than large companies.
Small companies obtaining debt finance usually use overdrafts or loans from banks, which require security to reduce the level
of risk associated with the debt finance. Since small companies are likely to possess little by way of assets to offer as security,
banks usually require a personal guarantee instead, and this limits the amount of finance available.
Marketability of ordinary shares
The equity issued by small companies is difficult to buy and sell, and sales are usually on a matched bargain basis, which
means that a shareholder wishing to sell has to wait until an investor wishes to buy. There is no financial intermediary willing
to buy the shares and hold them until a buyer comes along, so selling shares in a small company can potentially take a long
time. This lack of marketability reduces the price that a buyer is willing to pay for the shares. Investors in small company
shares have traditionally looked to a flotation, for example on the UK Alternative Investment Market, as a way of realising their
investment, but this has become increasingly expensive. Small companies are likely to be very limited in their ability to offer
new equity to anyone other than family and friends.
Tax considerations
Individuals with cash to invest may be encouraged by the tax system to invest in large institutional investors rather than small
companies, for example by tax incentives offered on contributions to pension funds. These institutional investors themselves
usually invest in larger companies, such as stock-exchange listed companies, in order to maintain what they see as an
acceptable risk profile, and in order to ensure a steady stream of income to meet ongoing liabilities. This tax effect reduces
the potential flow of funds to small companies.
Cost
Since small companies are seen as riskier than large companies, the cost of the finance they are offered is proportionately
higher. Overdrafts and bank loans will be offered to them on less favourable terms and at more demanding interest rates than
debt offered to larger companies. Equity investors will expect higher returns, if not in the form. of dividends then in the form
of capital appreciation over the life of their investment.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-01-22
- 2021-01-13
- 2021-10-22
- 2020-04-03
- 2021-01-13
- 2021-01-22
- 2021-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-03
- 2021-02-26
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-21
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-08-13
- 2020-05-05
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-02-28