ACCA机考与笔考考试难度一样吗?读完这篇你就明白了
发布时间:2020-02-28
ACCA机考与笔考考试难度一样吗?目前ACCA考试发布了新的考试政策:机考形式。今天就和51题库考试学习网一起来详细地了解一下这个新的考试形式吧!关注51题库考试学习网可以查看更多考试相关资讯哦!
ACCA证书是财经领域中比较火热的一款证书,无论是它的考试内容、考试形式以及考试重难点等等,无不是与时俱进的。目前,ACCA官方的考试政策中共出现了两种考试形式,分别为机考和笔考,但机考又分为了随时机考和分季机考两种。ACCA前九科考试已全面采用机考考试,但战略课程依旧采用着笔考的形式。
1.考试难度相同吗?
两者大题考试难度相同,但由于考试的形式不同,对不同考生来讲所能接受的程度也有所不同。对于上机操作能力较强的考生来说,机考的格式可以省去很多时间,提高答题的效率。考试时间上,机考考试为3小时而纸质考试为3小时15分钟,但是会在考试开始之前提供10分钟让学员阅读操作指南界面。考试会在10分钟后自动开始,但是学员可以在这段时间的任何时刻提前开始考试。只要考试开始,计时器将开始计时,计时结束后考试将自动结束。这就意味着学员可以在任何时刻开始考试,但直到考试结束后才能离开考试中心。学员只需要点击“Help”按钮,可在考试期间的任何时刻阅读考试操作指南。
2.除了考试难度、时间之外,纸质考试和机考有什么不同?
纸质考试和机考测试的学习目标和试卷结构是一致的。每一种模式都会有相同的考试格式。唯一不同的是学生回答问题的方式。在纸质考试中,学生仅需要在客观测试部分回答单项选择题,然而在机考中还可以利用其他类型的题型,比如“拖放题”和“填空题”。在主观答题区域,参加机考的学员将使用电子表格和文字处理功能完成作答,有的题目会在答题区域提供预先谁定的格式。
3.税务在机考中有哪些地区的税法考试可供选择?
目前税务的机考仅提供英国税法的考试。税务考试中其它地区税法仍采用纸质考试的形式。
4.为什么在机考中会使用不同的客观题题型,而在纸质考试中仅使用单项选择题,这是不是就意味着机考会更难一些?
鉴于判分系统运作的方式,纸质考试中我们只能使用单项选择题。认为其它类型的客观题比单项选择题要难的看法,从教育的角度上来说是不正确的。也有一些例子呈现单项选择题比其它类型的题目要困难,ACCA有严格的程序和方式来保障纸质考试和机考难度的一致性。我们提供机考并提供广泛的ACCA题型是因为其提供了更多的灵活性便于以更贴近工作场景的方式测试学员。
5.机考和纸质考试是否需要采用不同的授课/学习方式,纸质考试和机考的学习成果是一致的。在授课过程中纸质和机考学员的知识点讲授应该没有区别。但是在ACCA复习和冲刺阶段,我们建议学员务必要加强练习,熟悉考试题型和功能等。
好的,今天51题库考试学习网分享了关于ACCA考试的相关问题,相信大家看完以上内容都会觉得豁然开朗了。想了解更多考试相关资讯的小伙伴们请及时关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
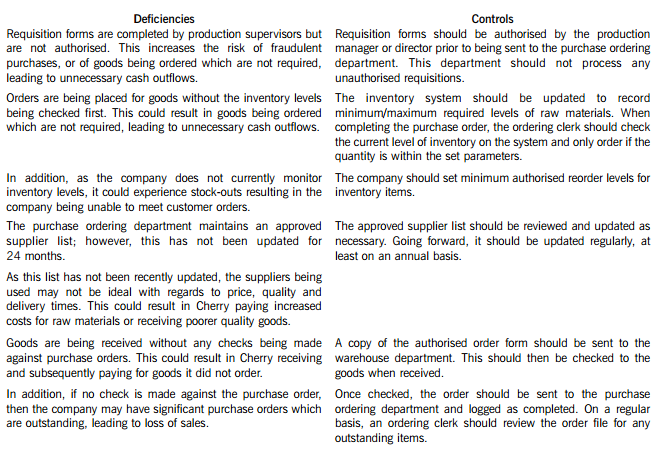
Cherry Blossom Co (Cherry) manufactures custom made furniture and its year end is 30 April. The company purchases its raw materials from a wide range of suppliers. Below is a description of Cherry’s purchasing system.
When production supervisors require raw materials, they complete a requisition form. and this is submitted to the purchase ordering department. Requisition forms do not require authorisation and no reference is made to the current inventory levels of the materials being requested. Staff in the purchase ordering department use the requisitions to raise sequentially numbered purchase orders based on the approved suppliers list, which was last updated 24 months ago. The purchasing director authorises the orders prior to these being sent to the suppliers.
When the goods are received, the warehouse department verifies the quantity to the suppliers despatch note and checks that the quality of the goods received are satisfactory. They complete a sequentially numbered goods received note (GRN) and send a copy of the GRN to the finance department.
Purchase invoices are sent directly to the purchase ledger clerk, who stores them in a manual file until the end of each week. He then inputs them into the purchase ledger using batch controls and gives each invoice a unique number based on the supplier code. The invoices are reviewed and authorised for payment by the finance director, but the actual payment is only made 60 days after the invoice is input into the system.
Required:
In respect of the purchasing system of Cherry Blossom Co:
(i) Identify and explain FIVE deficiencies; and
(ii) Recommend a control to address each of these deficiencies.
Note: The total marks will be split equally between each part.
Cherry Blossom Co’s (Cherry) purchasing system deficiencies and controls

(ii) Explain the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and capital gains tax (CGT) implications arising on
the grant to and exercise by an employee of an option to buy shares in an unapproved share option
scheme and on the subsequent sale of these shares. State clearly how these would apply in Henry’s
case. (8 marks)
(ii) Exercising of share options
The share option is not part of an approved scheme, and will not therefore enjoy the benefits of such a scheme. There
are three events with tax consequences – grant, exercise and sale.
Grant. If shares or options over shares are sold or granted at less than market value, an income tax charge can arise on
the difference between the price paid and the market value. [Weight v Salmon]. In addition, if options can be exercised
more than 10 years after the date of the grant, an employment income charge can arise. This is based on the market
value at the date of grant less the grant and exercise priced.
In Henry’s case, the options were issued with an exercise price equal to the then market value, and cannot be exercised
more than 10 years from the grant. No income tax charge therefore arises on grant.
Exercise. On exercise, the individual pays the agreed amount in return for a number of shares in the company. The price
paid is compared with the open market value at that time, and if less, the difference is charged to income tax. National
insurance also applies, and the company has to pay Class 1 NIC. If the company and shareholder agree, the national
insurance can be passed onto the individual, and the liability becomes a deductible expense in calculating the income
tax charge.
In Henry’s case on exercise, the difference between market value (£14) and the price paid (£1) per share will be taxed
as income. Therefore, £130,000 (10,000 x (£14 – £1)) will be taxed as income. In addition, national insurance will
be chargeable on the company at 12·8% (£16,640) and on Henry at the rate of 1% (£1,300).
Sale. The base cost of the shares is taken to be the market value at the time of exercise. On the sale of the shares, any
gain or loss arising falls under the capital gains tax rules, and CGT will be payable on any gain. Business asset taper
relief will be available as the company is an unquoted trading company, but the relief will only run from the time that
the share options are exercised – i.e. from the time when the shares were acquired.
In Henry’s case, the sale of the shares will immediately follow the exercise of the option (6 days later). The sale proceeds
and the market value at the time of exercise are likely to be similar; thus little to no gain is likely to arise.
(c) Discuss the usefulness of the managerial grid in assessing the attributes of managers. (5 marks)
Part (c):
This all assumes that leadership styles can be categorised into the two dimensions and that the results can be plotted on the grid.
The position of team management is accepted as the best form. of leadership. This may not be practical or indeed advisable. In
many industries, concern for the task may be more important than concern for people, and vice versa. It will always depend on
the individual situation; behaving in a way which is alien to one’s attitudes will be seen as inconsistent and confusing.
However, if the grid has relevance to leadership skills, it can provide the basis for training and for management development. One
way in which it could be useful is (for example) to support a 9,1 leader with a 1,9 subordinate.
The managerial grid also links in to the motivational ideas of Douglas Macgregor. Theory X assumes that the average person has
an inherent dislike of work. The approach is likely to be task driven, and thus managers will have a high score on the x axis.
Theory Y is based on the idea that the goals of the individual and the organisation can be integrated. In this case, the approach
is likely to be concerned with the individual and thus managers will have a high score on the y axis.
(b) Compare and contrast Gray, Owen and Adams’s ‘pristine capitalist’ position with the ‘social contractarian’
position. Explain how these positions would affect responses to stakeholder concerns in the new stadium
project. (8 marks)

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-07
- 2019-08-04
- 2021-04-23
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-09-12
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-04
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-03-26